Abstract
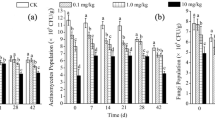
Cadmium (Cd) pollution can alter soil flora and fauna, as well as the microbial community associated with the main biogeochemical cycles of a soil. The present study was conducted to investigate the effect of two different concentrations of Cd pollutant, 6.5 mg kg−1 (low level) and 12.5 mg kg−1 (high level) on microbial community activity, abundance, and structure in a semiarid soil after a 60-day incubation period at laboratory level. Available Cd, water soluble carbon (WSC), microbial biomass carbon (Cmic), adenosine triphosphate (ATP) content, and real-time polymerase chain reaction were used to measure the influence of Cd on the abundance and activity of the microbial community. Bacteria and fungi community structure and diversity based on denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) analysis were also analyzed. The percentage of Cd extracted by diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid increased with the higher total concentration of Cd added to the soil, being 16.9% at low level and 77.9% at the high level. WSC, Cmic, and ATP content decreased significantly as soil Cd concentration increased (WSC 29% and 34%, Cmic 27% and 35%, and ATP 32% and 47%, at low and high levels, respectively). While fungal diversity already decreased with low levels of Cd concentration, and was even more negatively affected by the higher pollution levels, bacterial (acidobacteria, α-proteobacteria, and β proteobacteria) diversity only showed a decline with the higher Cd concentration. The fungi-to-bacteria ratio showed by the different treatments could imply that fungi abundance is less influenced by increased Cd pollution, although fungi diversity as revealed by DGGE analysis diminished as soil Cd concentration increased.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar, J., Dorronso, C., Gomez-Ariz, J. L., & Galan, E. (1999). Los criterios y estándares para declarar un suelo contaminado en Andalucía y la metodología y técnicas de toma de muestras y análisis para su investigación. In: Universidad de Sevilla (Ed.), Investigación y desarrollo medioambiental en Andalucía, Sevilla, Spain (pp. 45–59).
Albadalejo, J., Martinez-Mena, M., & Roldan, A. V. (1998). Soil degradation and desertification induced by devegetation removal in semiarid environment. Soil Use and Management, 14, 1–5. doi:10.1111/j.1475-2743.1998.tb00602.x.
Alloway, B. J. (1995). Cadmium. In B. J. Alloway (Ed.), Heavy metals in soil (pp. 122–151). Suffolk: Chapman and Hall.
Arretxe, M., Heap, J. M., & Christofi, N. (1997). The effect of toxic discharges on ATP content in activated sludge. Environmental Toxicology and Water Quality, 12, 23–29. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2256(1997)12:1<23::AID-TOX4>3.0.CO;2-A.
Bááth, E., Arnebrant, K., & Nordgren, A. (1991). Microbial biomass and ATP in smelter-polluted forest humus. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 47, 278–282. doi:10.1007/BF01688652.
Boon, N., De Windt, W., Verstraete, W., & Top, E. M. (2002). Evaluation of nested PCR-DGGE (denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis) with group-specific 16S rRNA primers fro the analysis of bacterial communities from different wastewater treatments plants. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 39, 101–112.
Boyer, S. L., Flechtner, V. R., & Johansen, J. R. (2001). Is the 16S-23S r RNA internal transcribed spacer region a good tool for use in molecular systematic and population genetics? A case study in cyanobacteria. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 18, 1057–1069.
Ceccanti, B., & Garcia, C. (1994). Coupled chemical and biochemical methodologies to characterize a composting process and the humic substances. In N. Senesi, & T. M. Miano (Eds.), Humic substances in the global environment and implications on human health (pp. 1279–1284). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Ciardi, C., & Nannipieri, P. (1990). A comparison of methods for measuring ATP in soil. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 22, 725–727. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(90)90022-R.
Dice, L. R. (1945). Measures on the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology, 26, 297–302. doi:10.2307/1932409.
Eriksson, M., Ka, J. O., & Mohn, W. W. (2001). Effects of low temperature and freeze–thaw cycles on hydrocarbon biodegradation in Antartic tundra soil. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 5107–5112. doi:10.1128/AEM.67.11.5107-5112.2001.
Flieβbach, A., Martens, R., & Reber, H. H. (1994). Soil microbial biomass and microbial activity in soils treated with heavy metal contaminated sewage sludge. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 26, 1201–1205.
Frey, B., Stemmer, M., Widmer, F., Luster, J., & Sperisen, C. (2006). Microbial activity and community structure of a soil after heavy metal contamination in a model forest ecosystem. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 38, 1745–1756.
Giller, K., Witter, E., & McGrath, S. P. (1998). Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: a review. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 30, 1389–1414.
Girva, M. S., Campbell, C. D., Killham, K., Prosser, J. L., & Glover, L. A. (2005). Bacterial diversity promotes community stability and functional resilience after perturbation. Environmental Microbiology, 7, 301–313.
Guisquiani, P. L., Concezzi, L., Businelli, M., & Macchinoni, A. (1998). Fate of pig sludge liquid fraction in calcareous soil: agricultural and environmental implications. Journal of Environmental quality, 27, 364–371.
Hattori, H. (1992). Influence of heavy metals on soil microbial activities. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 38, 93–100.
Head, I. M., Hiorns, W. D., Embley, T. M., McCarthy, A. J., & Saunders, J. R. (1993). The phylogeny of autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria as determined by analysis of 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Journal of general Microbiology, 139, 1147–1153.
Heuer, H., & Smalla, K. (1997). Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis for studying soil microbial communities. In J. D. Van Elsas, J. T. Trevors, & E. M. H. Wellington (Eds.), Modern soil microbiology (pp. 353–373). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Hill, T. C. J., Walsh, K. A., Harris, J. A., & Moffett, B. F. (2003). Using ecological diversity measures with bacterial communities. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 43, 1–11.
Hiroki, M. (1992). Effects of heavy-metal contamination on soil microbial-population. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 38, 141–147.
Janssen, P. H. (2006). Identifying the dominant soil bacterial taxa in libraries of 16SrRNA genes. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 71, 1719–1728.
Kandeler, E., Tscherko, D., Bruce, K. D., Stemmer, M., Hobbs, P. J., Bardgett, R. D., et al. (2000). Structure and function of the soil microbial community in microhabitats of a heavy metal polluted soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 32, 390–400.
Landi, I., Renella, G., Moreno, J. L., Falchini, L., & Nannipieri, P. (2000). Influence of Cd on the metabolic quotient, L-D-glutamic acid respiration ratio and enzyme activity: microbial biomass ratio under laboratory conditions. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 32, 8–16.
Lazzaro, A., Hartmann, M., Blazer, P., Widmer, F., Schulli, R., & Frey, B. T. (2006). Bacterial comunity structure and activity in different Cd-treated forest soils. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 58, 278–292.
Lindsay, W. L., & Norwell, W. A. (1978). Development of DTPA test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 42, 421–428.
Lofts, S., Spurgeon, D. J., Svendsen, C., & Tipping, E. (2004). Deriving soil critical limits for Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb: a method based on free ion concentrations. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 3623–3631.
Moreno, J. L., Garcia, C., Landi, L., Falcchini, F., Pietramellara, G., & Nannipieri, P. (2001). The ecological dose value (ED50) for assessing Cd toxicity on ATP content and dehydrogenase and urease activities of soil. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 33, 483–489.
Moreno, J. L., Hernandez, T., Perez, A., & Garcia, C. (2002). Toxicity of cadmium to soil microbial activity: effect of sewage sludge addition to soil on the ecological dose. Applied Soil Ecology, 21, 149–158.
Muyzer, G., de Waal, E. C., & Uitterlinden, A. G. (1993). Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59, 695–700.
Nannipieri, P., Grego, S., & Ceccanti, B. (1990). Ecological significance of the biological activity in soil. In J. M. Bollag & G. Stotzky (Eds.), Soil biochemistry (vol. 6, pp. 293–355). New York: Dekker.
Niklinska, M., Laskowski, R., & Maryanski, M. (1998). Effect of heavy metals and storage time on two types of forest litter: basal respiration rate and exchangeable metals. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safely, 41, 8–18.
Nolan, A. L., McLaughlin, M. J., & Mason, S. D. (2003). Chemical separation of Zn, cd, Cu and Pb in pore waters of agricultural and contaminated soils using Donnan dialysis. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 90–98.
Parr, J. F., & Papendick, R. I. (1997). Soil quality: relationship and strategies for sustainable dry land farming systems. Annals of Arid Zones, 36, 181–191.
Prokop, Z., Cupr, P., Zlevorova-Zlamalikova, V., Komarek, J., Dusek, L., & Holoubek, I. (2003). Mobility, bioavailability, and toxic effects of cadmium in soil samples. Environmental Research, 91, 119–126.
Ranjard, L., Richaume, A., Jocteur-Monrozier, L., & Nazaret, S. (1997). Response of soil bacteria to Hg (II) in relation to soil characteristics and cell location. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 24, 321–331.
Renella, G., Ortigoza, A. L. R., Landi, L., & Nannipieri, P. (2003). Additive effects of copper and zinc on cadmium toxicity on phosphatase activities and ATP content of soil as estimated by the ecological dose (ED50). Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 35, 1203–1210.
Renella, G., Mench, M., van der Lelie, D., Pietramellara, G., Ascher, J., Ceccherini, M. T., et al. (2004). Hydrolase activity, microbial biomass and community structure in long-term Cd-contaminated soils. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 36, 443–451.
Salles, J., van Veen, J. A., & van Elsas, J. D. (2004). Multivariate analyses of Burkholderia species in soil: Effect of crop and land use history. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 4012–4020.
Sauvé, S., Dumestre, A., McBride, M., & Hendershot, W. (1998). Derivation of soil quality criteria using predicted chemical speciation of Pb2+ and Cu2+. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 17, 1481–1489.
Seghers, D., Verthe, K., Reheul, D., Bulcke, R., Siciliano, S. D., Verstraete, W., et al. (2003). Effect of long-term herbicide applications on the bacterial community structure and function in an agricultural soil. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 1566, 1–8.
Shoun, H., Kim, D. H., Uchiyama, H., & Sugiyama, J. (1992). Denitrification by fungi. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 93, 177–180.
Simpson, E. H. (1949). Measurement of diversity. Nature, 163, 688.
Smit, E., Leeflang, P., Gommands, S., van de Broek, J., van Mil, S., & Wernars, K. (2001). Diversity and seasonal fluctuations of the dominant members of the bacterial soil community in a wheat field as determined by cultivation and molecular methods. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 2284–2291.
Smolders, E., Brans, K., & Merckx, R. (1999). Cadmium fixation in soils measured by isotopic dilution. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 63, 78–85.
Torsvik, V., Ovreas, L., & Thingstad, T. (2002). Prokaryotic diversity—magnitude, dynamics, and controlling factors. Science, 296, 1064–1066.
Vainio, E. J., & Hantula, J. (2000). Direct analysis of wood-inhabiting fungi using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of amplified ribosomal DNA. Mycological Research, 104, 927–936.
Van Elsas, J. D., Trevors, J. T., & Wellington, E. M. H. (1997). Modern soil microbiology. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Vance, E. D., Brookes, P. C., & Jenkinson, D. S. (1987). An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 19, 703–707.
Ward, J. H. (1963). Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 58, 236–244.
Webster, J. J., Hampton, G. J., & Leach, F. R. (1984). ATP in soil. A new extractant and extraction procedure. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 16, 335–342.
Yeomans, J. C., & Bremner, J. M. (1989). A rapid and precise method for routine determination of organic carbon in soil. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 19, 1467–1476.
Yergeau, E., Bokhorst, S., Huiskers, A. H. L., Boschker, H. T. S., Aerts, R., & Kowalchuck, G. A. (2007). Size and structure of bacterial, fungal and nematode communities along an Antartic environmental gradient. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 59, 436–451.
Zhou, J., Xia, B., Huang, H., Palumbo, A., & Tiedje, J. (2004). Microbial diversity and heterogeneity in sandy subsurface soils. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 70, 1723–1734.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ros, M., Pascual, J.A., Moreno, J.L. et al. Evaluation of Microbial Community Activity, Abundance and Structure in a Semiarid Soil Under Cadmium Pollution at Laboratory Level. Water Air Soil Pollut 203, 229–242 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0006-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0006-z