Abstract
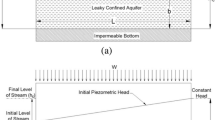
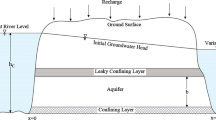
This research presents new analytical expressions to analyze interactions between streams of varying water level and a confined aquifer. The stream water level is assumed to vary exponentially with time. The expressions are obtained by means of Laplace and Fourier transform methods and the results are verified with those obtained from MODFLOW. In fact, we derive a new analytical expression for predicting of the groundwater level and flow rate in a confined aquifer between two streams of varying water level at the north and the right boundaries and two constant head boundaries at the left and the south ends. Also, a numerical example is used to investigate about the aquifer response to stream water level changes. Therefore the effects of variation water level of each stream on the flow rate at the left and the south boundaries and also at four points of the aquifer are discussed. Finally, some other new analytical expressions are also deduced for other types of boundary conditions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bansal RK (2012) Groundwater fluctuations in sloping aquifers induced by time-varying replenishment and seepage from a uniformly rising stream. Transp Porous Media 94:817–836. doi:10.1007/s11242-012-0026-9
Bansal R, Das S (2009a) Analytical solution for transient hydraulic head, flow rate and volumetric exchange in an aquifer under recharge condition. J Hydrol Hydromech 57:113–120. doi:10.2478/v10098-009-0010-4
Bansal RK, Das SK (2009b) Effects of bed slope on water head and flow rate at the interfaces between the stream and groundwater: analytical study. J Hydrol Eng 14:832–838. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000048
Bansal RK, Das SK (2010a) Analytical study of water table fluctuation in unconfined aquifers due to varying bed slopes and spatial location of the recharge basin. J Hydrol Eng 15:909–917. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000267
Bansal RK, Das SK (2010b) Water table fluctuations in a sloping aquifer: analytical expressions for water exchange between stream and groundwater. J Porous Media 13:365–374
Bansal RK, Das SK (2011) Response of an unconfined sloping aquifer to constant recharge and seepage from the stream of varying water level. Water Resour Manag 25:893–911. doi:10.1007/s11269-010-9732-7
Bansal RK, Lande CK, Warke A (2016) Unsteady groundwater flow over sloping beds: analytical quantification of stream–aquifer interaction in presence of thin vertical clogging layer. J Hydrol Eng 04016017:1–15. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001362
Barthel R, Banzhaf S (2016) Groundwater and surface water interaction at the regional-scale–A review with focus on regional integrated models. Water Resour Manag 30:1–32. doi:10.1007/s11269-015-1163-z
Benedini M, Tsakiris G (2013) Progress in numerical modelling: the finite difference method. In: Water Quality Modelling for Rivers and Streams. Springer, pp 125–148
Bobba AG (2012) Ground Water-Surface Water Interface (GWSWI) modeling: recent advances and future challenges. Water Resour Manag 26:4105–4131. doi:10.1007/s11269-012-0134-x
Boufadel MC, Peridier V (2002) Exact analytical expressions for the piezometric profile and water exchange between stream and groundwater during and after a uniform rise of the stream level. Water Resour Res 38:27.1–27.6. doi:10.1029/2001WR000780
Brown JW, Churchill RV, Lapidus M (1996) Complex variables and applications, vol 7. McGraw-Hill New York
Chen X, Chen X (2003) Stream water infiltration, bank storage, and storage zone changes due to stream-stage fluctuations. J Hydrol 280:246–264. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(03)00232-4
Cooper HH, Rorabaugh MI (1963) Ground-water movements and bank storage due to flood stages in surface streams. US Government Printing Office
Dever RJ, Cleary RW (1979) Unsteady-state, two-dimensional response of leaky aquifers to stream stage fluctuations. Adv Water Resour 2:13–18. doi:10.1016/0309-1708(79)90002-2
Fen C-S, Yeh H-D (2012) Effect of well radius on drawdown solutions obtained with Laplace transform and Green’s function. Water Resour Manag 26:377–390. doi:10.1007/s11269-011-9922-y
Ferris JG (1952) Cyclic fluctuations of water level as a basis for determining aquifer transmissibility. US Geol Surv. doi:10.3133/70133368
Ghosh NC et al (2015) Semi-analytical model for estimation of unsteady seepage from a large water body influenced by variable flows. Water Resour Manag 29:3111–3129. doi:10.1007/s11269-015-0985-z
Gill MA (1985) Bank storage characteristics of a finite aquifer due to sudden rise and fall of river level. J Hydrol 76:133–142. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(85)90094-0
Hall FR, Moench AF (1972) Application of the convolution equation to stream‐aquifer relationships. Water Resour Res 8:487–493. doi:10.1029/WR008i002p00487
Hantush MS (1967) Flow of groundwater in relatively thick leaky aquifers. Water Resour Res 3:583–590. doi:10.1029/WR003i002p00583
Intaraprasong T (2007) Stream aquifer interactions: analytical solution to estimate stream depletions caused by stream stage fluctuations and pumping wells near streams. Dissertation, Texas A&M University
Kalin L, Govindaraju R, Parlange J-Y (2000) Steady-state analysis of water movement in a semi-infinite unconfined aquifer under constant accretion. Transp Porous Media 40:165–169. doi:10.1023/A:1006652007287
Katsifarakis K (2008) Groundwater pumping cost minimization–an analytical approach. Water Resour Manag 22:1089–1099. doi:10.1007/s11269-007-9212-x
Kim KY, Kim T, Kim Y, Woo NC (2007) A semi‐analytical solution for groundwater responses to stream‐stage variations and tidal fluctuations in a coastal aquifer. Hydrol Process 21:665–674. doi:10.1002/hyp.6255
Lal AW (2001) Modification of canal flow due to stream-aquifer interaction. J Hydraul Eng 127:567–576. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2001)127:7(567)
Liang X, Zhang Y-K (2012) A new analytical method for groundwater recharge and discharge estimation. J Hydrol 450:17–24. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.05.036
Mahdavi A (2015) Transient-state analytical solution for groundwater recharge in anisotropic sloping aquifer. Water Resour Manag 29:3735–3748. doi:10.1007/s11269-015-1026-7
Mahdavi A, Seyyedian H (2013) Transient-state analytical solution for groundwater recharge in triangular-shaped aquifers using the concept of expanded domain. Water Resour Manag 27:2785–2806. doi:10.1007/s11269-013-0315-2
Manglik A, Rai S (2015) Modeling water table fluctuations in anisotropic unconfined aquifer due to time varying recharge from multiple heterogeneous basins and pumping from multiple wells. Water Resour Manag 29:1019–1030. doi:10.1007/s11269-014-0857-y
Manglik A, Rai S, Singh V (2013) A generalized predictive model of water table fluctuations in anisotropic aquifer due to intermittently applied time-varying recharge from multiple basins. Water Resour Manag 27:25–36. doi:10.1007/s11269-012-0136-8
Mas-Pla J, Menció A, Marsiñach A (2013) Basement groundwater as a complementary resource for overexploited stream-connected alluvial aquifers. Water Resour Manag 27:293–308. doi:10.1007/s11269-012-0186-y
Moench A, Barlow P (2000) Aquifer response to stream-stage and recharge variations. I. Analytical step-response functions. J Hydrol 230:192–210. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(00)00175-X
Moutsopoulos KN (2013) Solutions of the Boussinesq equation subject to a nonlinear Robin boundary condition. Water Resour Res 49:7–18. doi:10.1029/2012WR012221
Mylopoulos N, Mylopoulos Y, Tolikas D, Veranis N (2007) Groundwater modeling and management in a complex lake-aquifer system. Water Resour Manag 21:469–494. doi:10.1007/s11269-006-9025-3
Pérez-Martín MA, Estrela T, Andreu J, Ferrer J (2014) Modeling water resources and river-aquifer interaction in the Júcar River Basin, Spain. Water Resour Manag 28:4337–4358. doi:10.1007/s11269-014-0755-3
Pistiner A (2008) Similarity solution to unconfined flow in an aquifer. Transp Porous Media 71:265–272. doi:10.1007/s11242-007-9124-5
Pistiner A (2011) An analytical solution for unsteady flow in a phreatic aquifer in the case of continuous rise. Transp Porous Media 86:815–825. doi:10.1007/s11242-010-9655-z
Pulido‐Velazquez D, Sahuquillo A, Andreu J, Pulido‐Velazquez M (2007) An efficient conceptual model to simulate surface water body‐aquifer interaction in conjunctive use management models. Water Resour Res 43, W07407. doi:10.1029/2006WR005064
Pulido‐Velazquez D, Sahuquillo A, Andreu J (2012) A conceptual–numerical model to simulate hydraulic head in aquifers that are hydraulically connected to surface water bodies. Hydrol Process 26:1435–1448. doi:10.1002/hyp.8214
Rai S, Manglik A (2012) An analytical solution of Boussinesq equation to predict water table fluctuations due to time varying recharge and withdrawal from multiple basins, wells and leakage sites. Water Resour Manag 26:243–252. doi:10.1007/s11269-011-9915-x
Saeedpanah I, Jabbari E, Shayanfar M (2011) Numerical simulation of ground water flow via a new approach to the local radial point interpolation meshless method. Int J Comput Fluid D 25:17–30. doi:10.1080/10618562.2010.545772
Safavi HR, Esmikhani M (2013) Conjunctive use of surface water and groundwater: application of support vector machines (SVMs) and genetic algorithms. Water Resour Manag 27:2623–2644. doi:10.1007/s11269-013-0307-2
Sophocleous M (2002) Interactions between groundwater and surface water: the state of the science. Hydrogeol J 10:52–67. doi:10.1007/s10040-001-0170-8
Sparks TD, Bockelmann-Evans BN, Falconer RA (2013) Development and analytical verification of an integrated 2-D surface water—Groundwater model. Water Resour Manag 27:2989–3004. doi:10.1007/s11269-013-0327-y
Teloglou IS, Bansal RK (2012) Transient solution for stream–unconfined aquifer interaction due to time varying stream head and in the presence of leakage. J Hydrol 428:68–79. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.01.024
Tsakiris G, Alexakis D (2014) Karstic spring water quality: the effect of groundwater abstraction from the recharge area. Desalin Water Treat 52:2494–2501. doi:10.1080/19443994.2013.800253
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saeedpanah, I., Golmohamadi Azar, R. New Analytical Expressions for Two-Dimensional Aquifer Adjoining with Streams of Varying Water Level. Water Resour Manage 31, 403–424 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1533-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1533-1