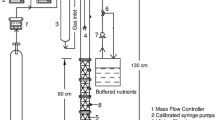
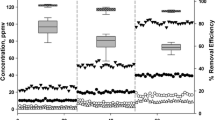
Abstract
Carbon dioxide served as a proxy for biodegradation in the biofiltration of multiple organic solvents in a batch biofilter. The solvents were injected into the batch biofilter system and were biodegraded with the biomass immobilized on a column of fibrous media; the immobilized biomass was acclimated to ethanol in a continuous biofilter. Time profiles of CO2 concentration were obtained for substrate utilization and for biomass endogenous respiration. The CO2 and substrate concentration profiles provided insight for the biodegradation of multiple substrates in a biofilter. Experimental results indicate that the biomass utilized the solvents simultaneously but at different rates. The utilization rates were in the order: acetaldehyde > ethanol > propanol > isopropanol, acetone > methanol > butanol. Isopropanol was transformed to acetone, which was then utilized and converted to CO2, and propanol was also utilized through the formation of an intermediate. The biodegradation of ethanol was inhibited by acetaldehyde. Total CO2 production was contributed by the endogenous respiration of the biomass as well as by the biodegradation of all the substrates present to the biomass, and the total CO2 rate might not reach its maximum potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aizpuru, A., Malhautier, L., Roux, J.C., & Fanlo, J.L. (2003). Biofiltration of a mixture of volatile organic compounds on granular activated carbon. Biotechnology Bioengineering, 83, 479–488.
Arulneyam, D., & Swaminathan, T. (2004). Biodegradation of mixture of VOC's in a biofilter . Journal of Environment Science—China, 16, 30–33.
Auria, R., Frere, G., Morales, M., Acuna, M.E., & Revah, S. (2000). Influence of mixing and water addition on the removal rate of toluene vapors in a biofilter. Biotechnology Bioengineering, 68, 448–455.
Barona, A., Elias, A., Arias, R., Cano, I., & Gonzalez, R. (2004). Biofilter response to gradual and sudden variations in operating conditions. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 22, 25–31.
Bustard, M.T., Whiting, S., Cowan, D.A., & Wright, P.C. (2002). Biodegradation of high-concentration isopropanol by a solvent-tolerant thermophile, Bacillus pallidus. Extremophiles, 6, 319–323.
Chang, K., & Lu, C. (2003). Biofiltration of isopropyl alcohol and acetone mixtures by a trickle-bed air biofilter. Process Biochemistry, 39, 415–423.
Christen, P., Domenech, F., Michelena, G., Auria, R., & Revah, S. (2002). Biofiltration of volatile ethanol using sugar cane bagasse inoculated with Candida utilis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 89, 253–265.
Cherry, R.S., & Thompson, D.N. (1997). The shift from growth to nutrient-limited maintenance kinetics during acclimation of a biofilter. Biotechnology Bioengineering, 56, 330–339.
Deshusses, M.A., & Johnson, C.T. (2000). Development and validation of a simple protocol to rapidly determine the performance of biofilters for VOC treatment. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 461–467.
Fürer, C., & Deshusses, M.A. (2000). Biodegradation in Biofilters: Did the Microbe Inhale the VOC?. In Proceedings of the annual meeting and exhibition of the air and waste management association. AWMA, Pittsburgh, PA. USA, Salt lake City, Utah, June 18–22, 2000, pp. 799–812.
Keesman, K.J., & Spanjers, H. (2000). Endogenous model state and parameter estimation from an extensive batch experiment. Biotechnology Bioengineering, 68, 422–429.
Keesman, K.J., Spanjers, H., & van Straten, G. (1998). Analysis of endogenous process behaviour. Water Science Technology, 37, 227–235.
Kennes, C., & Thalasso, F. (1998). Waste gas biotreatment technology. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 72, 303–319.
Leethochawalit, M., Goodwin, J.A.S., Meeyoo, V., Bustard, M.T., & Wright, P.C. (2004). Application of a solvent - tolerant microbial consortium for biofiltration of extremely high concentration gaseous solvent streams. Environmental Technology, 25, 491–499.
Liu, Y., Quan, X., Zhao, Y., Chen, S., & Zhao, H. (2005). Removal of ternary VOCs in air streams at high loads using a compost-based biofilter. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 23, 85–95.
Lu, C., Chang, K., & Hsu, S. (2004). A model for treating isopropyl alcohol and acetone mixtures in a trickle-bed air biofilter. Process Biochemical, 39, 1849–1858.
Mankad, T., & Bungay, H.R. (1988) Model for microbial-growth with more than one limiting nutrient. Journal of Biotechnology, 7, 161–166.
McEvoy, E., Wright, P.C., & Bustard, M.T. (2004). The effect of high concentration isopropanol on the growth of a solvent-tolerant strain of Chlorella vulgaris. Enzyme Microbiology and Technology, 35, 140–146.
Metris, A., Gerrard, A.M., Cumming, R.H., Weigner, P., & Paca, J. (2001), Modelling shock loadings and starvation in the biofiltration of toluene and xylene. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 76, 565–572.
Monod, J.: 1942, Recherches sur la croissance des cultures bateriennes. Paris: Herman er Cie, Paris.
Morgenroth, E., Schroeder, E.D., Chang, D.P.Y., Scow, K.M. (1996). Nutrient limitation in a compost biofilter degrading hexane. Journal of Air Waste Management Assocication, 46, 300–308.
Morita, R.Y. (1997). Bacteria in oligotrophic environments (pp. 274–348). Chapman & Hall, New York: International Thompson Publishing.
Okaygun, M.S., Green, L.A., & Akgerman, A. (1992). Effects of consecutive pulsing of an inhibitory substrate on biodegradation kinetics. Environmental Science and Technology, 26, 1746–1752.
Pitter, P., & Chudoba, J. (1990). Biodegradability of Organic Substances in the Aquatic Environment. CRC PR I LLC.
Prado, O.J., Veiga, M.C., & Kennes, C. (2004). Biofiltration of waste gases containing a mixture of formaldehyde and methanol. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 65, 235–242.
Radianingtyas, H., & Wright, P.C. (2003). 2-Propanol degradation by Sulfolobus solfataricus. Biotechnological Letters., 25, 579–583.
Sipkema, E.M., de Koning, W., Ganzeveld, K.J., Janssen, D.B., & Beenackers, A.A.C.M. (1998). Experimental pulse technique for the study of microbial kinetics in continuous culture. Journal of Biotechnology, 64, 159–176.
Spigno, G., & De Faveri, D.M. (2005). Modeling of a vapor-phase fungi bioreactor for the abatement of hexane: Fluid dynamics and kinetic aspects. Biotechnology Bioengineering, 89, 319–328.
Standing, C.N., Fredrickson, A.G., & Tsuchiya, H.M. (1972). Batch- and continuous-culture transients for two substrate systems. Applied Microbiology, 23, 354–359.
Stanley, G.A., Douglas, N.G., Every, E.J., Tzanatos, T., & Pamment, N.B. (1993). Inhibition and stimulation of yeast growth by acetaldehyde. Biotechnological Letters, 15, 1199–1204.
Tabak, H.H., & Govind, R. (1993). Prediction of biodegradation kinetics using a nonlinear group contribution method. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 12, 251–260.
Tseng, M.M. (1974). Kinetics of growth of Proteus vulgaris and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in pure and mixed culture systems. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toronto, 241 pp.
Vanrolleghem, P.A., Sin, G., & Gernaey, K.V. (2004). Transient response of aerobic and anoxic activated sludge activities to sudden substrate concentration changes. Biotechnology Bioengineering, 86, 277–290.
Volcik, V., Hoffmann, J., Ruzicka, J., & Sergejevova, M. (2005). Trichloroethylene (TCE) removal in a single pulse suspension bioreactor. Journal of Environment. Management, 74, 293–304.
Zarook, S.M., Shaikh, A.A., Ansar, Z., & Baltzis, B.C. (1997). Biofiltration of volatile organic compound (VOC) mixtures under transient conditions. Chemical Engineering Science, 52, 4135–4142.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Y., Govind, R. CO2 Response to Doses of Organic Solvents Biodegraded in a Batch Biofilter. Water Air Soil Pollut 175, 33–48 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9107-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9107-0