Abstract
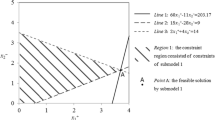
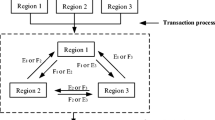
Rapid population growth and economy development have led to increasing reliance on water resources. It is even aggravated for agricultural irrigation systems where more water is necessary to support the increasing population. In this study, an inexact programming method based on two-stage stochastic programming and interval-parameter programming is developed to obtain optimal water-allocation strategies for agricultural irrigation systems. It is capable of handling such problems where two-stage decisions need to be suggested under random- and interval-parameter inputs. An interactive solving procedure derived from conventional interval-parameter programming makes it possible for the impact of lower and upper bounds of interval inputs to be well reflected in the resulting solutions. An agricultural irrigation management problem is then provided to demonstrate the applicability, and reasonable solutions are obtained. Compared to the solutions from a representative interval-parameter programming model where only one decision-stage exists, the interval of optimized objective-function value is narrow, indicating more alternatives could be provided when water-allocation targets are rather high. However, chances of obtaining more benefits exist in association with a risk of paying more penalties; such a relationship becomes apparent when the variation of water availability is much intensive.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolpour B, Javan M (2007) Optimization model for allocating water in a river basin during a drought. J Irrigation Drainage Eng 133(6):559–572
Abrishamchi A, Marino MA, Afshar A (1991) Reservoir planning for irrigation district. J Water Res Plan Manage 117:74–85
Bonaccorso B, Cancelliere A, Rossi G (2003) An analytical formulation of return period of drought severity. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 17(3):157–174
Farmani R, Abadia R, Savic D (2007) Optimum design and management of pressurized branched irrigation networks. J Irrigation Drainage Eng 133(6):528–537
Faulkner JW, Steenhuis T, van de Giesen N, Andreini M, Liebe JR (2008) Water use and productivity of two small reservoir irrigation schemes in Ghana's Upper East Region. Irrigation Drainage 57:151–163. doi:10.1002/ird.384
Georgiou PE, Papamichail DM, Vougioukas SG (2006) Optimal irrigation reservoir operation and simultaneous multi-crop cultivation area selection using simulated annealing. Irrigation Drainage 55(2):129–144
He L, Huang GH, Lu HW et al (2008a) Optimization of surfactant-enhanced aquifer remediation for a laboratory BTEX system under parameter uncertainty. Environ Sci Technol. doi: 10.1021/es071106y
He L, Huang GH, Zeng GM et al (2008b) Identifying optimal regional solid waste management strategies through a new inexact integer programming model containing infinite objectives and constraints. Waste Manage. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2008.02.003
He L, Huang GH, Zeng GM et al (2008c) Identification of the optimal urban solid waste flow schemes under impacts of energy prices. Environ Eng Sci 25(5). doi:10.1089/ees.2007.0078
Heidari A, Saghafian B, Maknoon R (2006) Assessment of flood forecasting lead time based on generalized likelihood uncertainty estimation approach. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 20(5):363–380
Huang GH, Moore RD (1993) Grey linear programming, its solving approach, and its application to water pollution control. Int J Syst Sci 24(1):159–172
Huang GH, Loucks DP (2000) An inexact two-stage stochastic programming model for water resources management under uncertainty. Civil Eng Environ Syst 17:95–118
Huang GH, Baetz BW, Patry GG (1992) A grey linear programming approach for municipal solid waste management planning under uncertainty. Civil Eng Syst 9:319–335
Huang GH, Sae-Lim N, Liu L et al (2001) An interval-parameter fuzzy-stochastic programming approach for municipal solid waste management and planning. Environ Model Assess 6(4):271–283
Kentel E, Aral MM (2004) Probabilistic-fuzzy health risk modeling. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 18(5):324–338
Kipkorir EC, Raes D, Labadie J (2001) Optimal allocation of short-term irrigation supply. Irrigation Drainage Syst 15(3):247–267
Lejano RP (2006) Optimizing the layout and design of branched pipeline water distribution systems. Irrigation Drainage Syst 20(1):125–137
Lin YP, Huang GH, Lu HW, et al (2008) Modeling of substrate degradation and oxygen consumption in waste composting processes. Waste Manage 28(8):1375–1385. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2007.09.016
Llamas MR, Custodio E (eds) (2003) Intensive use of groundwater: challenges and opportunities. Taylor & Francis Group, London
Loaiciga HA, Marino MA (1987) The inverse problem and ground water management. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 1(3):161–168
Lu HW, Huang GH, Zeng GM, et al (2007a) An inexact two-stage fuzzy-stochastic programming model for water resources management. Water Res Manage. doi:10.1007/s11269-007-9206-8
Lu HW, Huang GH, He L, et al (2007b) An inexact dynamic optimization model for municipal solid waste management in association with greenhouse gas emission control. J Environ Manage. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.10.011
Lu HW, Huang GH, Liu L, et al (2008) An interval-parameter fuzzy-stochastic programming approach for air quality management under uncertainty. Environ Eng Sci 25(6):895–910. doi:10.1089/ees.2007.0165
Maqsood I, Huang GH, Huang YF et al (2005) ITOM: an interval-parameter two-stage optimization model for stochastic planning of water resources systems. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 19:125–133
Montazar A, Rahimikob A (2008) Optimal water productivity of irrigation networks in arid and semi-arid regions. Irrigation Drainage. doi: 10.1002/ird.376
Onta PR, Loof R, Banskota M (1995) Performance based irrigation planning under water shortage. Irrigation Drainage Syst 9(2):143–162
Paudyal GN, Gupta AD (1990) Irrigation management by multilevel optimization. J Irrigation Drainage Eng 116:273–291
Sahoo B, Lohani AK, Sahu RK (2006) Fuzzy multiobjective and linear programming based management models for optimal land-water-crop system. Water Res Manage 20(6):931–948
Spiliotis M, Tsakiris G (2007) Minimum cost irrigation network design using interactive fuzzy integer programming. J Irrigation Drainage Eng 133(3):242–248
Tsakiris G, Spiliotis M (2006) Cropping pattern planning under water supply from multiple sources. Irrigation Drainage Systems 20:57–68
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of MOST (2005CB724200 and 2006CB403307) and the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada. The authors are grateful to the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H.W., Huang, G.H. & He, L. An inexact programming method for agricultural irrigation systems under parameter uncertainty. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 23, 759–768 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-008-0256-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-008-0256-0