Abstract
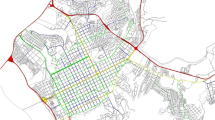
Urban regeneration is an important strategy for land redevelopment, to address the urban decay in cities. Among many tasks, urban layout is the foundation for urban regeneration. In this paper, we target a new task called function-aware urban layout regeneration, and propose UrbanEvolver, a function-aware deep generative model for the task. Given a target region to be regenerated, our model outputs a regenerated urban layout (i.e., roads and buildings) for the target region by considering the function (i.e., land use type) of the target region and its surrounding context (i.e., the functions and urban layouts of the surrounding regions). UrbanEvolver first extracts implicit regeneration rules from the target function and the surrounding context by encoding them separately in different scales through the function-layout adaptive (FA) blocks, and then constrains the regenerated urban layout based on the learned regeneration rules. To enforce the regenerated layout to be valid and to follow the road structure, we design a set of losses covering both pixel-level and geometry-level constraints. To train our model, we collect a large-scale urban layout dataset covering more than 147 K regions under 1300 km\(^2\) with rich annotations, including functions, region shapes, urban road layouts, and urban building layouts. We conduct extensive experiments to show that our model outperforms the baseline methods in generating practical and function-aware urban layouts based on the given target function and surrounding context.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets that support the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. We will release the dataset and code in the following link, https://github.com/LittleQBerry/UrbanEvolver.
Notes
www.sketchup.com.
References
Aliaga, D. G., Vanegas, C. A., & Benes, B. (2008). Interactive example-based urban layout synthesis. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 27(5), 1–10.
Amazon Web Services. (2016). SpaceNet dump retrieved from https://registry.opendata.aws/spacenet
Amirtahmasebi, R., Orloff, M., Wahba, S., et al. (2016). Regenerating urban land: A practitioner’s guide to leveraging private investment. Washington, D.C: Urban Development, World Bank Publications.
Atkins, C. B. (2008). Blocked recursive image composition. In ACM multimedia (pp. 821–824).
Belli, D., Kipf, T. (2019). Image-conditioned graph generation for road network extraction. In NeurIPS Workshops.
Benny, Y., Galanti, T., Benaim, S., et al. (2021). Evaluation metrics for conditional image generation. International Journal of Computer Vision, 129(5), 1712–1731.
Brock, A., Donahue, J., Simonyan, K. (2019). Large scale GAN training for high fidelity natural image synthesis. In ICLR.
Campen, M., Bommes, D., & Kobbelt, L. (2012). Dual loops meshing: Quality quad layouts on manifolds. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 31(4), 1–11.
Chang, K. H., Cheng, C. Y., Luo, J., et al. (2021). Building-GAN: Graph-conditioned architectural volumetric design generation. In ICCV (pp. 11,956–11,965).
Chen, G., Esch, G., Wonka, P., et al. (2008). Interactive procedural street modeling. ACM Transactions on Graphics. https://doi.org/10.1145/1399504.1360702
Chen, R. (2011). The development of 3d city model and its applications in urban planning. In ICG (pp. 1–5).
Chen, Y., Li, H., He, B., et al. (2015). Multi-objective genetic algorithm based innovative wind farm layout optimization method. Energy Conversion and Management, 105, 1318–1327.
Chen, Z., Ma, X., Yu, W., et al. (2021). Measuring the similarity of building patterns using graph Fourier transform. Earth Science Informatics, 14, 1953–1971.
Choi, Y., Uh, Y., Yoo, J., et al. (2020). Stargan v2: Diverse image synthesis for multiple domains. In CVPR (pp. 8185–8194).
Chu, H., Li, D., Acuna, D., et al. (2019). Neural turtle graphics for modeling city road layouts. In ICCV (pp. 4522–4530).
Eitz, M., Hays, J., & Alexa, M. (2012). How do humans sketch objects? ACM Transactions on Graphics, 31(4), 1–10.
Fisher, M., Savva, M., & Hanrahan, P. (2011). Characterizing structural relationships in scenes using graph kernels. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 30(4), 34. https://doi.org/10.1145/2010324.1964929
Fisher, M., Ritchie, D., Savva, M., et al. (2012). Example-based synthesis of 3D object arrangements. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 31(6), 1–11.
Fisher, M., Savva, M., Li, Y., et al. (2015). Activity-centric scene synthesis for functional 3D scene modeling. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 34(6), 1–13.
Fu, J., Liu, J., Tian, H., et al. (2019). Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In CVPR (pp. 3146–3154).
González-Morcillo, C., Martin, V., Fernandez, D. V., et al. (2010). Gaudii: An automated graphic design expert system. In IAAI (pp. 1775–1780).
Groenewegen, S. A., Smelik, R. M., de Kraker, K. J., et al. (2009). Procedural city layout generation based on urban land use models. In Eurographics (Short Paper) (pp. 45–48).
Guo, S., Jin, Z., Sun, F., et al. (2021a). Vinci: An intelligent graphic design system for generating advertising posters. In ACM CHI (pp 1–17).
Guo, X., Yang, H., & Huang, D. (2021b). Image inpainting via conditional texture and structure dual generation. In ICCV (pp. 14,134–14,143).
Gupta, K., Lazarow, J., Achille, A., et al. (2021). Layouttransformer: Layout generation and completion with self-attention. In ICCV (pp. 984–994).
Hartmann, S., Weinmann, M., Wessel, R., et al. (2017). Streetgan: Towards road network synthesis with generative adversarial networks. In ICCECGVCV.
Henderson, P., Subr, K., & Ferrari, V. (2017). Automatic generation of constrained furniture layouts. arXiv:1711.10939
Heusel, M., Ramsauer, H., Unterthiner, T., et al. (2017). Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. In NeurIPS (pp. 6626–6637).
Hu, R., Huang, Z., Tang, Y., et al. (2020). Graph2plan: Learning floorplan generation from layout graphs. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 39(4), 118.
Hudson, D., & Zitnick, L. (2021). Compositional transformers for scene generation. In NeurIPS (pp. 9506–9520).
Johnson, J., Alahi, A., & Fei-Fei, L. (2016). Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In ECCV (pp. 694–711).
Jyothi, A. A., Durand, T., He, J., et al. (2019). Layoutvae: Stochastic scene layout generation from a label set. In ICCV (pp. 9894–9903).
Kargly. (2017). Qd-imd: Quick draw irregular mask dataset. https://github.com/karfly/qd-imd/
Kelly, T. (2021). Cityengine: An introduction to rule-based modeling. Urban Informatics. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-8983-6_35
Khrulkov, V., & Oseledets, I. (2018). Geometry score: A method for comparing generative adversarial networks. In ICML (pp. 2626–2634).
Lechner, T., Ren, P., Watson, B., et al. (2006). Procedural modeling of urban land use. In ACM SIGGRAPH (Poster).
Lee, D., Liu, S., Gu, J., et al. (2018). Context-aware synthesis and placement of object instances. In NeurIPS (pp. 10,414–10,424).
Lee, D. T., & Lin, A. K. (1986). Generalized Delaunay triangulation for planar graphs. Discrete Computational Geometry, 1(3), 201–217.
Lenormand, M., Picornell, M., Cantú-Ros, O. G., et al. (2015). Comparing and modelling land use organization in cities. Royal Society Open Science, 2(12), 150,449.
Li, J., Yang, J., Hertzmann, A., et al. (2019). Layoutgan: Generating graphic layouts with wireframe discriminators. In ICLR (Poster).
Lipp, M., Scherzer, D., Wonka, P., et al. (2011). Interactive modeling of city layouts using layers of procedural content. Computer Graphics Forum, 30(2), 345–354.
Liu, G., Reda, F., Shih, K., et al. (2018). Image inpainting for irregular holes using partial convolutions. In ECCV (pp. 89–105).
Liu, H., Jiang, B., Song, Y., et al. (2020). Rethinking image inpainting via a mutual encoder-decoder with feature equalizations. In ECCV (pp. 725–741).
Merrell, P., Schkufza, E., & Koltun, V. (2010). Computer-generated residential building layouts. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 29(6), 181. https://doi.org/10.1145/1882261.1866203
Merrell, P., Schkufza, E., Li, Z., et al. (2011). Interactive furniture layout using interior design guidelines. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 30(4), 1–10.
Mi, L., Zhao, H., Nash, C., et al. (2021). Hdmapgen: A hierarchical graph generative model of high definition maps. In CVPR (pp. 4227–4236).
Nauata, N., Chang, K. H., Cheng, C. Y., et al. (2020). House-GAN: Relational generative adversarial networks for graph-constrained house layout generation. In ECCV (pp. 162–177).
Nauata, N., Hosseini, S., Chang, K. H., et al. (2021). House-GAN++: Generative adversarial layout refinement network towards intelligent computational agent for professional architects. In CVPR (pp. 13,632–13,641).
Nazeri, K., Ng, E., Joseph, T., et al. (2019). Edgeconnect: Generative image inpainting with adversarial edge learning. In ICCV Workshops.
Nishida, G., Garcia-Dorado, I., & Aliaga, D. G. (2016). Example-driven procedural urban roads. Computer Graphics Forum, 35(6), 5–17.
OpenStreetMap Contributors. (2017). Map features. https://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Map_features
OpenStreetMap Contributors. (2017). Planet dump. Retrieved from https://planet.osm.org
Ovsjanikov, M., Ben-Chen, M., Solomon, J., et al. (2012). Functional maps: A flexible representation of maps between shapes. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 31(4), 1–11.
Owaki, T., & Machida, T. (2020). Roadnetgan: Generating road networks in planar graph representation. In ICONIP (pp. 535–543).
O’Donovan, P., Agarwala, A., & Hertzmann, A. (2014). Learning layouts for single-pagegraphic designs. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 20(8), 1200–1213.
Pang, X., Cao, Y., Lau, R. W., et al. (2016). Directing user attention via visual flow on web designs. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 35(6), 1–11.
Panozzo, D., Block, P., & Sorkine-Hornung, O. (2013). Designing unreinforced masonry models. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 32(4), 1–12.
Parish, Y., & Müller, P. (2001). Procedural modeling of cities. In ACM SIGGRAPH (pp. 301–308).
Park, T., Liu, M. Y., Wang, T. C., et al. (2019). Semantic image synthesis with spatially-adaptive normalization. In CVPR (pp. 2337–2346).
Pautrat, R., Lin, J. T., Larsson, V., et al. (2021). \(\text{Sold}^2\): Self-supervised occlusion-aware line description and detection. In CVPR (pp. 11,368–11,378).
Peng, C. H., Yang, Y. L., & Wonka, P. (2014). Computing layouts with deformable templates. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 33(4), 1–11.
Qiao, X., Zheng, Q., Cao, Y., et al. (2019). Tell me where i am: Object-level scene context prediction. In CVPR (pp. 2633–2641).
Ripon, K. S. N., Glette, K., Khan, K. N., et al. (2013). Adaptive variable neighborhood search for solving multi-objective facility layout problems with unequal area facilities. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 8, 1–12.
Ryu, D. S., Chung, W. K., & Cho, H. G. (2010). Photoland: A new image layout system using Spatio-temporal information in digital photos. In ACM SAC (pp. 1884–1891).
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2015). Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In ICLR.
(2009). Street generator. https://sketchucation.com/forums/viewtopic.php?f=180 &t=19410
Sushko, V., Gall, J., & Khoreva, A. (2021). One-shot GAN: Learning to generate samples from single images and videos. In CVPR Workshops (pp. 2596–2600).
Suvorov, R., Logacheva, E., Mashikhin, A., et al. (2022). Resolution-robust large mask inpainting with Fourier convolutions. In WACV (pp. 3172–3182).
Suzuki, S., et al. (1985). Topological structural analysis of digitized binary images by border following. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, 30(1), 32–46.
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., et al. (2016). Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In CVPR (pp. 2818–2826).
Ueno, M., & Satoh, S. (2021). Continuous and gradual style changes of graphic designs with generative model. In IUI (pp. 280–289).
Umetani, N., Igarashi, T., & Mitra, N. J. (2012). Guided exploration of physically valid shapes for furniture design. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 31(4), 86.
Wang, Z., Simoncelli, E., & Bovik, A. (2003). Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In ACSSC (pp. 1398–1402).
Weber, B., Müller, P., Wonka, P., et al. (2009). Interactive geometric simulation of 4d cities. Computer Graphics Forum, 28(2), 481–492.
Yang, X., Mei, T., Xu, Y. Q., et al. (2016). Automatic generation of visual-textual presentation layout. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 12(2), 1–22.
Yang, Alhalawani S., Yl Wonka, P., et al. (2014). What makes London work like London? Computer Graphics Forum, 33(5), 157–165.
Yang, Y. L., Wang, J., Vouga, E., et al. (2013). Urban pattern: Layout design by hierarchical domain splitting. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 32(6), 1–12.
Yu, L. F., Yeung, S. K., Tang, C. K., et al. (2011). Make it home: Automatic optimization of furniture arrangement. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 30(4), 86.
Žalik, B. (2001). Merging a set of polygons. Computers and Graphics, 25(1), 77–88.
Zhang, H., Goodfellow, I., Metaxas, D., et al. (2019). Self-attention generative adversarial networks. In ICML (pp. 7354–7363).
Zhang, P., Li, C., & Wang, C. (2020). Smarttext: Learning to generate harmonious textual layout over natural image. In ICME (pp. 1–6).
Zhang, W., Zhu, J., Tai, Y., et al. (2021). Context-aware image inpainting with learned semantic priors. In IJCAI (pp. 1323–1329).
Zhang, Y., Li, X., Wang, A., et al. (2015). Density and diversity of OpenStreetMap road networks in China. Journal of Urban Management, 4(2), 135–146.
Zhao, K., Han, Q., Zhang, C. B., et al. (2021). Deep hough transform for semantic line detection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 44, 4793–4806.
Zheng, X., Qiao, X., Cao, Y., et al. (2019). Content-aware generative modeling of graphic design layouts. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 38(4), 1–15.
Zheng, Y. (2015). Methodologies for cross-domain data fusion: An overview. IEEE Transactions on Big Data, 1(1), 16–34.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under grant number 2022YFC2407000, the Interdisciplinary Program of Shanghai Jiao Tong University under grant number YG2023LC11 and YG2022ZD007, National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant number 62272298 and 62077037.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Arun Mallya.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Corresponding author: Bin Sheng. Rynson Lau and Bin Sheng lead this project.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Y., Zhao, N., Yang, J. et al. UrbanEvolver: Function-Aware Urban Layout Regeneration. Int J Comput Vis (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-024-02030-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-024-02030-w