Abstract
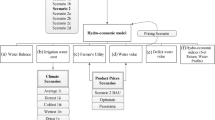
Hydro-economic models are valuable tools that can be used in irrigated agriculture in order to improve the understanding of the status quo of water resources, the role of water in agriculture, and the system behavior under changing conditions. The present paper attempts to give insights on how different water management objectives and data availability may influence the specification/application of hydro-economic modeling, as well as the reliability and interpretation of their results. A Greek rural watershed located in Central Greece (Region of Thessaly) is used as a case study application. A common hydro-economic framework for sustainable water resources management in irrigated agriculture is examined, aiming to provide a simple and understandable tool for policymakers. In this framework two hydro-economic models (HEMs) were developed to address challenges regarding data limitations, spatial analysis, and scenario-based problems (e.g. agri-economic scenarios, water policy scenarios, environmental scenarios, etc.). A set of selection criteria was then used to qualitatively compare these two models, based on their advantages and disadvantages. The results of this analysis indicate that HEMs’ development must be quite flexible about their settings and must take into consideration the desired accuracy level that is likely to satisfy their main purpose/goal. The optimal approach is the one that can achieve a balance between simplicity, flexibility, accuracy and robustness.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data available after request from the authors.
References
Alamanos A, Latinopoulos D, Xenarios S, Tziatzios G, Mylopoulos N, Loukas A (2019a) Combining hydro-economic and water quality modeling for optimal management of a degraded watershed. J Hydroinf 21(6):1118–1129. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2019.079
Alamanos A, Latinopoulos D, Papaioannou G, Mylopoulos N (2019b) Integrated hydro-economic modeling for sustainable water resources management in data-scarce areas. Water Resour Manag 2775–2790:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02241-8
Alamanos A, Latinopoulos D, Mylopoulos N (2020) A methodological framework for an easy and reliable estimation of the full cost of irrigation water. Water Environ J. https://doi.org/10.1111/wej.12556
Barthel R, Reichenau TG, Krimly T, Dabbert S, Schneider K, Mauser W (2012) Integrated Modeling of Global Change Impacts on Agriculture and Groundwater Resources. Water Resour Manag 26:1929–1951. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0001-9
Bekchanov M, Sood A, Jeuland M (2015) Review of hydro-economic models to address river basin management problems: structure, applications and research gaps. Colombo, Sri Lanka: International Water Management Institute. 60p (IWMI Working Paper 167). https://doi.org/10.5337/2015.218
Bekchanov M, Aditya S, Pinto A, Jeuland M (2017) Systematic review of water-economy modeling applications. J Water Resour Plan Manag 143(8):04017037. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000793
Blanco-Gutiérrez I, Varela-Ortega C, Purkey DR (2013) Integrated assessment of policy interventions for promoting sustainable irrigation in semi-arid environments: a hydro-economic modeling approach. J Environ Manag 128:144–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.04.037
Blaney HF, Criddle WD (1962) Determining consumptive use and irrigation water requirements. U.S. Dept. Agr. Agricultural Research Service Tech Bull 1275. 59p
Common Implementation Strategy Working Group 2 (WATECO) EU Guidance Document: Economics and the Environment. The Implementation Challenge of the Water Framework Directive. August 2002, WATECO. Available online: http://forum.europa.eu.int/Public/irc/env/wfd/library. Accessed 30 April 2015
Cornelissen T, Diekkrüger B, Giertz S (2013) A comparison of hydrological models for assessing the impact of land use and climate change on discharge in a tropical catchment. J Hydrol 498:221–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.06.016
EU Commission (2000) Water Framework Directive (WFD) 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, of 23 October 2000, establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Official Journal of the European Economics L327/1,22.12.2000: http://europa.eu.int/comm/environment/water/water-framework/index_en.html
FAO (2015) Cropwat. http://www.fao.org/nr/water/infores_databases_cropwat.html (Accessed: 30 Nov 2018)
Gibbons DC (1986) The economic value of water. Resources for the Future, Washington, DC
Greek Ministry of Environment, Energy and Climate Change, Special Water Secretariat (2012) Water Resources Management Plans for the Water Districts of Thessaly, Epirus and Central Greece, according to the Requirements of the Water Framework Directive 2000/60/EC, the Law 3199/2003 and the Presidential Decree 51/2007. Special Water Secretariat-YPEKA, Athens, Greek, 2012.
Greek Payment Authority of Common Agricultural Policy (GPACAP) www.opekepe.gr last Accessed: 26 Oct 2016
Harou JJ, Pulido-Velazquez M, Rosenberg DE, Medellín-Azuara J, Lund JR, Howitt RE (2009) Hydro-economic models: concepts, design, applications, and future prospects. J Hydrol 375:627–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.06.037
Heady EO (1952) Economics of Agricultural Production and Resource Use. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Krause P, Boyle DP, Base F (2005) Comparison of different efficiency criteria for hydrological model assessment. European Geosciences Union, Adv Geosci, (5): 89–97. https://doi.org/10.5194/adgeo-5-89-2005
Latinopoulos P (2005) Valuation and pricing of irrigation water: an analysis in Greek agricultural areas. Global Nest J 7(3):323–335
Latinopoulos D (2006) Application of Multicriteria Analysis for the economic assessment of agricultural water under Sustainable Water Resources Management. PhD thesis, Aristotle University, Department of Civil Engineering, Division of Hydraulics and Environmental Engineering
Loukas A, Mylopoulos N, Vasiliades L (2007) A modeling system for the evaluation of water resources management scenarios in Thessaly, Greece. Water Resour Manag 21(10):1673–1702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-006-9120-5
Loukas A, Tzabiras J, Spiliotopoulos M, Fafoutis C, Mylopoulos N (2014) Development of a District Information System for Water Management Planning and Strategic Decision Making. RSCy 2014, Second International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation 2014, 7-10 April 2014, Paphos, Cyprus
Myung JI, Pitt MA (2018) Model comparison in psychology. Stevens’ Handbook Experiment Psychol Cognit Neurosci:1–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119170174.epcn503
Nakic Z (2017) Integrated hydro-economic models as a tool for the sustainable management of water resources. J Environ Geol 2(1):11–12
Sherafatpour Z, Roozbahani A, Hasani Y (2019) Water Resour Manag (33): 2277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02240-9
Sidiropoulos P, Mylopoulos N, Loukas A (2013) Optimal Management of an Overexploited Aquifer under Climate Change: The Lake Karla Case. Water Resour Manag 27(6):1635–1649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0083-4
Spiliotopoulos M, Loukas A, Mylopoulos N (2015) A new remote sensing procedure for the estimation of crop water requirements. 3rd International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment 2015, 16-19 March 2015, Cyprus. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2192688
Tietenberg T, Lewis L (2011) Environmental & Natural Resource Economics 9th edition. Pearson, Boston
Tzabiras J, Vasiliades L, Sidiropoulos P, Loukas A, Mylopoulos N (2016) Evaluation of water resources management strategies to overturn climate change impacts on Lake Karla watershed. Water Resour Manag 30:5819–5844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1536-y
Water Evaluation And Planning System (WEAP), Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI) – www.weap21.org. Accessed 8 April 2019
Acknowledgements
A previous version of this work has been presented in the 11th World Congress on Water Resources and Environment (EWRA 2019): Alamanos A, Mylopoulos N, Loukas A, Latinopoulos D, Xenarios S (2019) Hydro-economic modelling approaches for agricultural water resources management in a Greek Watershed. 11th World Congress on Water Resources and Environment (EWRA 2019), Madrid, Spain, 25–29 June 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alamanos, A., Latinopoulos, D., Loukas, A. et al. Comparing Two Hydro-Economic Approaches for Multi-Objective Agricultural Water Resources Planning. Water Resour Manage 34, 4511–4526 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02690-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02690-6