Abstract
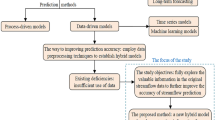
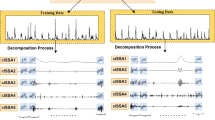
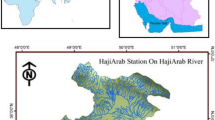
Reliable streamflow prediction is important for rational water resource planning. However, the strong nonlinearity and uncertainty of streamflow changes make accurate prediction challenging. Moreover, conventional streamflow prediction uses single-resolution data and provides deterministic prediction without uncertainty estimation, which leads to one-sidedness in data information extraction and risks in water resource decision-making. To improve streamflow prediction, this study proposes a probability prediction model integrating multi-resolution data for short-term streamflow prediction. In the proposed model, singular spectrum analysis (SSA) is utilized to process multi-resolution streamflow data to remove hidden noise. Then, support vector regression (SVR) is used for modelling, and grid search (GS) and cross-validation (CV) methods are employed to determine the optimal parameters of SVR. Finally, Gaussian process regression (GPR) is used for nonlinear fusion and probabilistic prediction. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed model, streamflow data from the Pingchuan bridge and Gaoya station with two different resolutions are collected, and several relevant models and indices are used for comparative analysis and comprehensive evaluation. The experimental results show that the proposed model significantly outperforms the relevant compared models, indicating that the proposed model effectively reduces the influence of interference signals on the modelling and fully utilizes the feature information provided by different resolution data to improve streamflow prediction. The results also confirm the superiority of integrating multi-resolution data over using single-resolution data in improving streamflow prediction. Moreover, the proposed model provides reliable uncertainty estimation in addition to providing accurate point prediction, which is helpful for water resource scheduling and decision-making. Therefore, the proposed model is recommended as a reliable method for streamflow prediction.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The data used in this study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Adnan RM, Mostafa RR, Kisi O, Yaseen ZM, Zounemat-Kermani M (2021) Improving streamflow prediction using a new hybrid ELM model combined with hybrid particle swarm optimization and grey wolf optimization. Knowl-Based Syst 230(6):107379
Borji M, Malekian A, Salajegheh A, Ghadimi M (2016) Multi-time-scale analysis of hydrological drought forecasting using support vector regression (SVR) and artificial neural networks (ANN). Arabian J Geosci 9:725
Chen Z, Nie Z, Zhang G, Wan L, Shen J (2006) Environmental isotopic study on the recharge and residence time groundwater in the Heihe River Basin, northwestern China. Hydrogeol J 14:1635–1651
Chu H, Wei J, Wu W, Jiang Y, Chu Q, Meng X (2021) A classification-based deep belief networks model framework for daily streamflow forecasting. J Hydrol 595:125967
Farjoudi SZ, Alizadeh Z (2021) A comparative study of total dissolved solids in water estimation models using gaussian process regression with different kernel functions. Environ Earth Sci 80:557
Freire PKDMM, Santos CAG, Silva GBLD (2019) Analysis of the use of discrete wavelet transforms coupled with ANN for short-term streamflow forecasting. Appl Soft Comput 80:494–505
Harraki WE, Ouazar D, Bouziane A, Harraki IE, Hasnaoui D (2021) Streamflow predition upstream of a dam using SWAT and assessement of the impact of land use spatial resolution on model performance. Envrion Process 8:1165–1186
Hu H, Zhang J, Li T (2021) A novel hybrid decompose-ensemble strategy with a VMD-BPNN approach for daily streamflow estimating. Water Resour Manag 35:5119–5138
Li Y, Huang J (2021) Leaf anthocyanin content retrieval with partial least squares and gaussian process regression from spectral reflectance data. Sensors 21:3078
Li Y, Liang Z, Hu Y, Li B, Wang D (2020) A multi-model integration method for monthly streamflow prediction: modified stacking ensemble strategy. J Hydroinform 22:310–326
Liu S, Xie Z, Zeng Y (2016a) Discharge estimation for an ungauged Inland River in an arid area related to anthropogenic activities: a case study of Heihe River Basin, Northwestern China. Adv Meteorol 6716501:1–11
Liu S, Xie Z, Zeng Y (2016b) Estimation of streamflow in ungauged basins using a combined model of black-box model and semi-distributed model: case study in the Yingluoxia watershed. J Beijing Normal Univ (Nat Sci) 52:393–401
Ma X, Yu J, Dong Q (2017) A generalized dynamic fuzzy neural network based on singular spectrum analysis optimized by brain storm optimization for short-term wind speed forecasting. Appl Soft Comput 54:296–312
Morikawa K, Nagao H, Ito SI, Terada Y, Sakai S, Hirata N (2021) Forecasting temporal variation of aftershocks immediately after a main shock using gaussian process regression. Geophys J Int 226:1018–1035
Mozaffari S, Javadi S, Moghaddam HK, Randhir TO (2022) Forecasting groundwater levels using a hybrid of support vector regression and particle swarm optimization. Water Resour Manag 36:1955–1972
Narsimlu B, Gosain AK, Chahar BR, Singh SK, Srivastava PK (2015) SWAT model calibration and uncertainty analysis for streamflow prediction in the Kunwari River Basin, India, using sequential uncertainty fitting. Environ Process 2:79–95
Niu WJ, Feng ZK (2021) Evaluating the performances of several artificial intelligence methods in forecasting daily streamflow time series for sustainable water resources management. Sustain Cities Soc 64:102562
Noorbeh P, Roozbahani A, Moghaddam HK (2020) Annual and monthly dam inflow prediction using Bayesian networks. Water Resour Manag 34:2933–2951
Pipia L, Amin E, Belda S, Delgado MS, Verrelst J (2021) Green LAI mapping and cloud gap-filling using gaussian process regression in google earth engine. Remote Sens 13:403
Sharma S, Ghimire GR, Siddique R (2023) Machine learning for postprocessing ensemble streamflow forecasts. J Hydroinform 25:1126
Shen J, Zou L, Dong Y, Xiao S, Zhao Y, Liu C (2022) Improving daily streamflow forecasting using deep belief net-work based on flow regime recognition. Water 14(14):2241
Singh VP, Cui H (2015) Entropy theory for streamflow forecasting. Environ Process 2:449–460
Sivapragasam C, Liong SY, Pasha MFK (2001) Rainfall and runoff forecasting with SSA-SVM approach. J Hydroinform 3(3):141–152
Tikhamarine Y, Souag-Gamane D, Kisi O (2019) A new intelligent method for monthly streamflow prediction: hybrid wavelet support vector regression based on grey wolf optimizer (WSVR–GWO). Arab J Geosci 12:540
Tyralis H, Papacharalampous G, Langousis A (2021) Super ensemble learning for daily streamflow forecasting: large-scale demonstration and comparison with multiple machine learning algorithms. Neural Comput Appl 33:3053–3068
Wagena MB, Goering D, Collick AS, Bock E, Easton ZM (2020) Comparison of short-term streamflow forecasting using stochastic time series, neural networks, process-based, and Bayesian models. Environ Modell Softw 126(4):104669
Wang L, Guo Y, Fan M (2022) Improving annual streamflow prediction by extracting information from high-frequency components of streamflow. Water Resour Manag 36(12):4535–4555
Wang L, Li X, Ma C, Bai Y (2019) Improving the prediction accuracy of monthly streamflow using a data-driven model based on a double-processing strategy. J Hydrol 573:733–745
Wang Y, Feng B, Hua QS, Sun L (2021) Short-term solar power forecasting: a combined long short-term memory and gaussian process regression method. Sustainability 13:3665
Wang Y, Yuan Y, Pan Y, Fan Z (2020) Modeling daily and monthly water quality indicators in a canal using a hybrid wavelet-based support vector regression structure. Water 12(5):1476
Wei S, Bai X (2022) Multi-step short-term building energy consumption forecasting based on singular spectrum analysis and hybrid neural network. Energies 15(5):1743
Wu J, Ding Y, Ye B, Yang Q, Zhang X, Wang J (2010) Spatio-temporal variation of stable isotopes in precipitation in the Heihe River Basin, Northwestern China. Environ Earth Sci 61:1123–1134
Wu J, Liu H, Wei G, Song T, Zhang C, Zhou H (2019) Flash flood forecasting using support vector regression model in a small mountainous catchment. Water 11(7):1327
Yaseen ZM, Ebtehaj I, Bonakdari H, Deo RC, Mehr AD, Mohtar WHM, Diop L, El-Shafie A, Singh VP (2017) Novel approach for streamflow forecasting using a hybrid ANFIS-FFA model. J Hydrol 554:263–276
Yuan L, Forshay KJ (2021) Enhanced streamflow prediction with SWAT using support vector regression for spatial calibration: a case study in the Illinois River watershed, U.S. PLoS One 16(14):e0248489
Zakhrouf M, Bouchelkia H, Kim S, Stamboul M (2021) Novel insights for streamflow forecasting based on deep learning models combined the evolutionary optimization algorithm. Phys Geog 1943126
Zakhrouf M, Bouchelkia H, Stamboul M, Kim S (2020) Novel hybrid approaches based on evolutionary strategy for streamflow forecasting in the Chellif River, Algeria. Acta Geophys 68:167–180
Zhao T, Wang QJ, Bennett JC, Robertson DE, Shao Q, Zhao J (2015) Quantifying predictive uncertainty of streamflow forecasts based on a Bayesian joint probability model. J Hydrol 528:329–340
Zhao X, Lv H, Lv S, Sang Y, Wei Y, Zhu X (2021) Enhancing robustness of monthly streamflow forecasting model using gated recurrent unit based on improved grey wolf optimizer. J Hydrol 601:126607
Funding
This work was supported by the Foundation of Northwest Normal University of China (NWNULKQN2019-18).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lili Wang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, review and editing. Zexia Li: Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. Fuqiang Ye: Validation, Writing – review and editing. Tongyang Liu: Investigation, Writing – review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Li, Z., Ye, F. et al. A Probability Model for Short-Term Streamflow Prediction Based on Multi-Resolution Data. Water Resour Manage 37, 5601–5618 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03620-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03620-y