Abstract
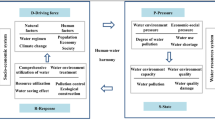
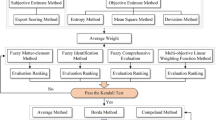
Water is not only the resource of life but also the important resource for a nation survival and development. Nowadays, the water crisis has become one of the most essential factors to restrict urban development. In this case, taking reasonable and effective method for comprehensive evaluation of urban water conservation level is helpful for promoting the construction of water-saving city. The main contribution of this paper is providing a new evaluation method for urban water saving. First, an urban water-saving evaluation index system is built. And the index system takes six water-saving standards including comprehensive water saving, domestic water saving, ecological water saving, industrial water saving, agricultural water saving and social economy as criteria. Then, the water-saving assessment model is proposed based on the Multi-grade Uncertain Comprehensive Evaluation (MUCE) Method. In this method, the important degree and the corresponding remark of each evaluation index are both considered to be uncertain variables due to the human uncertainty. The weights as well as the final evaluation result are obtained according to their uncertainty distributions and the votes of experts. At last, the comprehensive evaluation for water-saving level of Handan City located in North China is studied.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandrov V, Genev M (2003) Climate variability and change impact on water resources in Bulgaria. Eur Water 1–2:25–30
Anderson T W (1982) Introduction to multivariate statistical analysis. Wiley, New York
Anderson J (2003) The environmental benefits of water recycling and reuse. Water Supp 3(4):1–10
Angelakis A N, Gikas P (2014) Water reuse: overview of current practices and trends in the world with emphasis on EU states. Water Util. J 8:67–78
Cai Z, Li S (2006) Comprehensive assessment of urban water saving level based on AHM. Chin Water Waste Water 22(7):54–56. (in Chinese)
Chen J, Wang H, Yang W (2011) Research on water-saving society construction evaluation based on grey incidence model. Comput Sci Environ Eng Ecoinform 158:397–402
Chen J, Ma L, Wang C, Zhang H, Ha M (2014) Comprehensive evaluation model for coal mine safety based on uncertain random variables. Safe Sci 68(68):146–152
Deng J (1982) Control problems of grey systems. Syst Control Lett 1(5):288–294
Deng L, Chen S, Karney B (2012) Comprehensive evaluation method of urban water resources utilization based on dynamic reduct. Water Resour Manag 26 (10):2733–2745
Fraser G, Hill M P, Martin J A (2016) Economic evaluation of water loss saving due to the biological control of water hyacinth at New Years Dam, Eastern Cape province, South Africa. Afr J Aqua Sci 41(2):1–8
Gois E H B D, Rios C A S, Costanzi R N (2015) Evaluation of water conservation and reuse: a case study of a shopping mall in southern Brazil. J Clean Prod 96:263–271
Huang S, Shan L (2009) Water-saving social construction analysis of Yangtze River Basin. Express Water Resour Hydropower 2:12–15. (in Chinese)
Li S, Su Y (2007) Comprehensive assessment of city water-saving level based on the unascertained measure model. J Water-Saving Irrig 6:7–9. (in Chinese)
Liu B (2007) Uncertain theory, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Liu B (2010) Uncertain theory: a branch of mathematics for modeling human uncertainty. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Liu J (2011) Uncertain comprehensive evaluation method. J Inf Comput Sci 8 (2):336–344
Liu A, Giurco D, Mukheibir P (2016) Urban water conservation through customised water and end-use information. J Clean Prod 112:3164–3175
Maimone M, Labiak M (2014) Assessing Nassau Countys water conservation program. J Water Resour Plan Manag 120:90–100
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11(5):341–356
Prinz D, Malik A H (2004) More yield with less water. How efficient can be water conservation in agriculture Eur Water 5–6:47–58
Saaty T L (1980) The analytic hierarchy process. McGraw-Hill, New York
Sušnik J, Vamvakeridou-Lyroudia L S, Savić D A, Kapelan Z (2012) Integrated system dynamics modelling for water scarcity assessment: case study of the Kairouan region. Sci Total Environ 440(3):290–306
Tarnacki K (2013) Evaluating industrial water saving and water management options in order to mitigate water stress. Thesis PhD, RWTH Aachen
Tsakiris G (2015) The status of the European waters in 2015: a review. Environ Process 2(3):543–557
Umapathi S, Chong M N, Sharma A K (2013) Evaluation of plumbed rainwater tanks in households for sustainable water resource management: a real-time monitoring study. J Clean Prod 42(3):204–214
Wang P (1980) Brief introduction of fuzzy mathematics (I), (II). Math Pract Theory 2(3):45–59
Xie Y, Liu J, Ning Y, Sha H (2012) Multi-grade uncertain comprehensive evaluation method. Adv Inf Sci Serv Sci 4(6):1–8
Xu P, Tang Y, Zhang Y, Wang R (2010) Conceptual model used to construct an indicator system for evaluating a city’s water conservation level. Int Conf Manag Serv Sci 1–4
Yang H (2013) On comonotonic functions of uncertain variables. Fuzzy Optim Dec Mak 12(1):89–98
Yang F, Fu Y (2014) Uncertain comprehensive evaluation method based on expected value. J Syst Sci Inf 2(5):461–472
Zadeh L (1965) Fuzzy Sets Inf Control 8(65):338–353
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Hebei Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. G2013402063) and the Foundation of Hebei Education Department (Grant No. ZD2017016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Li, X. & Wang, J. Urban Water Conservation Evaluation Based on Multi-grade Uncertain Comprehensive Evaluation Method. Water Resour Manage 32, 417–431 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1817-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1817-0