Abstract
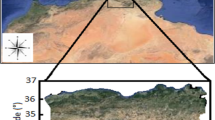
The precise estimation of reference crop evapotranspiration (ETO) is vital for regional and irrigation water resource management. It is also beneficial to the rational allocation of regional water resources and alleviates the disparity between water supply and demand. This study accurately estimates the ETO of 14 meteorological stations in southern China. Five neural network models (extreme learning machine [ELM], back-propagation neural network [BP], ant colony optimization [ACO]-BP, bird swarm algorithm [BSA]-BP, and cat swarm optimization [CSO]-BP) were introduced to predict ETO with limited factors using different methods. The results demonstrated that models involving T (average, maximum, and minimum air temperature), sunshine duration (n), and relative humidity (RH) exhibited the highest accuracy of all studied combinations; the role of T, n, RH, wind speed (U2) and average atmospheric pressure (AP) regarding ETO gradually decreased. These three biological heuristic algorithms (ACO, BSA, and CSO) each significantly enhanced the capability of the BP model. The accuracy and computational cost of the CSO-BP model are better than those built by other algorithms. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to use the CSO-BP model for ETO estimation in southern China. This result serves as a reference for a more accurate estimation of ETO for future irrigation decision-making and water resource management in southern China.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Available upon request.
References
Abbas F, Fan P (2018) Clustering-based reliable low-latency routing scheme using ACO method for vehicular networks. Veh Commun 12:66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2018.02.004
Agrawal Y, Kumar M, Ananthakrishnan S, Kumarapuram G (2022) Evapotranspiration modeling using different tree based ensembled machine learning algorithm. Water Resour Manag 36:1025–1042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03067-7
Ahi Y, Coşkun Dilcan Ç, Köksal DD, Gültaş HT (2022) Reservoir evaporation forecasting based on climate change scenarios using artificial neural network model. Water Resour Manag 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03365-0
Ahmadi F, Mehdizadeh S, Mohammadi B, Pham QB, Doan TNC, Vo ND (2021) Application of an artificial intelligence technique enhanced with intelligent water drops for monthly reference evapotranspiration estimation. Agric Water Manag 244:106622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106622
Altay EV, Alatas B (2020) Bird swarm algorithms with chaotic mapping. Artif Intell Rev 53(2):1373–1414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-019-09704-9
Arora A, Arabameri A, Pandey M, Siddiqui MA, Bhardwaj A (2021) Optimization of state-of-the-art fuzzy-metaheuristic ANFIS-based machine learning models for flood susceptibility prediction mapping in the Middle Ganga Plain. India. Sci Total Environ 750:141565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141565
Bellido-Jiménez JA, Estévez J, García-Marín AP (2020) New machine learning approaches to improve reference evapotranspiration estimates using intra-daily temperature-based variables in a semi-arid region of Spain. Agric Water Manag 245:106558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106558
Chu S, Tsai P, Pan J (2006) Cat swarm optimization. Lect Notes Comput Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/11801603_94
Cui Y, Jia L, Fan W (2021) Estimation of actual evapotranspiration and its components in an irrigated area by integrating the Shuttleworth-Wallace and surface temperature-vegetation index schemes using the particle swarm optimization algorithm. Agric For Meteorol 307:108488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2021.108488
Dong J, Zhu Y, Jia X, Han X, Qiao J, Bai C, Tang X (2022) Nation-scale reference evapotranspiration estimation by using deep learning and classical machine learning models in China. J Hydrol 604:127207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.12720727207
dos Santos Farias DB, Althoff D, Rodrigues LN, Filgueiras R (2020) Performance evaluation of numerical and machine learning methods in estimating reference evapotranspiration in a Brazilian agricultural frontier. Theor Appl Climatol 142(3):1481–1492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03380-4
Elkatoury A, Alazba AA, Mossad A (2020) Estimating evapotranspiration using coupled remote sensing and three SEB models in an arid region. Environ Process 7(1):109–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-019-00410-w
Fan J, Yue W, Wu L, Zhang F, Cai H, Wang X, Lu X, Xiang Y (2018) Evaluation of SVM, ELM and four tree-based ensemble models for predicting daily reference evapotranspiration using limited meteorological data in different climates of China. Agric for Meteorol 263:225–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2018.08.019
Feng Y, Jia Y, Zhang Q, Gong D, Cui N (2018) National-scale assessment of pan evaporation models across different climatic zones of China. J Hydrol 564:314–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.07.013
Gocić M, Arab Amiri M (2021) Reference evapotranspiration prediction using neural networks and optimum time lags. Water Resour Manag 35:1913–1926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02820-8
Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK (2006) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70:489–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126
Huang J, Asteris PG, Pasha MKS, Mohammed AS, Hasanipanah M (2020) A new auto-tuning model for predicting the rock fragmentation: a cat swarm optimization algorithm. Eng Comput 2020:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01207-4
Laura R, Matteo B, Gianluca R (2008) On ant routing algorithms in ad hoc networks with critical connectivity. Ad Hoc Netw 6(6):827–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2007.07.003
Lin K, Zhang K, Huang Y, Hung J, Yen N (2016) Feature selection based on an improved cat swarm optimization algorithm for big data classification. J Supercomput 72(8):3210–3221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-016-1631-0
Liu T, Xu T, Yu F, Yuan Q, Guo Z, Xu B (2021) A method combining ELM and PLSR (ELM-P) for estimating chlorophyll content in rice with feature bands extracted by an improved ant colony optimization algorithm. Comput Electron Agric 186:106177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2021.106177
Maqsood J, Farooque AA, Abbas F, Esau T, Wang X, Acharya B, Afzaal H (2022) Application of artificial neural networks to project reference evapotranspiration under climate change scenarios. Water Resour Manag 36:835–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02997-y
Meng X, Gao X, Lu L, Liu Y, Zhang H (2016) A new bio-inspired optimisation algorithm: Bird Swarm Algorithm. J Exp Theor Artif Intell 28(4):673–687. https://doi.org/10.1080/0952813X.2015.1042530
Ravindran SM, Bhaskaran SKM, Ambat SKN (2021) A deep neural network architecture to model reference evapotranspiration using a single input meteorological parameter. Environ Process 8(4):1567–1599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-021-00543-x
Rodrigues GC, Braga RP (2021) Estimation of reference evapotranspiration during the irrigation season using nine temperature-based methods in a hot-summer mediterranean climate. Agriculture 11(2):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11020124
Roy DK (2021) Long short-term memory networks to predict one-step ahead reference evapotranspiration in a subtropical climatic zone. Environ Process 8(2):911–941. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-021-00512-4
Wang S, Liu S, Che X, Wang Z, Zhang J, Kong D (2020) Recognition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using fluorescence spectrometry combined with bird swarm algorithm optimization support vector machine. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 224:117404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.117404
Wu L, Fan J (2019) Comparison of neuron-based, kernel-based, tree-based and curve-based machine learning models for predicting daily reference evapotranspiration. PLoS ONE 14(5):0217520. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217520
Wu L, Zhou H, Ma X, Fan J, Zhang F (2019) Daily reference evapotranspiration prediction based on hybridized extreme learning machine model with bio-inspired optimization algorithms: Application in contrasting climates of China. J Hydrol 577:123960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.123960
Xing X, Liu Y, Zhao W, Kang D, Yu M, Ma X (2016) Determination of dominant weather parameters on reference evapotranspiration by path analysis theory. Comput Electron Agric 120(22):10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2015.11.001
Zhang J, Xia K, He Z, Fan S (2020) Dynamic multi-swarm differential learning quantum bird swarm algorithm and its application in random forest classification model. Comput Intell Neurosci 6858541:24. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6858541
Zhang Z, Gong Y, Wang Z (2018) Accessible remote sensing data based reference evapotranspiration estimation modelling. Agric Water Manag 210:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.07.039
Zhao L, Zhao X, Zhou H, Wang X, Xing X (2021) Prediction model for daily reference crop evapotranspiration based on hybrid algorithm and principal components analysis in Southwest China. Comput Electron Agric 190:106424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2021.106424
Zhu B, Feng Y, Gong D, Jiang S, Zhao L, Cui N (2020) Hybrid particle swarm optimization with extreme learning machine for daily reference evapotranspiration prediction from limited climatic data. Comput Electron Agric 173:105430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2020.105430
Zhu L, Wang Y, Meng Z, Wang T (2022) Critical current and n-value prediction of second-generation high temperature superconducting conductors considering the temperature-field dependence based on the back propagation neural network with encoder. Supercond Sci Technol 35(10). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-668/ac88fc
Acknowledgements
Our research would not have been possible without the climate database provided by the China Meteorological Administration.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51922072, 51779161, 51009101), Key R&D and Promotion Projects in Henan Province (Science and Technology Development) (No. 222102110452 and No. 2023–1836), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2019CDPZH-10), PhD research start up the foundation of Henan University of Science and Technology (No. 13480025 and No. 13480033) and Key Scientific Research Projects of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province(22B416002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.Z: Validation, L.X: Methodology and Writing, L.Z: Conceptualization and Writing, N.C: Conceptualization, S.C: Data curation, X.Z: Data curation, Y.S: Methodology, Y.W: Methodology and Writing, Z.L: Data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
All authors give their consent to participate.
Consent to Publish
All authors give their consent to publish.
Competing Interests
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L., Xing, L., Wang, Y. et al. Prediction Model for Reference Crop Evapotranspiration Based on the Back-propagation Algorithm with Limited Factors. Water Resour Manage 37, 1207–1222 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03423-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03423-7