Abstract
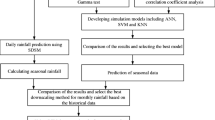
The study proposes a statistical downscaling procedure for regional rainfall. In the multistage procedure, the spatial downscaling stage using Relevance Vector Machine (RVM) model captures the climate change signals in the monthly scale simulations from the climate models by considering a predictor set that is based on the regional climatic phenomena. The spatially downscaled monthly rainfall is then disaggregated into daily scale using a modified weather generator. In the temporal downscaling stage using a weather generator, the transition matrix is modified to account for the non-stationarities in the rainfall. The proposed methodology is validated in the Bharathapuzha River Basin, India by downscaling rainfall data from climate models, BNU-ESM, CESM1-BGC, CMCC-ESM2, FGOALS-G2, FIO-ESM-2.0, and MIROC4H. The process-based indices specified in the VALUE framework developed from the downscaled rainfall data closely matches the indices developed from the observed rainfall data for the historical period, with absolute PBIAS less than 14% across all the indices considered. The reduction in uncertainty achieved is studied using average band width of the simulations, which is seen to reduce from 186 mm to 52 mm after downscaling. The capability of the downscaling procedure for capturing the non-stationarity in the climate is tested by comparing the performance of the procedure over warm and cold phases of ENSO, and it is found to be satisfactory.
Highlights
The study proposes a multi stage, stochastic approach for statistical downscaling of rainfall.
It combines the strength of RVM models and weather generators.
The statistical downscaling relationship is based on the regional climatic phenomena.
Downscaled rainfall series captures the occurrence and distribution characteristics of regional observed rainfall and its non-stationarity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adarsh S, Janga Reddy M (2019) Links between global climate teleconnections and indian Monsoon Rainfall. Climate change signals and response. Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp 61–72
Ajayamohan RS, Merryfield WJ, Kharin VV (2010) Increasing trend of synoptic activity and its relationship with extreme rain events over central India. J Clim 23:1004–1013. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JCLI2918.1
Boers N, Goswami B, Rheinwalt A et al (2019) Complex networks reveal global pattern of extreme-rainfall teleconnections. Nature 566:373–377. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0872-x
Chandran LR, Jairaj PG (2019) Downscaling of precipitation for Bharathapuzha river basin in Kerala. In: Recent Advances in Materials, Mechanics and Management: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Materials, Mechanics and Management (IMMM 2017), July 13–15, 2017, Trivandrum, Kerala, India. p 110
Chen J, Brissette FP, Leconte R (2010) A daily stochastic weather generator for preserving low-frequency of climate variability. J Hydrol 388:480–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.05.032
Comiso JC, Hall DK (2014) Climate trends in the Arctic as observed from space. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Clim Chang 5:389–409. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcc.277
Ehteram M, Ahmed AN, Sheikh Khozani Z, El-Shafie A (2023) Convolutional neural network -support vector machine model-gaussian process regression: a New Machine Model for Predicting Monthly and Daily Rainfall. Water Resour Manag 37:3631–3655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03519-8
Fischer EM, Beyerle U, Knutti R (2013) Robust spatially aggregated projections of climate extremes. Nat Clim Chang 3:1033–1038. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2051
Fletcher T (2010) Relevance Vector Machines Explained. Tech Rep - Univ Coll London 1–9
George J, P Athira (2020) Long-term changes in climatic variables over the Bharathapuzha river basin, Kerala, India. Theor Appl Climatol 142:269–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03255-8
George J, Athira P (2022) Process informed selection of climate models for climate change impact assessment in the Western Coast of India. Theor Appl Climatol 805–828. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-04197-z
Ghosh S, Mujumdar PP (2008) Statistical downscaling of GCM simulations to streamflow using relevance vector machine. Adv Water Resour 31:132–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2007.07.005
Huang B, Thorne PW, Banzon VF et al (2017) Extended reconstructed Sea surface temperature, Version 5 (ERSSTv5): upgrades, validations, and intercomparisons. J Clim 30:8179–8205. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0836.1
Ihara C, Kushnir Y, Cane MA, De La Peña VH (2007) Indian summer monsoon rainfall and its link with ENSO and Indian Ocean climate indices. Int J Climatol 27:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1394
IPCC (2022) Summary for Policymakers: Climate Change 2022_ Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability_Working Group II contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernamental Panel on Climate Change
Jebeile J, Lam V, Räz T (2021) Understanding climate change with statistical downscaling and machine learning. Synthese 199:1877–1897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11229-020-02865-z
Jeong DI, St-Hilaire A, Ouarda TBMJ, Gachon P (2012) Multisite statistical downscaling model for daily precipitation combined by multivariate multiple linear regression and stochastic weather generator. Clim Change 114:567–591
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R et al (1996) The NCEP / NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project
Legasa MN, Manzanas R, Calviño A, Gutiérrez JM (2022) A Posteriori Random forests for Stochastic Downscaling of Precipitation by Predicting Probability Distributions. Water Resour Res 58:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021WR030272
Liu Y, Feng J, Shao Y, Li JL (2019) Identify optimal predictors of statistical downscaling of summer daily precipitation in China from three-dimensional large-scale variables. Atmos Res 224:99–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.03.022
Mishra AK, Dwivedi S, Das S (2020) Role of Arabian Sea warming on the indian summer monsoon rainfall in a regional climate model. Int J Climatol 40:2226–2238. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6328
Mullan D, Chen J, Zhang XJ (2016) Validation of non-stationary precipitation series for site-specific impact assessment: comparison of two statistical downscaling techniques. Clim Dyn 46:967–986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2626-x
Nourani V, Razzaghzadeh Z, Baghanam AH, Molajou A (2019) ANN-based statistical downscaling of climatic parameters using decision tree predictor screening method. Theor Appl Climatol 137:1729–1746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2686-z
Olmo ME, Bettolli ML (2022) Statistical downscaling of daily precipitation over southeastern South America: assessing the performance in extreme events. Int J Climatol 42:1283–1302. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.7303
Pai DS, Sridhar L, Rajeevan M et al (2014) Development of a new high spatial resolution (0.25° × 0.25°) long period (1901–2010) daily gridded rainfall data set over India and its comparison with existing data sets over the region. Mausam 65:1–18
Raj EE, Kumar RR, Ramesh KV (2020) El niño–southern oscillation (ENSO) impact on tea production and rainfall in south India. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 59:651–664. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAMC-D-19-0065.1
Rayner D, Achberger C, Chen D (2016) A multi-state weather generator for daily precipitation for the Torne River basin, northern Sweden/western finland. Adv Clim Chang Res 7:70–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.accre.2016.06.006
Sachindra DA, Ahmed K, Rashid MM et al (2018) Statistical downscaling of precipitation using machine learning techniques. Atmos Res 212:240–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.05.022
Schneider SH, Kuntz-Duriseti K (2002) Uncertainty and climate change policy. Clim Chang Policy a Surv 53–87
Sulaiman NAF, Shaharudin SM, Ismail S et al (2022) Predictive modelling of statistical Downscaling based on Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Daily Rainfall in East-Coast Peninsular Malaysia. Symmetry (Basel) 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14050927
Tipping ME (2001) Sparse bayesian learning and the relevance Vector Machine. J Mach Learn Res 1:211–244. https://doi.org/10.1162/15324430152748236
Wada IM, Usman HS, Nwankwegu AS et al (2023) Selection and downscaling of CMIP6 climate models in Northern Nigeria. Theor Appl Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-023-04534-w
Walsh JE, Bhatt US, Littell JS et al (2018) Downscaling of climate model output for alaskan stakeholders. Environ Model Softw 110:38–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2018.03.021
Zhang X-C, Chen J, Garbrecht JD, Brissette FP (2012) Evaluation of a weather generator-based method for statistically downscaling non-stationary climate scenarios for impact assessment at a point scale. Trans ASABE 55:1745–1756
Funding
The current study is funded by the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India under the INSPIRE Faculty scheme [DST/INSPIRE/04/2015/000382].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both the authors contributed to the study conception and design. The development and implementation of the methodology, analysis of the results and draft of the manuscript was prepared by Jose George. The supervision of the study and finalization of the manuscript was done by Athira.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
George, J., P., A. A Multi-stage Stochastic Approach for Statistical Downscaling of Rainfall. Water Resour Manage 37, 5477–5492 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03615-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-023-03615-9