Abstract
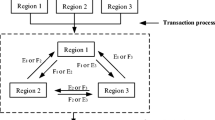
In this study, an improved single-step method (SSM) is developed based on two-step method (TSM) to solve the interval-parameter linear programming (ILP) model of which the right-hand sides are highly uncertain. Two numerical examples are presented to ascertain appropriate value of λ in SSM. The risk preference degree of λ could be 0.8 for maximum objective function type. To demonstrate the applicability of the developed method, an agricultural water management problem has been provided in the case study section. The results show that SSM is more effective than TSM for complete solutions. There is only partial solution obtained from the first submodel of TSM, because the right-hand side of the wheat output constraint is highly uncertain. Finally, local farmers’ net benefit reaches to [8.949, 12.442] × 108 RMB (the unit of Chinese currency). The priority order of crops that are needed to be irrigated by surface water is maize > wheat > cotton.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allahdadi M, Nehi HM (2013) The optimal solution set of the interval linear programming problems. Optim Lett 7(8):1893–1911
Cai YP, Huang GH, Li CH, Tan Q (2011) Identifying optimal strategies for environmental management in the mixed fuzzy stochastic environment. International Conference on Environmental Pollution and Public Health 2011. Engineering Information Institute, China
Chinneck JW, Ramadan K (2000) Linear programming with interval coefficients. J Oper Res Soc 51(2):209–220
Dantzig G (1998) Linear programming and extensions. Princeton University Press, New Jersey
Dorfman R, Samuelson PA, Solow RM (1987) Linear programming and economic analysis. Dover Publications, New York
Fan YR, Huang GH (2012) A robust Two-Step method for solving interval linear programming problems within an environmental management context. J Environ Inform 19(1):1–9
Fan YR, Huang GH, Li YP, Cao MF, Cheng GH (2009) A fuzzy linear programming approach for municipal solid-waste management under uncertainty. Eng Optim 41(12):1081–1101
Fan YR, Huang GH, Guo P, Yang AL (2012a) Inexact two-stage stochastic partial programming: application to water resources management under uncertainty. Stoch Env Res Risk A 26(2):281–293
Fan YR, Huang GH, Li YP (2012b) Robust interval linear programming for environmental decision making under uncertainty. Eng Optim 44(11):1321–1336
Fu DZ, Li YP, Huang GH (2013) A factorial-based dynamic analysis method for reservoir operation under fuzzy-stochastic uncertainties. Water Resour Manag 27(13):4591–4610
Fu Y, Li M, Guo P (2014) Optimal allocation of water resources model for different growth stages of crops under uncertainty. Am Soc Civ Eng 140(6):1272–1273
Gass SI (2010) Linear programming: methods and applications. Dover Publications, New York
Guo P, Huang GH (2009a) Inexact fuzzy-stochastic mixed-integer programming approach for long-term planning of waste management - part a: methodology. J Environ Manag 91(2):461–470
Guo P, Huang GH (2009b) Two-stage fuzzy chance-constrained programming: application to water resources management under dual uncertainties. Stoch Env Res Risk A 23(3):349–359
Guo P, Huang GH (2011) Inexact fuzzy-stochastic quadratic programming approach for waste management under multiple uncertainties. Eng Optim 43(5):525–539
Guo P, Huang GH, Li YP (2008) Interval stochastic quadratic programming approach for municipal solid waste management. J Environ Eng Sci 7(6):569–579
Guo P, Huang GH, He L, Li HL (2009a) Interval-parameter fuzzy-stochastic semi-infinite mixed-integer linear programming for waste management under uncertainty. Environ Model Assess 14(4):521–537
Guo P, Huang GH, He L, Zhu H (2009b) Interval-parameter two-stage stochastic semi-infinite programming: application to water resources management under uncertainty. Water Resour Manag 23(5):1001–1023
Guo P, Huang GH, Li YP (2010) An inexact fuzzy-chance-constrained two-stage mixed-integer linear programming approach for flood diversion planning under multiple uncertainties. Adv Water Resour 33(1):81–91
Hladık M (2010) Linear programming-new frontiers in theory and applications. Nova Science, New York
Huang GH, Cao MF (2011) Analysis of solution methods for interval linear programming. J Environ Inform 17(2):54–64
Huang GH, Loucks DP (2000) An inexact two-stage stochastic programming model for water resources management under uncertainty. Civ Eng Environ Syst 17(2):95–118
Huang GH, Baetz BW, Park SW (1995a) Grey fuzzy integer programming - an application to regional waste management planning under uncertainty. Socio Econ Plan Sci 29(1):17–38
Huang GH, Baetz BW, Patry GG (1995b) Grey integer programming - an application to waste management planning under uncertainty. Eur J Oper Res 83(3):594–620
Huang GH, Sae-Lim N, Liu L, Chen Z (2001) An interval-parameter fuzzy-stochastic programming approach for municipal solid waste management and planning. Environ Model Assess 6(4):271–283
Jansson C (1988) A self-validating method for solving linear programming problems with interval input data. Springer Vienna, USA
Jin L, Huang G, Fan Y, Nie X, Cheng G (2012) A hybrid dynamic dual interval programming for irrigation water allocation under uncertainty. Water Resour Manag 26(5):1183–1200
Khare D, Jat MK, Ediwahyunan X (2006) Assessment of counjunctive use planning options: a case study of sapon irrigation command area of Indonesia. J Hydrol 328(3,4):764–777
Kim HK, Jang TI, Im SJ, Park SW (2009) Estimation of irrigation return flow from paddy fields considering the soil moisture. Agric Water Manag 96(5):875–882
Li YP, Huang GH (2006) An inexact two-stage mixed integer linear programming method for solid waste management in the City of Regina. J Environ Manag 81(3):188–209
Li YP, Huang GH (2007) Fuzzy two-stage quadratic programming for planning solid waste management under uncertainty. Int J Syst Sci 38(3):219–233
Li YP, Huang GH, Xiao HN (2008) Municipal solid waste management under uncertainty: an interval-fuzzy Two-stage stochastic programming approach. J Environ Inform 12(2):96–104
Li MW, Li YP, Huang GH (2011a) An interval-fuzzy two-stage stochastic programming model for planning carbon dioxide trading under uncertainty. Energy 36(9):5677–5689
Li YP, Huang GH, Nie SL (2011b) Optimization of regional economic and environmental systems under fuzzy and random uncertainties. J Environ Manag 92(8):2010–2020
Li M, Guo P, Yang GQ, Fang SQ (2014) IB-ICCMSP: an integrated irrigation water optimal allocation and planning model based on inventory theory under uncertainty. Water Resour Manag 28(1):241–260
Lin QG, Huang GH (2010) An inexact two-stage stochastic energy systems planning model for managing greenhouse gas emission at a municipal level. Energy 35(5):2270–2280
Lin QG, Huang GH (2011) Interval-fuzzy stochastic optimization for regional energy systems planning and greenhouse-gas emission management under uncertainty-a case study for the Province of Ontario, Canada. Clim Chang 104(2):353–378
Lin QG, Huang GH, Bass B, Qin XS (2009) IFTEM: an interval-fuzzy two-stage stochastic optimization model for regional energy systems planning under uncertainty. Energ Policy 37(3):868–878
Liu Y, Huang G, Cai Y, Dong C (2011) An inexact Mix-Integer Two-Stage linear programming model for supporting the management of a Low-Carbon energy system in china. Energies 4(10):1657–1686
Lu HW, Huang GH, He L (2009) An inexact programming method for agricultural irrigation systems under parameter uncertainty. Stoch Env Res Risk A 23(6):759–768
Luo J, Li W (2013) Strong optimal solutions of interval linear programming. Linear Algebra Appl 439(8):2479–2493
Mráz F (1998) Calculating the exact bounds of optimal values in LP with interval coefficients. Ann Oper Res 81:51–62
Nie XH, Huang GH, Wang D, Li HL (2008) Robust optimisation for inexact water quality management under uncertainty. Civ Eng Environ Syst 25(2):167–184
Reeb JE, Leavengood SA, Others (1998) Using the graphical method to solve linear programs. Oregon State University, USA
Sahinidis NV (2004) Optimization under uncertainty: state-of-the-art and opportunities. Comput Chem Eng 28(6):971–983
Sengupta A, Pal TK, Chakraborty D (2001) Interpretation of inequality constraints involving interval coefficients and a solution to interval linear programming. Fuzzy Sets Syst 119(1):129–138
Sun Y, Li Y, Huang G (2010) Development of a Fuzzy-Queue-Based interval linear programming model for municipal solid waste management. Environ Eng Sci 27(6):451–468
Tan Q, Huang GH, Cai YP (2008) Planning of municipal solid waste management systems under mixed fuzzy and stochastic environment. Annual Conference of the Canadian Society for Civil Engineering 2008 Canadian Society for Civil Engineering, Canada
Tong F, Guo P (2013) Simulation and optimization for crop water allocation based on crop water production functions and climate factor under uncertainty. Appl Math Model 37:7708–7716
Xi BD, Su J, Huang GH, Qin XS, Jiang YH, Huo SL, Ji DF, Yao B (2010) An integrated optimization approach and multi-criteria decision analysis for supporting the waste-management system of the City of Beijing, China. Eng Appl Artif Intell 23(4):620–631
Xu Y, Huang G, Qin X (2009a) Inexact Two-Stage stochastic robust optimization model for water resources management under uncertainty. Environ Eng Sci 26(12):1765–1776
Xu Y, Huang GH, Qin XS, Huang Y (2009b) SRFILP: a stochastic robust fuzzy interval linear programming model for municipal solid waste management under uncertainty. J Environ Inform 14(2):74–82
Xu Y, Huang GH, Qin XS, Cao MF, Sun Y (2010) An interval-parameter stochastic robust optimization model for supporting municipal solid waste management under uncertainty. Waste Manag 30(2):316–327
Yang G, Guo P, Huo L, Ren C (2015) Optimization of the irrigation water resources for Shijin irrigation district in north China. Agric Water Manag 158:82–98
Zhu H, Huang GH (2011) SLFP: a stochastic linear fractional programming approach for sustainable waste management. Waste Manag 31(12):2612–2619
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Government Public Research Funds for Projects of Ministry of Agriculture (No. 201203077), International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China (2013DFG70990), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51321001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, G., Guo, P., Li, M. et al. An Improved Solving Approach for Interval-Parameter Programming and Application to an Optimal Allocation of Irrigation Water Problem. Water Resour Manage 30, 701–729 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1186-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-1186-5