Abstract
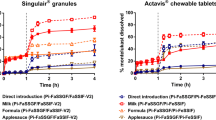
Feed and water components may interact with drugs and affect their dissolution and bioavailability. The impact of the vehicle of administration (feed and water) and the prandial condition of weaner piglets on amoxicillin´s oral bioavailability was evaluated. First, amoxicillin’s in vitro dissolution and stability in purified, soft, and hard water, as well as release kinetics from feed in simulated gastric and intestinal media were assessed. Then, pharmacokinetic parameters and bioavailability were determined in fasted and fed pigs using soft water, hard water, or feed as vehicles of administration following a balanced incomplete block design. Amoxicillin showed similar dissolution profiles in soft and hard water, distinct from the dissolution profile obtained with purified water. Complete dissolution was only achieved in purified water, and merely reached 50% in soft or hard water. Once dissolved, antibiotic concentrations decreased by around 20% after 24 h in all solutions. Korsmeyer-Peppas model best described amoxicillin release from feed in simulated gastric and intestinal media. Feed considerably reduced antibiotic dissolution in both simulated media. In vivo, amoxicillin exhibited significantly higher bioavailability when delivered via water to fasted than to fed animals, while in-feed administration yielded the lowest values. All treatments showed a similar rate of drug absorption. In conclusion, we demonstrated that water and feed components, as well as feed present in gastrointestinal tract of piglets decrease amoxicillin´s oral bioavailability. Therefore, the use of oral amoxicillin as a broad-spectrum antibiotic to treat systemic infections in pigs should be thoroughly revised.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Agersø H, Friis C (1998) Bioavailability of Amoxicillin in pigs. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 21(1):41–46
Al-Khodir FAI, Refat MS (2016) Synthesis, spectroscopic, and antimicrobial study of ca (II), Fe (III), pd (II), and au (III) complexes of Amoxicillin antibiotic drug. Russ J Gen Chem 86(3):708–717
Anfossi P, Zaghini A, Grassigli G, Menotta S, Fedrizzi G (2002) Relative oral bioavailability of microgranulated Amoxicillin in pigs. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 25(5):329–334
Bretschneider B, Brandsch M, Neubert R (1999) Intestinal transport of β-lactam antibiotics: analysis of the affinity at the H+/peptide symporter (PEPT1), the uptake into Caco-2 cell monolayers and the transepithelial flux. Pharm Res 16:55–61
Burch DGS, Sperling D (2018) Amoxicillin—current use in swine medicine. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 41(3):356–368
Carmo LP, Müntener C, Chevance A, Moulin G, Magouras I (2017) Approaches for quantifying antimicrobial consumption peranimal species based on national sales data: a Swiss example, 2006 to 2013. Eurosurveillance 22(6):30458
Cirelli AF, Schenone N, Carrera ALP, Volpedo AV (2010) Calidad De agua para la producción de especies animales tradicionales y no tradicionales en Argentina. AUGMDomus 1:45–66
Costa P, Sousa Lobo JM (2001) Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur J Pharm Sci 13(2):123–133
Cvijic S, Parojc J, Langguth P (2014) Viscosity-mediated negative food effect on oral absorption of poorly-permeable drugs with an absorption window in the proximal intestine: in vitro experimental simulation and computational verification. Eur J Pharm Sci 61:40–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2014.04.008
Dai C, Zhao T, Yang X, Xiao X, Velkov T, Tang S (2017) Pharmacokinetics and relative bioavailability of an oral Amoxicillin-Apramycin combination in pigs. PLoS ONE, 12(4), e0176149
De Arruda EGR, Rocha BA, Barrionuevo M, Aðalsteinsson HM, Galdino FE, Loh W, Abbehausen C (2019) Zn (II) coordination sphere and chemical structure influence over the reactivity of metallo-β-lactamase model compounds. Dalton Trans 48:2900–2916. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8DT03905D
Decundo JM, Diéguez SN, Martínez G, Romanelli A, Fernandez Paggi MB, Gaudio P, Soraci DS, A. L (2019) Impact of water hardness on oxytetracycline oral bioavailability in fed and fasted piglets. Vet Med Sci 5(4):517–525
Decundo JM, Diéguez SN, Amanto FA, Martínez G, Perez Gaudio DS, Fernandez Paggi MB, Soraci AL (2021) Potential interactions between an oral fosfomycin formulation and feed or drinking water: impact on bioavailability in piglets. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 44(5):783–792
Del Castillo JRE, Wolff T (2006) Therapeutic lung exposure to feedadministered chlortetracycline is premix brand dependent. Proceedings⁄ AASV. 143–148
Del Castillo J, Roy JJ, Messier S, Higgins R, Besner JG, Martineau GP (1998) Métaphylaxie de Streptococcus suis chez le porcelet sevré avec l’amoxicilline orale. Journ Rech Porc Fr30:411–416
Deng J, Zhu X, Chen Z, Fan CH, Kwan HS, Wong CH, Lam TNA (2017) Review of food–drug interactions on oral drug absorption. Drugs 77:1833–1855
Dewulf J, Joosten P, Chantziaras I, Bernaerdt E, Vanderhaeghen W, Postma M, Maes D (2022) Antibiotic use in European Pig production: less is more. Antibiotics 11(11):1493
Doadrio Villarejo A, Vallet Regí M (2006) Liberación De fármacos en matrices biocerámicas. Monografía XIX. Avances Y perspectivas. Instituto De España. Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia
Dutra MC, Moreno LZ, Dias RA, Moreno AM (2021) Antimicrobial use in Brazilian swine herds: Assessment of use and reduction examples. Microorganisms 9(4):881
Edwards L, Crabb H (2021) Water quality and management in the Australian pig industry. Anim Prod Sci 61(7):637–644
El-sayed MG, El-komy AA, Elbarawy AE, Mustafa GE (2014) Pharmacokinetical interactions of Amoxicillin and amprolium in broiler chickens. J Physiol Pharmacol Adv 4:515–524
EMA: Categorisation of Antibiotics in the European Union. EMA/CVMP/CHMP/682198/2017. (2019). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/categorisation-antibiotics-europeanunion-answer-request-european-commission-updating-scientific_en.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2019)
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), & European Medicines Agency (EMA), (2017). ECDC/EFSA/EMA second joint report on the integrated analysis of the consumption of antimicrobial agents and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from humans and food-producing animals: joint interagency Antimicrobial Consumption and Resistance Analysis (JIACRA) Report. EFSA J, 15(7), e04872
Farrier DS (1997) PK solutions (ver. 2.0. 2): a noncompartmental pharmacokinetic data analysis program. Summit Research Services, Ashlanh, OH, USA
FDA (1997) Guidance for Industry Dissolution Testing of Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms. Evaluation, 4, 15–22. Retrieved from http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs//Guidances/ucm070246.pdf
Felix IMB, Moreira LC, Chiavone-Filho O, Mattedi S (2016) Solubility measurements of Amoxicillin in mixtures of water and ethanol from 283.15 to 298.15 K. Fluid Phase Equilib. 422:78–86
Fernández JA, Santos RG, Estévez GF (2009) Cinética De liberación de cefalexiana desde un biomaterial compuesto por HAP-200/POVIAC/CaCO3. An R acad Nac Farm. 75 (3)
Ferran AA, Roques BB (2019) Can oral group medication be improved to reduce antimicrobial use? Vet Rec. 5–7
Filippitzi ME, Callens B, Pardon B, Persoons D, Dewulf J, Unit VE, Health H (2014) Antimicrobial use in pigs, broilers andveal calves in Belgium. Vlaams Diergeneeskundig Tijdschrift 83:215–224
Fleisher D, Li C, Zhou Y, Pao LH, Karim A (1999) Drug, meal and formulation interactions influencing drug absorption after oral administration. Clin Pharmacokinet 36(3):233–254
Galassi G, Battelli M, Verdile N, Rapetti L, Zanchi R, Arcuri S, Crovetto GM (2021) Effect of a polyphenol-based additive in Pig diets in the early stages of growth. Animals 11(11):3241
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (2007) Noncompartmental analysis based on statistical moment theory. I. M. Gibaldi, & D. Perrier (Eds.), Pharmacokinetics (2nd ed., p. 413). Informa healthcare
Godoy C, Castells G, Marti G, Capece BPS, Perez F, Colom H, Cristòfol C (2011) Influence of a pig respiratory disease on the pharmacokinetic behaviour of Amoxicillin after oral ad libitum administration in medicated feed. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 34(3):265–276
Gupta P, Premavalli KS (2011) In-vitro studies on functional properties of selected natural dietary fibers. Int J Food Prop 14(2):397–410
Hémonic A, Chauvin C, Delzescaux D, Verliat F, Corrégé I (2018) Reliable estimation of antimicrobial use and its evolution between 2010 and 2013 in French swine farms. Porc Health Manag 4(1):1–11
Hernandez E, Rey R, Puig M, Garcia MA, Solans C, Bregante MA (2005) Pharmacokinetics and residues of a new oral Amoxicillin formulation in piglets: a preliminary study. Vet J 170(2):237–242
Jensen GM, Lykkesfeldt J, Frydendahl K, Møller K, Svendsen O (2006) Pharmacokinetics of Amoxicillin administered in drinking water to recently weaned 3-to 4-week-old pigs with diarrhea experimentally induced by Escherichia coli O149: F4. Am J Vet Res 67(4):648–653
Jerzsele Á, Nagy G (2009) The stability of Amoxicillin trihydrate and potassium clavulanate combination in aqueous solutions. Acta Vet Hung 57(4):485–493
Kaur SP, Rao R, Nanda SANJ (2011) UAmoxicillin: a broad spectrum antibiotic. Int J Pharm Sci 3(3):30–37
Khadka P, Ro J, Kim H, Kim I, Tae J, Kim H, Lee J (2014) Pharmaceutical particle technologies: an approach to improve drug solubility, dissolution and bioavailability. Asian J Pharm 9(6):304–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2014.05.005
Kiss T, Timár Z, Szabó A, Lukács A, Velky V, Oszlánczi G, Csupor D (2019) Effect of green tea on the gastrointestinal absorption of Amoxicillin in rats. BMC 49 40
Korsmeyer RW, Gumy R, Doelker E, Buri P, Peppas NA (1983) Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int J Pharm 15(15):25–35
Lekagul A, Tangcharoensathien V, Yeung S (2019) Patterns of antibiotic use in global pig production: a systematic review. Vet Anim Sci 7:100058
Levy G, Jusko WJ (1965) Effect of viscosity on drug absorption. J Pharm Sci 54(2):219–225
Little SB, Crabb HK, Woodward AP, Browning GF, Billman-Jacobe H (2019) Water medication of growing pigs: sources of between-animal variability in systemic exposure to antimicrobials. Animal 13(12):3031–3040
Little S, Woodward A, Browning G, Billman-Jacobe H (2021) Water distribution systems in pig farm buildings: critical elements of design and management. Animals 11(11):3268
Lutz M, Espinoza J, Arancibia A, Araya M, Pacheco I, Brunser O (1987) Effect of structured dietary fiber on bioavailability of Amoxicillin. Clin Pharmacol Ther 42(2):220–224
Martir J, Flanagan T, Mann J, Fotaki NJAP (2020) Impact of Food and Drink Administration Vehicles on Paediatric Formulation performance: part 1—Effects on solubility of poorly soluble drugs. AAPS PharmSciTech 21:1–12
Menegat MB, Goodband RD, DeRouchey JM, Tokach MD, Woodworth JC, Dritz SS (2019) Kansas State University Swine Nutrition Guide. Feed Additives in Swine Diets
Morthorst D (2002) Bio-availability of amoxicillin in weaning piglets after oral and parenteral administration by feed and water under different conditions [in German, with English Abstract]. Inaugural-Dissertation, Tierärztliche Hochschule, Hannover
Murcia VN, Beneitez AH, Jofre C, Kloster F, Perez NS, Savio MM, M (2022) Estudio exploratorio y descriptivo de la composición mineral del agua de bebida en producciones porcinas de las localidades de anguil y Uriburu, La Pampa, Argentina. Facultad de Ciencias Veterinarias, Universidad Nacional de La Pampa
National Research Council; Division on Earth and Life Studies; Board on Agriculture and Natural Resources; Committee on Nutrient Requirements of Swine (2012) Nutrient requirements of swine. 11th rev. ed. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press
Nielsen P, Gyrd-Hansen N (1996) Bioavailability of oxytetracycline, tetracycline and chlortetracycline after oral administration to fed and fasted pigs. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 19(4):305–311. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2885.1996.tb00054.x
Papich MG (2014) Pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic (PK–PD) modeling and the rational selection of dosage regimes for the prudent use of antimicrobial drugs. Vet Microbiol 171(3–4):480–486
Patel SJ, Wellington M, Shah RM, Ferreira MJ (2020) Antibiotic stewardship in food-producing animals: challenges, progress, and opportunities. Clin Ther 42(9):1649–1658
Polianciuc SI, Gurzău AE, Kiss B, Ştefan MG, Loghin F (2020) Antibiotics in the environment: causes and consequences. Med Pharm Rep 93(3):231
Radwan A, Zaid AN, Jaradat N, Odeh Y (2017) Food effect: the combined effect of media pH and viscosity on the gastrointestinal absorption of cipro floxacin tablet. Eur J Pharm Sci 101:100106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2017.01.030
Shurson GC, Hung YT, Jang JC, Urriola PE (2021) Measures Matter—determining the true nutri-physiological value of feed ingredients for Swine. Animals 11(5):1259
Slavin J (2013) Fiber and Prebiotics: mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients 5(4):1417–1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu5041417
Soraci AL, Amanto F, Pérez DS, Martínez G, Dieguez SN, Vega G, Tapia MO (2010) Metodología de cateterismo yugular en lechones de destete. Analecta Vet 30(1):12–15
Soraci AL, Amanto F, Tapia MO, De la Torre E, Toutain PL (2014) Exposure variability of fosfomycin administered to pigs in food or water: impact of social rank. Res Vet Sci 96(1):153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2013.12.003
Sultana N, Nath AK, Islam MM, Das J (2015) In vitro interaction of Amoxicillin with Calcium Chloride (fused) at pH 2.4 and pH 7.4. J App Pharm Sci 5(03):098–101
Toutain PL, Bousquet-Mélou A (2004) Bioavailability and its assessment. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 27(6):455–466. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2885.2004.00604
U.S. Department of Health and Human (2018) Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Center for Veterinary Medicine, (CVM). Guidance for Industry, Bioanalytical Method Validation
USP (2019) The United States Pharmacopeia USP 42, the National Formulary NF 37. United States Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc, Rockville, Maryland
Vahdat L (2000) Factors influencing the rate of degradation of Amoxycillin sodium and potassium clavulanate in the liquid and frozen states. Doctoral dissertation, Curtin University
Van Boeckel TP, Brower C, Gilbert M, Grenfell BT, Levin SA, Robinson TP, Laxminarayan R (2015) Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(18):5649–5654
Van Rennings L, von Münchhausen C, Ottilie H, Hartmann M, Merle R, Honscha W, Kreienbrock L (2015) Cross-sectional study on antibiotic usage in pigs in Germany. PLoS ONE 10(3), e0119114
Vandael F, Filippitzi ME, Dewulf J, Daeseleire E, Eeckhout M, Devreese M, Croubels S (2019) Oral group medication in pig production: characterising medicated feed and drinking water systems. Vet Rec 185(13):405
Vandael F, de Carvalho Ferreira HC, Devreese M, Dewulf J, Daeseleire E, Eeckhout M, Croubels S (2020) Stability, Homogeneity and carry-over of Amoxicillin, doxycycline, Florfenicol and Flubendazole in Medicated feed and drinking water on 24 Pig farms. Antibiotics 9(9):563
Yamaoka K (1978) Application of Akaike´s Information Criterion (AIC)in the evaluation of Linear pharmacokinetic equations. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 6(2):165–175
Zhang Y, Huo M, Zhou J, Zou A, Li W, Yao C, Xie S (2010) DDSolver: an add-inprogram for modeling and comparison of drug dissolution profiles. AAPS J 12(3). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-010-9185-1
Funding
This work was supported by CIVETAN-CONICET.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contributions: JMD: experimental design, surgery assistance, in-farm work and animal handling, sample collection, in vitro study, analytical procedure, results of pharmacokinetic and statistical analysis, and paper writing. SND: analytical method development and validation, analytical procedure, analysis and discussion of results, and paper writing and correction GM: in-farm work and animal handling and sampling and discussion of results; FAA: in-farm work, animal handling, and sample collection; DSPG: analysis and discussion of pharmacokinetic results. ALS: Project Director, experimental design, animal surgery, in-farm work and animal handling, analytical procedure, statistical analysis results analysis and discussion and paper writing and correction. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
For animal handling we followed the Guidelines of the Animal Welfare Committee of the University of the Center of Buenos Aires Province, in compliance with EU Directive 2010/63/EU. The experimental design and procedures were evaluated and approved by the Animal Welfare Committee FCV-UNCPBA (Res Nº 087/02, May 11, 2016).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Decundo, J.M., Dieguez, S.N., Martínez, G. et al. The vehicle of administration, feed or water, and prandial state influence the oral bioavailability of amoxicillin in piglets. Vet Res Commun (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-024-10378-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-024-10378-0