Abstract
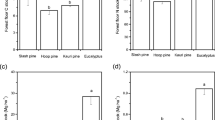
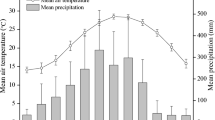
To evaluate soil organic carbon (SOC) and total nitrogen (TN) stocks of ash, alder and oak tree stands in Karacabey floodplain forest and adjacent Calabrian pine forest, grassland, cropland and sand dune in relation to soil depths (0-130 cm), a study in three replicate sites for each tree and the adjacent sites was carried out in northwest Turkey. The results indicated that among the tree species, alder stands had the greatest SOC (3.97%) and TN (0.328%) and total accumulation of SOC (405 Mg ha-1) and TN (34.4 Mg ha-1), followed by ash tree (3.11%, 0.302%, 393 Mg ha-1 and 26.2 Mg ha-1 respectively) and oak (2.43%, 0.220%, 293 Mg ha-1 and 28.6 Mg ha-1 respectively). However, the grassland showed the highest cumulative SOC densities within 0-130 cm depth (678 Mg ha-1) compared to the tree species. It also showed higher TN densities (27.5 Mg ha-1) than the ash tree and the Calabrian pine stands, whereas lower than the alder and oak stands. The sand dunes showed the lowest SOC and TN values. Compared to the soil depth of 0–30 cm, mean SOC and TN stored in 30–130 cm soil depth accounted for 58% and 40% in ash stands, 41% and 45% in alder stands, 52% and 56% in oak stands, 57% and 66% in Calabrian pine stands respectively. Thick alluvial soil and dry climate in the region could be responsible for the better root system development, and thus much higher SOC and TN stocks into deeper soil layers.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data produced from this study are available from Temel Sariyildiz (temel.sariyildiz@btu.edu.tr) on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Akay AE, Gencal B, Taş İ (2017) Spatiotemporal change detection using landsat imagery: the case study of Karacabey flooded forest, Bursa, Turkey. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Volume IV-4/W4, 4th International GeoAdvances Workshop, 14–15 October, Safranbolu, Karabuk, Turkey
Allen SE (1989) Chemical Analysis of Ecological Materials. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford
Atwood TB, Connolly RM, Almahasheer H, Carnell PE, Duarte CM, Lewis CJE et al (2017) Global patterns in mangrove soil carbon stocks and losses. Nat Clim Change 7:523–528. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3326
Batjes NH (2011) Soil organic carbon stocks under native vegetation - Revised estimates for use with the simple assessment option of the Carbon Benefits Project system. Agric Ecosyst Environ 142(3–4):365–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.06.007
Binkley D, Kaye J, Barry M, Michael GR (2004) First rotation changes in soil carbon and nitrogen in a Eucalyptus plantation in Hawaii. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:1713–1719. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2004.1713
Black CA (1965) Methods of soil analysis. Am Soc Agron 1:1570–1572
Bouyoucos GJ (1962) Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analysis of soils. Agron J 54:464–465
Cartisano R, Mattioli W, Corona P, Mugnozza GS, Sabatti M, Ferrari B (2013) Assessing and mapping biomass potential productivity from poplar dominated riparian forests: A case study. Biomass Bioenerg 54(7):293–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.10.023
Chen L, Gong J, Fu B, Huang Z, Huang Y, Gui L (2007) Effect of land use conversion on soil organic carbon sequestration in the loess hilly area, loess plateau of China. Ecol Res 22(4):641–648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-006-0065-1
Cierjacks A, Kleinschmit B, Babinsky M, Kleinschroth F, Markert A, Menzel M, Ziechmann U, Schiller T, Graf M, Lang F (2010) Carbon stocks of soil and vegetation on Danubian floodplains. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 173:644–653. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.200900209
Conant RT, Paustian K, Elliott ET (2001) Grassland management and conversion into grassland: Effects on soil carbon. Ecol Appl 11:343–355. https://doi.org/10.1890/1051-0761
Çiçek E (2002) Stand structures and necessary silvicultural treatments on bottomland forest of Süleymaniye-Adapazari. Dissertation, University of İstanbul
Daily GC (1997) Nature’s Services: Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems. Island, Washington, DC
Davidson NC (2014) How much wetland has the world lost? Long-term and recent trends in global wetland area. Mar Freshw Res 65:934–941. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF14173
Davis AA, Stolt MH, Compton JE (2004) Spatial distribution of soil carbon in southern New England hardwood forest landscapes. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68:895–903. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2004.8950
D’Elia AH, Liles GC, Viers JH, Smart DR (2017) Deep carbon storage potential of buried floodplain soils. Sci Rep 7:8181. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06494-4
Don A, Schumacher J, Scherer-Lorenzen M, Scholten T, Schulze E-D (2007) Spatial and vertical variation of soil carbon at two grassland sites: Implications for measuring soil carbon stocks. Geoderma 141:272–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.06.003
Don A, Schumacher J, Freibauer A (2011) Impact of tropical land-use change on soil organic carbon stocks - a meta-analysis. Global Change Biol 17(4):1658–1670. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02336.x
Dumig A, Schad P, Kohok M, Beyerlein P, Schwimmer W, Koger-Knabner I (2006) A mosaic of nonallophanic Andosols, Umbrisols and Cambisols on rhyodacite in the southern Brazilian highlands. Geoderma 145:158–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2008.01.013
Evrendilek F, Celik I, Kilic S (2004) Changes in soil organic carbon and other physical soil properties along adjacent Mediterranean forest, grassland, and cropland ecosystems in Turkey. J Arid Environ 59:743–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2004.03.002
Francaviglia R, Renzi G, Doro L, Parras-Alcantara L, Lozano-Garcia B, Ledda L (2017) Soil sampling approaches in Mediterranean agro-ecosystems. Influence on soil organic carbon stocks. CATENA 158:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.06.014
Hall R, Baker M, Arp C, Koch B (2009) Hydrologic control of nitrogen removal, storage and export in a mountain stream. Limnol Oceanogr 54:2128–2142. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2009.54.6.2128
Hansen VD, Nestlerode JA (2014) Carbon sequestration in wetland soils of the northern Gulf of Mexico coastal region. Wetl Ecol Manag 22:289–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-013-9330-6
Hao S, Zhou P, Zhang YZ, Kuzyakov Y, Zhou Q, Tida G et al (2015) Loss of labile organic carbon from subsoil due to land-use changes in subtropical China. Soil Biol Biochem 88:148–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.05.015
Hertzberg M, Schreuder H (2016) Role of atmospheric carbon dioxide in climate change. Energy Environ 27(6–7):785–797. https://www.jstor.org/stable/90006767
Hillel D (2004) Introduction to Environmental Soil Physics. Elsevier Academic Press
Hughes F, Richards K, Girel J, Moss T, Muller E, Nilsson C, Rood S (2003) The Flooded Forest: Guidance for Policy Makers and River Managers in Europe on the Restoration of Floodplain Forests. The FLOBAR2 Project. Department of Geography, University of Cambridge, Cambridge
Göl C, Yılmaz H (2017) The effect of land use type / land cover and aspect on soil properties at the Gökdere catchment in northwestern Turkey. Å umarski list 141(9–10):459–468. https://doi.org/10.31298/sl.141.9-10.2
Grüneberg E, Ziche D, Wellbrock N (2014) Organic Carbon Stocks and Sequestration Rates of Forest Soils in Germany. Global Change Biol 20:2644–2662. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12558
Gülçür F (1974) Physical and chemical analyzing methods of soil properties. University of İstanbul. Issue No: 201 İstanbul, Turkey
Guo LB, Gifford RM (2002) Soil carbon stocks and land use change: a meta analysis. Global Change Biol 8(4):345–360. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1354-1013.2002.00486.x
IPCC (2006) IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventory. Hayama, Japan, IPCC/IGES
IPCC (2014) In: Pachauri RK, Meyer LA (eds) Climate Change 2014. Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Core Writing Team. IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland, p 151
Jin Z, Dong Y, Wang Y et al (2014) Natural vegetation restoration is more beneficial to soil surface organic and inorganic carbon sequestration than tree plantation on the Loess Plateau of China. Sci Total Environ 485–486:615–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.03.105
Junk WJ (1989) Flood tolerance and tree distribution in Central Amazonian floodplains. In: Nielsen LB, Nielsen IC, Balslev H (eds) Tropical Forests: Botanical Dynamics, Speciation and Diversity. Academic Press, London
Kalra YP, Maynard DG (1991) Methods Manual for Forest Soil and Plant Analysis. Forestry Canada, Northern Forestry Publications. Alberta, Canada
Kern JS (1994) Spatial patterns of soil organic carbon in the contiguous United States. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:439–455. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1994.03615995005800020029x
Kimmins JP (2004) Forest ecology: a foundation for sustainable forest management and environment ethics in forestry, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Kolka R, Trettin C, Tang W, Krauss K, Bansal S, Drexler J, Wickland K, Chimner R, Hogan D, Pindilli EJ, Benscoter B, Tangen B, Kane E, Bridgham S, Richardson C (2018) : Chap. 13: Terrestrial wetlands. In Second State of the Carbon Cycle Report (SOCCR2): A Sustained Assessment Report [Cavallaro N, Shrestha G, Birdsey R, Mayes MA, Najjar RG, Reed SC, Romero-Lankao P, Zhu Z (eds.)]. U.S. Global Change Research Program, Washington, DC, USA, pp. 507–567, https://doi.org/10.7930/SOCCR2.2018.Ch13
Kondo M, Saitohb TM, Satoa H, Ichiia K (2017) Comprehensive synthesis of spatial variability in carbon flux across monsoon Asian forests. Agric For Meteorol 232:623–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2016.10.020
Korkonc SY (2014) Effect of afforestation on soil organic carbon and other soil properties. CATENA 123:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.07.009
Kucuk M, Yener I, Duman A (2019) Effects of vegetation cover/land use and slope aspect on surface soil properties near the copper smelter factory in Murgul, Turkey. Appl Ecol Environ Res 17(5):12305–12321. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1705_1230512321
Lal R (1987) Tropical Ecology and Physical Edaphology. John Willy and Sons, New York, USA
Lepcha NT, Devi NB (2020) Effect of land use, season, and soil depth on soil microbial biomass carbon of Eastern Himalayas. Ecol Process 9:65. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-020-00269-y
Lee J, Hopmans JW, Rolston DE, Baer SG, Six J (2009) Determining soil carbon stock changes: Simple bulk density corrections fail. Agric Ecosyst Environ 134:251–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2009.07.006
Liu C, Hoist J, Yao Z, Bruggemann N, Butterbach-Bahl K, Han S, Han X, Tas B, Susenbeth A, Zheng X (2009) Growing season methane budget of an Inner Mongolian steppe. Atmos Environ 43(19):3086–3095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.03.014
Lugo AE, Brown S (1993) Management of tropical soils as sinks or sources of atmospheric carbon. Plant Soil 149(1):27–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010760
McClain ME, Boyer EW, Dent CL, Gergel SE, Grimm NB, Groffman PM, Hart SC, Harvey JW, Johnston CA, Mayorga E, McDowell WH, Pinay G (2003) Biogeochemical hot spots and hot moments at the interface of terrestrial and aquatic. Ecosyst 6:301–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-003-0161-9
Melack JM, Novo EMLM, Forsberg BR, Piedade MT, Maurice L (2009) Floodplain ecosystem processes. In: Keller M, Bustamante MG, Dias PS (eds) Amazonia and global change. American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C., pp 525–541
Nahlik AM, Fennessy MS (2016) Carbon storage in US wetlands. Nat Commun 7:13835. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13835
Naiman RJ, Decamps H, McClain ME, Likens GE (2005) Riparian Ecology, Conservation, and Management of Streamside Communities. Academic Press, Burlington, MA
Nath S, Nath AJ, Sileshi GW, Das AK (2017) Biomass stocks and carbon storage in Barringtonia acutangula floodplain forests in North East India. Biomass Bioenergy 98:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2017.01.014
Oates LG, Jackson ARD, Allen-Diaz B (2008) Grazing removal decreases the magnitude of methane and the variability of nitrous oxide emissions from spring-fed wetlands of a California oak savanna. Wetlands Ecol Manage 16:395–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-007-9076-0
Pamay B (1967) Studies on silvicultural analysis of Demirköy-İğneada floodplain forests and silvicultural measures to be taken to make them efficient. Publication by General Directorate of Forestry. (in Turkish) No:43, İstanbul
Perrin AS, Fujisaki K, Petitjean C, Sarrazin M, Godet M, Garric B et al (2014) Conversion of forest to agriculture in Amazonia with the chop-and-mulch method: Does it improve the soil carbon stock? Agric Ecosyst Environ 184:101–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2013.11.009
Pinay G, Clément JC, Naiman RJ (2002) Basic principles and ecological consequences of changing water regime for nitrogen cycling in fluvial systems. Environ Manage 30:481–491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-002-2736-1
Ramos Scharrón CE, Castellanos EJ, Restrepo C (2012) The transfer of modern organic carbon by landslide activity in tropical montane ecosystems. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 117(3):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JG001838
Reichstein M, Carvalhais N (2019) Aspects of Forest Biomass in the Earth System: Its Role and Major Unknowns. Surv Geophys 40:693–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-019-09551-x
Ricker MC, Stolt MH, Donohue SW, Blazejewski GA, Zavada MS (2013) Soil organic carbon pools in riparian landscapes of southern New England. Soil Sci Soc Am J 77:1070–1079. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2012.0297
Rodríguez-Murillo JC (2001) Organic carbon content under different types of land use and soil in Peninsular Spain. Biol Fertil Soils 33:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740000289
Rothe A, Cromack K Jr, Resh SC, Makineci E, Son Y (2002) Soil carbon and nitrogen changes under Douglas-fir with and without red alder. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:1988–1995. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2002.1988
Sariyildiz T, Savacı G, Kravkaz İS (2016) Effects of tree species, stand age and land-use change on soil carbon and nitrogen stock rates in northwest of Turkey. iForest - Biogeosc For 9:165–170. https://doi.org/10.3832/ifor1567-008
Schimel DS, House JI, Hibbard KA et al (2001) Recent patterns and mechanisms of carbon exchange by terrestrial ecosystems. Nature 414:169–172. https://doi.org/10.1038/35102500
Sigua GC, Coleman SW, Albano J (2009) Beef cattle pasture to wetland reconversion: impact on soil organic carbon and phosphorus dynamics. Ecol Eng 35:1231–1236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.05.004
Soleimani A, Hosseini SM, Bavani ARM, Jafari M, Francaviglia R (2019) Influence of land use and land cover change on soil organic carbon and microbial activity in the forest of northern Iran. CATENA 177:227–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.02.018
Specht A, West PW (2003) Estimation of biomass and sequestered carbon on farm forest plantations in northern New South Wales, Australia. Biomass Bioenergy 25:363–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0961-9534(03)00050-3
Sutfin NA, Wohl EE, Dwire KA (2016) Banking carbon: a review of organic carbon storage and physical factors influencing retention in floodplains and riparian ecosystems. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 41:38–60. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3857
Tate KR, Scott NA, Ross DJ, Parshotam A, Claydon JJ (2000) Plant effects on soil carbon storage and turnover in a montane beech (Nothofagus) forest and adjacent tussock grassland in New Zealand. Soil Res 38(3):685–698. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR99092
Tecimen HB, Kavgacı A (2010) Comparison of soil and forest floor properties of floodplain and surrounding forests in Igneada, Turkey. J Environ Biol 31:129–134
Umrit G, Cheong RN, Gillabel J, Merckx R (2014) Effect of conventional versus mechanized sugarcane cropping systems on soil organic carbon stocks and labile carbon pools in Mauritius as revealed by 13 C natural abundance. Plant Soil 379:177–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2053-5
UNFCCC COP 15 (2009) Available online: https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/conferences/past-conferences/copenhagen-climate-change%20conference-december-2009/cop-15. Accessed on 18 December 2021
Ursavaş S, Keçeli T (2018) Weissia multicapsularis, a rare moss species new to Turkey and Asia. Plant Biosyst 153(5):669–672. https://doi.org/10.1080/11263504.2018.1536086
Ursavaş S, Keçeli T (2019) The Moss Flora of Kocaçay Delta (Karacabey-Bursa) Floodplain Forests in Turkey. Anatol Bryol 5(1):22–34. https://doi.org/10.26672/anatolianbryology.517253
URL-1 :https://www.dailysabah.com/gallery/life/turkeys-karacabey-wetland%20home-to-rich-biodiversity
van Asselen S, Verburg PH, Vermaat JE, Janse JH (2013) Drivers of wetland conversion: a global meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 8(11):e81292. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081292
Vesterdal L, Raulund-Rasmussen K (1998) Forest floor chemistry under seven tree species along a soil fertility gradient. Can J For Res 28:1636–1647. https://doi.org/10.1139/x98-140
Wei XR, Shao MA, Gale W, Li LH (2014) Global pattern of soil carbon losses due to the conversion of forests to agricultural land. Sci Rep 4:4062. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04062
Wickland KP, Krusche AV, Kolka RK, Kishimoto-Mo AW, Chimner R, Ogle SM, Srivastava N(2013) Inland wetland mineral soils. 2013 Supplement to the 2006 IPCC guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories: wetlands, 5.1–5.34. https://digitalcommons.mtu.edu/michigantech-p/514
Wiesmeier M, Munro S, Barthold F, Steffens M, Schad P, Kögel-Knabner I (2015) Carbon storage capacity of semi-arid grassland soils and sequestration potentials in northern China. Glob Chang Biol 21:3836–3845. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12957
Wu J, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1993) Formation and destruction of microbialbiomass during decomposition of glucose and ryegrass in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 25:1435–1441. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(93)90058-J
Yang SH, Zhang HT, Chen JY (2015) The spatial variability of soil organic carbonin plain-hills transition belt and its environmental impact. China Environ Sci 35:3728–3736 (in Chinese)
Yao Z, Wolf B, Chen W, Butterbach-Bahl K, Brüggemann N, Wiesmeier M, Dannenmann M, Blank, B, Zheng X (2010) Spatial variability of N2O, CH4 and CO2 fluxes within the Xilin River catchment of Inner Mongolia, China: a soil core study. Plant Soil 331: 341-359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0257-x
Yeasmin S, Jahan E, Molla A, Islam AKMM, Anwar P, Rashid HO, Chungopast S (2020) Effect of Land Use on Organic Carbon Storage Potential of Soils with Contrasting Native Organic Matter Content. Int J Agron Volume 2020 Article ID 8042961:9pages. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8042961
Zhang L, Zhao R, Xie Z (2014) Response of soil properties and C dynamics to land-use change in the west of Loess Plateau. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 60(4):586–597. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2014.922407
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank:
The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) for its financial support to carry out this research.
General Directorate of Forestry, Department of International Relations, Education and Research for granting permission to work in Karacabey Floodplain Forest protected by the International Ramsar Agreement.
Funding
This research was funded by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) with the project number 119O263.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.S. designed the study, T.S., D.O.A., S.P. and M.T. collected soil samples; S.P., D.O.A. and M.T. measured stand characteristics; D.O.A. and M.T. prepared the soil samples for analysis. T.S. and D.O.A. prepared the tables and figures. T.S. wrote the manuscript. All the authors contributed to editing and agreed on the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors have read this manuscript and consent to its publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sariyildiz, T., Aygun, D.O., Parlak, S. et al. Effects of Land Use Types and soil Depths on Soil Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen Stocks of Karacabey Floodplain Forests in Northwest Turkey. Wetlands 42, 102 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-022-01612-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-022-01612-z