Abstract
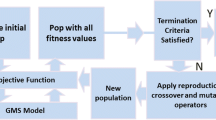
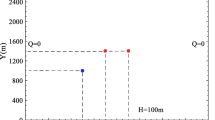
In this study, a simulation-optimization (SO) model is presented by coupling a meshfree based simulator using radial point collocation method (RPCM) and particle swarm optimization (PSO) as optimizer to identify the unknown groundwater contaminant sources from the measured/simulated contaminant concentration data in the aquifer. To demonstrate the approach, two case studies have been presented. The first example is a hypothetical case which simulates the contaminant releases from several disposal sites in an aquifer during four years release period. The second case considered is a field study where leaching of contaminant, during their storage, from disposal sites at several locations in the aquifer leads to contamination of the groundwater. The goal in both cases was to reconstruct the contaminant release history from the disposal sites and their magnitudes from the given historical concentration data at a few observation wells in the aquifer. It was observed that the source identification model could reconstruct the release histories from the waste disposal sites in both the cases accurately. This study demonstrated that PSO based optimization model with a meshfree flow and transport simulator can be effectively used for groundwater contaminant source identification problems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aral M, Guan J, Maslia M (2001) Identification of contaminant source location and release history in aquifers. J Hydrol Eng 6(3):225–234
Atmadja J, Bagtzoglou A (2001) State of the art report on Mathematical Methods for Groundwater Pollution Source Identification. Environ Forensic 2:205–214
Ayvaz MT (2010) A linked simulation-optimization model for solving the unknown groundwater pollution source identification problems. J Contam Hydrol 117:46–59
Bagtzoglou A, Atmadja J (2003) Marching-jury backward beam equation and quasi-reversibility methods for hydrologic inversion: application to contaminant plume spatial distribution recovery. Water Resour Res 39(2):10–14
Bagtzoglou A, Dougherty D, Tompson A (1992) Application of particle methods to reliable identification of groundwater pollution sources. Water Resour Manage 6:15–23
Bear J (1979) Hydraulics of groundwater. McGraw Hill Publishing, New York
Clerc M, Kennedy J (2002) The particle swarm - explosion, stability,and convergence in a multidimensional complex space. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6(1):58–73
Datta B, Chakrabarty D, Dhar A (2009) Optimal dynamic monitoring network design and identification of unknown groundwater pollution sources. Water Resour Manag 23(10):2031–2049
Datta B, Prakash O (2013) Efficient identification of unknown groundwater pollution sources using linked simulation-optimization incorporating monitoring location impact factor and frequency factor. Water Resour Manag 27(14):4959–4976
Freeze R, Cherry J (1979) Groundwater. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs,New York
Gorelick S, Evans B, Remson I (1983) Identifying sources of groundwater pollution: an optimization approach. Water Resour Res 19(3):779–790
Guneshwor LS, Eldho T, Vinod Kumar A (2016) Coupled groundwater flow and contaminant transport simulation in a confined aquifer using meshfree radial point collocation method(RPCM). Eng Anal Bound Elem 66:20–33
Hardy RL (1971) Multiquadric equations of topography and other irregular surfaces. J Geophys Res 76:1905–1915
Jha MK, Datta B (2014) Linked simulation-optimization based dedicated monitoring network design for unknown pollutant source identification using dynamic time warping distance. Water Resour Manag 28(12):4161–4182
Jiang S, Cai Y, Wang M, Zhou N (2012) Simultaneous identification of groundwater contaminant source and aquifer parameters by harmony search algorithm. J Hydraul Eng 43(12):1470–1477
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. Proc of IEEE International Conference on Neural, 1942–1948
Liu GR, Gu YT (2005) An introduction to meshfree methods and their programming. Springer, New York
Mahar P, Datta B (1997) Optimal monitoring network and groundwater pollution source identification. J Water Resour Plann Manage 123:199–207
Mahar P, Datta B (2000) Identification of pollution sources in transient groundwater systems. Water Resour Manag 14:209–227
Mahinthakumar G, Sayeed M (2005) Hybrid Genetic algorithm - local search methods for solving groundwater source identification inverse problems. J Water Resour Plan Manag 131(1):45–57
Meenal M, Eldho TI (2011) Simulation of groundwater flow in an unconfined aquifer using meshfree point collocation method. Eng Anal Bound Elem 35:700–707
Moutsopoulos KN, Tsihrintzis VA (2009) Analytical solutions and simulation approaches for double permeability aquifers. Water Resour Manag 23(3):395–415
Neupauer R, Wilson J (1999) Adjoint method for obtaining backward-in-time location and travel probabilities of a conservative groundwater contaminant. Water Resour Res 35(11):3389–3398
Sidauruk P, Cheng A-D, Ouazar D (1998) Groundwater contaminant source and transport parameter identification by correlation coefficient optimisation. Ground Water 36(2):208–214
Singh R, Datta B (2006) Identification of groundwater pollution sources using GA based linked simulation optimisation model. J Hydrol Eng 11(2):101–109
Singh R, Datta B (2007) Artificial neural network modeling for identification of unknown pollution sources in groundwater with partially missing concentration observation data. Water Resour Manage 21(3):557–572
Singh R, Datta B, Jain A (2004) Identification of unknown groundwater pollution sources using artificial neural netwroks. J Water Resour Plan Manag 130(6):506–514
Skagg T, Kabala Z (1995) Recovering the release history of a groundwater contaminant plume: method of quasi-reversibility. Water Resour Res 31(11):2669–2673
Snodgrass M, Kitanidis P (1997) A geo-statistical approach to contaminant source identification. Water Resour Res 33(4):537–546
Srivastava D, Singh R (2015) Groundwater system modeling for simultaneous identification of pollution sources and parameters with uncertainty characterization. Water Resour Manag 29:4607–4627
Srivastava D, Singh RM (2014) Breakthrough curves characterization and identification of an unknown pollution source in Groundwater System using Artificial Neural Networks. Environ Forensic 15(2):175–189
Sun A (2007) A robust maximum likelihood approach to contaminant source identification. Water Resour Res 43(2)
Wagner B (1992) Simultaneous parameter estimation and contaminant source characterisation for coupled groundwater flow and contaminant transport modeling. J Hydrol 135:275–303
Woodbury A, Ulrych T (1996) Minimum relative entropy inversion theory and application to recovering the release history of a groundwater contaminant. Water Resour Res 32(9):2671–2681
Yeh HD, Chang TH, Lin YC (2007) Groundwater contaminant source identification by a hybrid heuristic approach. Water Resour Res 43:W09420. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005WR004731
Zhao Y, Lu W, Xiao C (2016) A Kriging surrogate model coupled in simulation-optimization approach for identifying release history of groundwater sources. J Contam Hydrol 185-186:51–60
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guneshwor, L., Eldho, T.I. & Vinod Kumar, A. Identification of Groundwater Contamination Sources Using Meshfree RPCM Simulation and Particle Swarm Optimization. Water Resour Manage 32, 1517–1538 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1885-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1885-1