Abstract
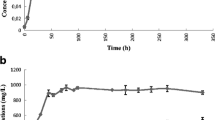
The aerobic biodegradation of high-concentration, to 24 g l–1, 2-propanol (IPA) by a thermophilic isolate ST3, identified as Bacillus pallidus, was successfully carried out for the first time. This solvent-tolerant B. pallidus utilized IPA as the sole carbon source within a minimal salts medium. Cultivation was carried out in 100-ml shake flasks at 60°C and compared with cultivation within a 1-l stirred tank reactor (STR). Specific growth rate (µ) was about 0.2 h–1 for both systems, with a maximum cell density of 2.4×108 cells ml–1 obtained with STR cultivation. During exponential growth and stationary phase, IPA biodegradation rates were found to be 0.14 and 0.02 g l–1 h–1, respectively, in shake-flask experiments, whereas corresponding values of 0.09 and 0.018 g l–1 h–1 were achievable in the STR. Generation of acetone, the major intermediate in aerobic IPA biodegradation, was also monitored as an indicator of microbial IPA utilization. Acetone levels reached a maximum of 2.2–2.3 g l–1 after 72 and 58 h for 100-ml and 1-l systems, respectively. Both IPA and acetone were completely removed from the medium following 160 and 175 h, respectively, during STR growth, although this was not demonstrated within shake-flask reactions. Growth of B. pallidus on acetone or IPA alone demonstrated that the maximum growth rate (µ) obtainable was 0.247 h–1 at 4 g l–1 acetone and 0.202 h–1 at 8 g l–1 IPA within shake-flask cultivation. These results indicate the potential of the solvent-tolerant thermophile B. pallidus ST3 in the bioremediation of hot solvent-containing industrial waste streams.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bustard, M.T., Whiting, S., Cowan, D.A. et al. Biodegradation of high-concentration isopropanol by a solvent-tolerant thermophile, Bacillus pallidus . Extremophiles 6, 319–323 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-001-0260-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-001-0260-5