Abstract
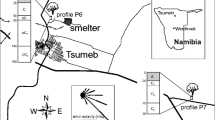
The content of Pb, Cd, Mn, K, Ca, Mg and 206Pb/207Pb isotope ratios in spruce tree rings (Picea abies) and peat cores from the Brdy Hills area (10 km W of the Pb smelter) were compared with those in spruce tree rings in the vicinity of the Pb smelter. Maximum Pb content in tree rings (up to 60 mg kg−1 Pb) corresponds to a peak of metallurgical production in the mid 1970s and highest smelter emissions in the early 1970s. The Pb concentration curves obtained from peat deposit profiles closely correlate with the Pb concentrations in tree rings at both sampling sites. The small differences between the individual tree cores, with the identical general trend, may be attributed to the difference in distance from the smelter and the altitude of each sampling site. Similar behaviour to Pb can be observed for Cd and Ca. Lead isotope composition in tree rings (206Pb/207Pb ~1.143–1.174) is controlled mainly by the smelter emissions (206Pb/207Pb ~1.16–1.17), with the exception of the youngest segments from the more distant locality from the smelter, which yield isotopic signatures corresponding to car-emission Pb (206Pb/207Pb ~1.143–1.150). Higher content of Mn, Mg and Ca in tree rings corresponding to the 1970s and 1980s may be related to soil chemistry changes caused by acid deposition. In addition, an increase in K, Mg (and in some cases also Mn) in the youngest part of wood cores corresponds to the physiological processes in sapwood, and may be influenced by a decrease in Pb in organic soil horizons, which limited the cycling of basic inorganic nutrients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appleby, P. G., & Oldfield, F. (1978). The calculation of 210Pb dates assuming a constant rate of supply of unsupported 210Pb to sediment. Catena, 5, 1–8.
Augustin, S., Stephanowitz, H., Wolff, B., Schröder, J., & Hoffmann, E. (2005). Manganese in tree rings of Norway spruce as an indicator for soil chemical changes in the past. European Journal of Forest Research, 124, 313–318.
Baes, C. F., & McLaughlin, S. B. (1984). Trace elements in tree rings: Evidence of recent and historical air pollution. Science, 224, 494–497.
Bambas, J. (1990). Březohorský rudní revír (Ore district of Březové Hory). Publication of Symposium on Mining in Příbram: Scientific and Technological Aspects. VZ Kamenná Publications, 198 pp. (in Czech).
Baron, S., Lavoie, M., Ploquin, A., Carignan, J., Pulido, M., & De Beaulieu, J. L. (2005). Record of metal workshop in peat deposits: History and environmental impact on the Mont Lozère Massif, France. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 5131–5140.
Bellis, D. J., Satake, K., & McLeod, C. W. (2004). A comparison of lead isotope ratios in the bark pockets and annual rings of two beech trees collected in Derbyshire and South Yorkshire, UK. Science of the Total Environment, 321, 105–113.
Bindler, R., Renberg, I., Klaminder, J., & Emteryd, O. (2004). Tree rings as Pb pollution archives? A comparison of 206Pb/207Pb isotope ratios in pine and other environmental media. Science of the Total Environment, 319, 173–183.
Cutter, B. E., & Guyette, R. P. (1993). Anatomical, chemical and ecological factors affecting tree species choice in dendrochemistry. Journal of Environmental Quality, 22, 611–619.
Dambrine, E., Le Goaster, S., & Ranger, J. (1991). Croissance et nutrition minérale d’un peuplement d’epicéa sur sol pauvre. III. Prélèvement racinaire et translocation d’elements minéraux au cours de la croissance. Acta Oecologica, 12, 791–808.
Ettler, V., Johan, Z., Baronnet, A., Jankovský, F., Gilles, C., Mihaljevič, M., et al. (2005a). Mineralogy of air-pollution-control residues from a secondary lead smelter: environmental implications. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 9309–9316.
Ettler, V., Mihaljevič, M., & Komárek, M. (2004). ICP-MS measurements of lead isotopic ratios in soils heavily contaminated by lead smelting: tracing the sources of pollution. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 378, 311–317.
Ettler, V., Vaněk, A., Mihaljevič, M., & Bezdička, P. (2005b). Contrasting lead speciation in forest and tilled soils heavily polluted by lead metallurgy. Chemosphere, 58, 1449–1459.
Fisher, S., Nicholas, N. S., & Scheuerman, P. R. (2002). Dendrochemical analysis of lead and calcium in southern Appalachian American Beech. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 1137–1145.
Hagemayer, J. (1995). Radial distributions of Cd in stems of oak trees (Quercus robur L.) re-analyzed after 10 years. Trees, 9, 200–203.
Kopáček, J., & Veselý, J. (2005). Sulfur and nitrogen emissions in the Czech Republic and Slovakia from 1850 till 2000. Atmospheric Environment, 39, 2179–2188.
Le Roux, G., Laverret, E., & Shotyk, W. (2006). Fate of calcite, apatite and feldspars in an ombrotrophic peat bog, Black Forest, Germany. Journal of the Geological Society, London, 163, 641–646.
Meerts, P. (2002). Mineral nutrient concentrations in sapwood and heartwood: A literature review. Annals of Forest Science, 59, 713–722.
Mihaljevič, M., Zuna, M., Ettler, V., Šebek, O., Strnad, L., & Goliáš, V. (2006). Lead fluxes, isotopic and concentration profiles in a peat deposit near a lead smelter (Příbram, Czech Republic). Science of the Total Environment, 372, 334–344.
Monna, F., Galop, D., Carozza, L., Tual, M., Beyrie, A., Marembert, F., et al. (2004). Environmental impact of early Basque mining and smelting recorded in a high ash minerogenic peat deposit. Science of the Total Environment, 327, 197–214.
Nabais, C., Freitas, H., & Hagemeyer, J. (1999). Dendroanalysis: a tool for biomonitoring environmetal pollution. Science of the Total Environment, 232, 33–37.
Patrick, G. J., & Farmer, J. G. (2006). A stable lead isotopic investigation of the use of sycamore tree rings as a historical biomonitor of environmental lead contamination. Science of the Total Environment, 362, 278–291.
Prohaska, T., Stadlbauer, C., Wimmer, R., Stingeder, G., Latkoczy, Ch., Hoffmann, E., et al. (1998). Investigation of element variability in tree rings of young Norway spruce by laser-ablation-ICPMS. Science of the Total Environment, 219, 29–39.
Savard, M. M., Bégin, C., Parent, M., Marion, J., & Smirnoff, A. (2006). Dendrogeochemical distinction between geogenic and anthropogenic emission of metals and gases near a copper smelter. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 6, 237–247.
Shortle, W. C., & Smith, K. T. (1988). Aluminium-Induced calcium deficiency syndrome in declining red spruce. Science, 20, 1017–1018.
Shotyk, W. (1996). Peat bog archives of atmospheric metal deposition: geochemical evaluation of peat profiles, natural variations in metal concentrations and metal enrichment factors. Environmental Review, 4, 149–183.
Shotyk, W. (1997). Atmospheric deposition and mass balance of major and trace elements in two oceanic peat bog profiles, northern Scotland and the Shetland Islands. Chemical Geology, 138, 55–72.
Steinmann, P., & Shotyk, W. (1997). Geochemistry, mineralogy and geochemical mass balance on major elements in two peat bog profiles (Jura Mountains, Switzerland). Chemical Geology, 138, 25–53.
Stuczynski, T. I., McCarty, G. W., & Siebelec, G. (2003). Response of soil microbiological activities to cadmium, lead and zinc salt amendments. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 1346–1355.
Urban, N. R., Eisenreich, S. J., Grigal, D. F., & Schurr, K. T. (1990). Mobility and diagenesis of Pb and 210Pb in peat. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 54, 3329–3346.
Vile, M. A., Wieder, R. K., & Novák, M. (1999). Mobility of Pb in Sphagnum-derived peat. Biogeochemistry, 45, 35–52.
Vurm, K. (2001). Dějiny příbramské hutě 1311–2000 (History of the Příbram Smelter 1311–2000). Kovohutě Příbram Editions, 200 pp. (in Czech).
Watmough, S. A. (1999). Monitoring historical changes in soil and atmospheric trace metal levels by dendrochemical analysis. Environmental Pollution, 106, 391–403.
Watmough, S. A., & Hutchinson, T. C. (1996). Analysis of tree rings using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry to record fluctuations in a metal pollution episode. Environmental Pollution, 93, 93–102.
Watmough, S. A., & Hutchinson, T. C. (2002). Historical changes in lead concentration in tree-rings of sycamore, oak and Scots pine in north-west England. Science of the Total Environment, 293, 85–96.
Watmough, S. A., Hutchinson, T. C., & Evans, R. D. (1997). Application of laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry in dendrochemical analysis. Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 114–118.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Marie Fayadová for assistance with laboratory work. The funding for this study was provided by Charles University (Nr. 271/2006/B-GEO) and the Ministry of Education of the Czech Republic (Nr. MSM0021620855). The reviews of two anonymous reviewers assisted greatly in improving the original manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mihaljevič, M., Zuna, M., Ettler, V. et al. A Comparison of Tree Rings and Peat Deposit Geochemical Archives in the Vicinity of a Lead Smelter. Water Air Soil Pollut 188, 311–321 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9546-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9546-2