Abstract
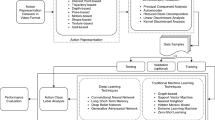
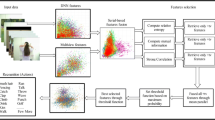
The performance of action recognition in video sequences depends significantly on the representation of actions and the similarity measurement between the representations. In this paper, we combine two kinds of features extracted from the spatio-temporal interest points with context-aware kernels for action recognition. For the action representation, local cuboid features extracted around interest points are very popular using a Bag of Visual Words (BOVW) model. Such representations, however, ignore potentially valuable information about the global spatio-temporal distribution of interest points. We propose a new global feature to capture the detailed geometrical distribution of interest points. It is calculated by using the 3D \({\mathcal {R}}\) transform which is defined as an extended 3D discrete Radon transform, followed by the application of a two-directional two-dimensional principal component analysis. For the similarity measurement, we model a video set as an optimized probabilistic hypergraph and propose a context-aware kernel to measure high order relationships among videos. The context-aware kernel is more robust to the noise and outliers in the data than the traditional context-free kernel which just considers the pairwise relationships between videos. The hyperedges of the hypergraph are constructed based on a learnt Mahalanobis distance metric. Any disturbing information from other classes is excluded from each hyperedge. Finally, a multiple kernel learning algorithm is designed by integrating the \(l_{2}\) norm regularization into a linear SVM classifier to fuse the \({\mathcal {R}}\) feature and the BOVW representation for action recognition. Experimental results on several datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach for action recognition.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armijo, L. (1966). Minimization of functions having Lipschitz continuous first partial derivatives. Pacific Journal of Mathematics, 16(1), 1–3.
Blank, M., Gorelick, L., Shechtman, E., Irani, M., & Basri, R. (2007). Actions as space-time shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 29(12), 2247–2253.
Bregonzio, M., Gong, S., & Xiang, T. (2009). Recognising action as clouds of space-time interest points. In CVPR (pp. 1948–1955).
Bregonzio, M., Li, J., Gong, S., & Xiang, T. (2011). Discriminative topics modelling for action feature selection and recognition. In BMVC (pp. 1–11).
Chapelle, O., Vapnik, V., Bousquet, O., & Mukherjee, S. (2002). Choosing multiple parameters for support vector machines. Machine Learning, 46(1–3), 131–159.
Choi, J., Jeon, W. J., & Lee, S. C. (2008). Spatio-temporal pyramid matching for sports videos. In ACM MIR (pp. 291–297).
Daras, P., Zarpalas, D., Tzovaras, D., & Strintzis, M. G. (2004). Shape matching using the 3D radon tranform. In 3DPVT (pp. 953–960).
Ellis, C., Masood, S., Tappen, M., LaViola, J., & Sukthankar, R. (2013). Exploring the trade-off between accuracy and observational latency in action recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 101(3), 420–436.
Gaidon, A., Harchaoui, Z., & Schmid, C. (2014). Activity representation with motion hierarchies. International Journal of Computer Vision, 107(3), 219–238.
Huang, Y., Liu, Q., Zhang, S., & Metaxas, D. (2010). Image retrieval via probabilistic hypergraph ranking. In CVPR (pp. 3376–3383).
Hong, C., Yu, J., & Chen, X. (2014). Structured action classification with hypergraph regularization. In IEEE international conference on systems, man and cybernetics (SMC) (pp. 2853–2858).
Ikizler-Cinbis, N. & Sclaroff, S. (2010). Object, scene and actions: Combining multiple features for human action recognition. In ECCV (pp. 494–507).
Kloft, M., Brefeld, U., Sonnenburg, S., & Zien, A. (2011). Lp-norm multiple kernel learning. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12, 953–997.
Kovashka, A. & Grauman, K. (2010). Learning a hierarchy of discriminative space-time neighborhood features for human action recognition. In CVPR (pp. 2046–2053).
Kulkarni, K., Evangelidis, G., Cech, J., & Horaud, R. (2014). Continuous action recognition based on sequence alignment. International Journal of Computer Vision, 112, 90–114.
Laptev, I., Marszalek, M., Schmid, C., & Rozenfeld, B. (2008). Learning realistic human actions from movies. In CVPR (pp. 1–8).
Laptev, I. (2005). On space-time interest points. International Journal of Computer Vision, 64(2), 107–123.
Lazebnik, S., Schmid, C., & Ponce, J. (2006). Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. In CVPR (pp. 2169–2178).
Le, Q., Zou, W., Yeung, S., & Ng, A. (2011). Learning hierarchical invariant spatio-temporal features for action recognition with independent subspace analysis. In CVPR (pp. 3361–3368).
Li, X., Hu, W., Shen, C., Dick, A., & Zhang, Z. (2014). Context-aware hypergraph construction for robust spectral clustering. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 26(10), 2588–2597.
Lianga, Z., Chi, Z., Fu, H., & Fenga, D. (2012). Salient object detection using content-sensitive hypergraph representation and partitioning. Pattern Recognition, 45, 3886–3901.
Liu, J., Ali, S., & Shah, M. (2008). Recognizing human actions using multiple features. In CVPR (pp. 1–8).
Marzalek, M., Laptev, I., & Schmid, C. (2009). Actions in context. In CVPR (pp. 2929–2936).
Mikolajczyk, K. & Uemura, H. (2008). Action recognition with motion-appearance vocabulary forest. In CVPR (pp. 1–8).
Ni, B., Moulin, P., & Yan, S. (2015). Pose adaptive motion feature pooling for human action analysis. International Journal of Computer Vision, 111(2), 229–248.
Niebles, J., Wang, H., & Fei-Fei, L. (2008). Unsupervised learning of human action categories using spatial–temporal words. International Journal of Computer Vision, 793, 299–318.
Oikonomopoulos, A., Patras, I., & Pantic, M. (2011). Spatiotemporal localization and categorization of human actions in unsegmented image sequences. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 20(4), 1126–1140.
Oshin, O., Gilbert, A., & Bowden, R. (2011). Capturing the relative distribution of features for action recognition. In IEEE international conference on automatic face and gesture recognition and workshops (FG 2011) (pp. 111–116).
Poppe, R. (2010). A survey on vision-based human action recognition. Image and Vision Computing, 28(6), 976–990.
Rodriguez, M. D., Ahmed, J., & Shah, M. (2008). Action MACH: A spatiotemporal maximum average correlation height filter for action recognition. In CVPR (pp. 1–8).
Savarese, S., Pozo, A., Niebles, J., & Fei-Fei, L. (2008). Spatial-temporal correlatons for unsupervised action classification. In IEEE workshop on motion and video computing (pp. 1–8).
Schuldt, C., Laptev, I., & Caputo, B. (2004). Recognizing human actions: A local SVM approach. In ICPR (pp. 32–36).
Shalev-Shwartz, S., Singer, Y., Srebro, N., & Cotter, A. (2011). Pegasos: Primal estimated sub-gradient solver for svm. Mathematical Programming, 127(1), 3–30.
Shi, Q., Cheng, L., Wang, L., & Smola, A. (2011). Human action segmentation and recognition using discriminative semi-Markov models. International Journal of Computer Vision, 93(1), 22–32.
Shkolnisky, Y., & Averbuch, A. (2003). 3D Fourier based discrete Radon transform. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 15(1), 33–69.
Sun, J., Wu, X., Yan, S., Cheong, L., Chua, T., & Li, J. (2009). Hierarchical spatio-temporal context modeling for action recognition. In CVPR (pp. 2004–2011).
Sun, X., Chen, M., & Hauptmann, A. (2009). Action recognition via local descriptors and holistic features. In CVPR (pp. 58–65).
Tabbone, S., Wendling, L., & Salmon, J. (2006). A new shape descriptor defined on the radon transform. In CVIU (pp. 42–51).
Varma, M. & Bodla, R. (2009). More generality in efficient multiple kernal learning. In ICML (pp. 1065–1072).
Wang, H., Kläser, A., Laptev, I., Schmid, C., & Liu, C. (2011). Action recognition by dense trajectories. In CVPR (pp. 3169–3176).
Wang, H., Kläser, A., Schmid, C., & Liu, C. (2013). Dense trajectories and motion boundary descriptors for action recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1031, 60–79.
Wang, H., Ullah, M. M., Kläser, A., Laptev, I., & Schmid, C. (2009). Evaluation of local spatio-temporal features for action recognition. In BMVC.
Wang, L., Zhou, H., Low, S. C., & Leckie, C. (2009). Action recognition via multi-feature fusion and gaussian process classification. In WACV (pp. 1–6).
Wang, H., & Yuan, J. (2015). Collaborative multi-feature fusion for transductive spectral learning. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 45(3), 465–475.
Wang, L., & Suter, D. (2007). Learning and matching of dynamic shape manifolds for human action recognition. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 16(6), 1646–1661.
Wang, Y., Huang, K., & Tan, T. (2007). Human activity recognition based on \({\cal R}\) transform. In CVPR (pp. 1–8).
Weng, C., & Yuan, J. (2015). Efficient mining of optimal AND/OR patterns for visual recognition. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 17(5), 626–635.
Wu, B., Yuan, C., & Hu, W. (2014). Human action recognition based on context-dependent graph kernels. In CVPR (pp. 2609–2616).
Weinberger, K., & Saul, L. (2009). Distance metric learning for large margin nearest neighbor classification. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 10, 207–244.
Yang, J., Zhang, D., Frangi, A. F., & Yang, J. (2004). Two-dimensional PCA: A new approach to appearance-based face representation and recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 26(1), 131–137.
Yeffet, L. & Wolf, L. (2009). Local trinary patterns for human action recognition. In ICCV (pp. 492–497).
Yu, J., Tao, D., & Wang, M. (2012). Adaptive hypergraph learning and its application in image classification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 21(7), 3262–3272.
Yuan, C., Li, X., Hu, W., Lin, H., Maybank, S., & Wang, H. (2013). 3D R transform on spatio-temporal interest points for action recognition. In CVPR (pp. 724–730).
Yuan, J., Wu, Y., & Yang, M. (2007). Discovery of collocation patterns: From visual words to visual phrases. In CVPR (pp. 1–8).
Yuan, J., & Wu, Y. (2012). Mining visual collocation patterns via self-supervised subspace learning. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, Cybernetics B, Cybernetics, 42(2), 334–346.
Yuan, J., Yang, M., & Wu, Y. (2011). Mining discriminative co-occurrence patterns for visual recognition, In CVPR (pp. 2777–2784).
Zhang, D., & Zhou, Z. (2005). \((2D)^{2}\text{ PCA }\): 2-Directional 2-Dimensional PCA for efficient face representation and recognition. Neurocomputing, 69(1–3), 224–231.
Zhang, L., Gao, Y., Hong, C., Feng, Y., Zhu, J., & Cai, D. (2014). Feature correlation hypergraph: Exploiting high-order potentials for multimodal recognition. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 44(8), 1408–1419.
Zhou, D., Huang, J., & Schölkopf, B. (2006). Learning with hypergraphs: Clustering, classification, and embedding. In NIPS (pp. 1601–1608).
Zhu, F., & Shao, L. (2014). Weakly-supervised cross-domain dictionary learning for visual recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 109(1–2), 42–59.
Acknowledgments
This work is partly supported by the 973 basic research program of China (Grant No. 2014CB349303), the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61472421, 61472420, 61303086, 61202327), the Project Supported by CAS Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology, and the Project Supported by Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. S2012020011081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Hebert.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, C., Wu, B., Li, X. et al. Fusing \({\mathcal {R}}\) Features and Local Features with Context-Aware Kernels for Action Recognition. Int J Comput Vis 118, 151–171 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-015-0867-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-015-0867-0