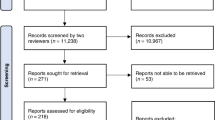
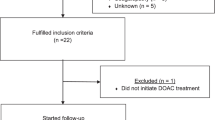
Abstract
Thromboembolism (TE) is a common and serious complication of nephrotic syndrome (NS). NS is associated with hypercoagulability, which may be induced by changes in coagulation, anticoagulant, and fibrinolytic factors. Moreover, accumulating evidence supports the hypothesis that the complex interactions between genetic and acquired risk factors in TE should be considered and that genetic susceptibility should not be ignored. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) also play unique roles. Further research on EVs may provide new insights into the discovery and treatment of TE associated with NS. The occurrence of NS accompanied by TE may be associated with various risk factors. Preventive anticoagulant therapy can not only reduce the risk of TE in patients but also aggravate the risk of bleeding. Heparin and vitamin K antagonists (VKAs), traditional anticoagulant drugs, have been extensively applied in the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic diseases, and emerging direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) also provide an alternative choice. Owing to the particularity of NS, the safe application of DOACs still needs to be addressed. This review aimed to comprehensively describe the pathophysiology of TE in NS, as well as analyze the associated risk factors, the opportunity for preventive anticoagulation, and current anticoagulant information.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data availability is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Abbreviations
- AT-III:
-
Antithrombin-III
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- C4BP:
-
C4B binding protein
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- DOACs:
-
Direct oral anticoagulants
- DVT:
-
Deep vein thrombosis
- EVs:
-
Extracellular vesicles
- Gla:
-
γ-Carboxyglutamic acid
- IMN:
-
Idiopathic membranous nephropathy
- INR:
-
International Standardized ratio
- Lp (a):
-
Lipoprotein (a)
- MN:
-
Membranous nephropathy
- MPs:
-
Microparticles
- NS:
-
Nephrotic syndrome
- NOACs:
-
Novel/new oral anticoagulants
- PAC:
-
Preventive anticoagulation
- PAI:
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor
- PCC:
-
Prothrombin complex concentrate
- PD:
-
Pharmacodynamics
- PE:
-
Pulmonary embolism
- PLG:
-
Plasminogen
- PK:
-
Pharmacokinetics
- PS:
-
Phosphatidylserine
- PT:
-
Prothrombin time
- RVT:
-
Renal venous thrombosis
- TxA2:
-
Thromboxane A2
- TE:
-
Thromboembolism
- TF:
-
Tissue factor
- TFPI:
-
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor
- VKAs:
-
Vitamin K antagonists
- VTE:
-
Venous thromboembolism
- LMWH:
-
Low-molecular-weight heparin
References
Cameron JS, Hicks J (2002) The origins and development of the concept of a “nephrotic syndrome.” Am J Nephrol 22:240–247. https://doi.org/10.1159/000063768
Hull RP, Goldsmith DJ (2008) Nephrotic syndrome in adults. BMJ 336:1185–1189. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39576.709711.80
Pavord S, Myers B (2011) Bleeding and thrombotic complications of kidney disease. Blood Rev 25:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2011.07.001
Orth SR, Ritz E (1998) The nephrotic syndrome. N Engl J Med 338:1202–1211. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199804233381707
Zhang LJ, Zhang Z, Li SJ, Meinel FG, Nance JW Jr, Zhou CS, Zhao YE, Schoepf UJ, Lu GM (2014) Pulmonary embolism and renal vein thrombosis in patients with nephrotic syndrome: prospective evaluation of prevalence and risk factors with CT. Radiology 273:897–906. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.14140121
Shinkawa K, Yoshida S, Seki T, Yanagita M, Kawakami K (2020) Risk factors of venous thromboembolism in patients with nephrotic syndrome: a retrospective cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfaa134
Kerlin BA, Ayoob R, Smoyer WE (2012) Epidemiology and pathophysiology of nephrotic syndrome-associated thromboembolic disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7:513–520. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.10131011
Leslom AN, Alrawiah ZMS, Al-Asmari AMA, Alqashaneen MDA, Alahmari AOT, Al-Ahmari H (2020) Prevalence of pulmonary thromboembolism in nephrotic syndrome patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Family Med Prim Care 9:497–501. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1076_19
Schafer AI (1985) The hypercoagulable states. Ann Intern Med 102:814–828. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-102-6-814
Dahlbäck B (1991) Protein S and C4b-binding protein: components involved in the regulation of the protein C anticoagulant system. Thromb Haemost 66:49–61
Rostoker G, Goualt-Heilmann M, Levent M, Robeva R, Lang P, Lagrue G (1987) High level of protein C and protein S in nephrotic syndrome. Nephron 46:220–221. https://doi.org/10.1159/000184351
Pabinger-Fasching I, Lechner K, Niessner H, Schmidt P, Balzar E, Mannhalter C (1985) High levels of plasma protein C in nephrotic syndrome. Thromb Haemost 53:5–7
Vigano-D’Angelo S, D’Angelo A, Kaufman CE Jr, Sholer C, Esmon CT, Comp PC (1987) Protein S deficiency occurs in the nephrotic syndrome. Ann Intern Med 107:42–47. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-107-1-42
Nishioka J, Suzuki K (1990) Inhibition of cofactor activity of protein S by a complex of protein S and C4b-binding protein. Evidence for inactive ternary complex formation between protein S, C4b-binding protein, and activated protein C. J Biol Chem 265:9072–9076
Lau SO, Tkachuck JY, Hasegawa DK, Edson JR (1980) Plasminogen and antithrombin III deficiencies in the childhood nephrotic syndrome associated with plasminogenuria and antithrombinuria. J Pediatr 96:390–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80678-0
Kauffmann RH, Veltkamp JJ, Van Tilburg NH, Van Es LA (1978) Acquired antithrombin III deficiency and thrombosis in the nephrotic syndrome. Am J Med 65:607–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(78)90848-3
Llach F (1985) Hypercoagulability, renal vein thrombosis, and other thrombotic complications of nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 28:429–439. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1985.149
Eneman B, Levtchenko E, van den Heuvel B, Van Geet C, Freson K (2016) Platelet abnormalities in nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 31:1267–1279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3173-8
Machleidt C, Mettang T, Stärz E, Weber J, Risler T, Kuhlmann U (1989) Multifactorial genesis of enhanced platelet aggregability in patients with nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 36:1119–1124. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1989.310
Yoshida N, Aoki N (1978) Release of arachidonic acid from human platelets. A key role for the potentiation of platelet aggregability in normal subjects as well as in those with nephrotic syndrome. Blood 52:969–977
Jackson CA, Greaves M, Patterson AD, Brown CB, Preston FE (1982) Relationship between platelet aggregation, thromboxane synthesis and albumin concentration in nephrotic syndrome. Br J Haematol 52:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb03862.x
Carvalho AC, Colman RW, Lees RS (1974) Platelet function in hyperlipoproteinemia. N Engl J Med 290:434–438. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm197402212900805
Rabelink TJ, Zwaginga JJ, Koomans HA, Sixma JJ (1994) Thrombosis and hemostasis in renal disease. Kidney Int 46:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1994.274
van Hylckama VA, Rosendaal FR (2003) High levels of fibrinogen are associated with the risk of deep venous thrombosis mainly in the elderly. J Thromb Haemost 1:2677–2678. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2003.0543b.x
Vayá A, Mira Y, Martínez M, Villa P, Ferrando F, Estellés A, Corella D, Aznar J (2002) Biological risk factors for deep vein trombosis. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 26:41–53
de Sain Velden MG, Kaysen GA, de Meer K, Stellaard F, Voorbij HA, Reijngoud DJ, Rabelink TJ, Koomans HA (1998) Proportionate increase of fibrinogen and albumin synthesis in nephrotic patients: measurements with stable isotopes. Kidney Int 53:181–8. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.1998.00729.x
Zwaginga JJ, Koomans HA, Sixma JJ, Rabelink TJ (1994) Thrombus formation and platelet-vessel wall interaction in the nephrotic syndrome under flow conditions. J Clin Invest 93:204–211. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci116947
McGinley E, Lowe GD, Boulton-Jones M, Forbes CD, Prentice CR (1983) Blood viscosity and haemostasis in the nephrotic syndrome. Thromb Haemost 49:155–157
Du XH, Glas-Greenwalt P, Kant KS, Allen CM, Hayes S, Pollak VE (1985) Nephrotic syndrome with renal vein thrombosis: pathogenetic importance of a plasmin inhibitor (alpha 2-antiplasmin). Clin Nephrol 24:186–191
Schlegel N (1997) Thromboembolic risks and complications in nephrotic children. Semin Thromb Hemost 23:271–280. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-996100
Hervio L, Chapman MJ, Thillet J, Loyau S, Anglés-Cano E (1993) Does apolipoprotein(a) heterogeneity influence lipoprotein(a) effects on fibrinolysis? Blood 82:392–397
Agrawal S, Zaritsky JJ, Fornoni A, Smoyer WE (2018) Dyslipidaemia in nephrotic syndrome: mechanisms and treatment. Nat Rev Nephrol 14:57–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2017.155
Castelli WP, Anderson K, Wilson PW, Levy D (1992) Lipids and risk of coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study Ann Epidemiol 2:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/1047-2797(92)90033-m
Jackson SP, Calkin AC (2007) The clot thickens–oxidized lipids and thrombosis. Nat Med 13:1015–1016. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0907-1015
Podrez EA, Byzova TV, Febbraio M, Salomon RG, Ma Y, Valiyaveettil M, Poliakov E, Sun M, Finton PJ, Curtis BR, Chen J, Zhang R, Silverstein RL, Hazen SL (2007) Platelet CD36 links hyperlipidemia, oxidant stress and a prothrombotic phenotype. Nat Med 13:1086–1095. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1626
Reich LM, Bower M, Key NS (2003) Role of the geneticist in testing and counseling for inherited thrombophilia. Genet Med 5:133–143. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.Gim.0000067987.77803.D0
Klarin D, Busenkell E, Judy R, Lynch J, Levin M, Haessler J, Aragam K, Chaffin M, Haas M, Lindström S, Assimes TL, Huang J, Min Lee K, Shao Q, Huffman JE, Kabrhel C, Huang Y, Sun YV, Vujkovic M, Saleheen D, Miller DR, Reaven P, DuVall S, Boden WE, Pyarajan S, Reiner AP, Trégouët DA, Henke P, Kooperberg C, Gaziano JM, Concato J, Rader DJ, Cho K, Chang KM, Wilson PWF, Smith NL, O’Donnell CJ, Tsao PS, Kathiresan S, Obi A, Damrauer SM, Natarajan P (2019) Genome-wide association analysis of venous thromboembolism identifies new risk loci and genetic overlap with arterial vascular disease. Nat Genet 51:1574–1579. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0519-3
Ismail G, Obrișcă B, Jurubiță R, Andronesi A, Sorohan B, Hârza M (2020) Inherited risk factors of thromboembolic events in patients with primary nephrotic syndrome. Medicina (Kaunas). https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56050242
van der Pol E, Böing AN, Gool EL, Nieuwland R (2016) Recent developments in the nomenclature, presence, isolation, detection and clinical impact of extracellular vesicles. J Thromb Haemost 14:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.13190
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W (2013) Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol 200:373–383. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201211138
Iraci N, Leonardi T, Gessler F, Vega B, Pluchino S (2016) Focus on extracellular vesicles: physiological role and signalling properties of extracellular membrane vesicles. Int J Mol Sci 17:171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020171
Kwon SH (2019) Extracellular vesicles in renal physiology and clinical applications for renal disease. Korean J Intern Med 34:470–479. https://doi.org/10.3904/kjim.2019.108
Owens AP 3rd, Mackman N (2011) Microparticles in hemostasis and thrombosis. Circ Res 108:1284–1297. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.110.233056
Karpman D, Ståhl AL, Arvidsson I (2017) Extracellular vesicles in renal disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 13:545–562. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2017.98
Zwaal RF, Schroit AJ (1997) Pathophysiologic implications of membrane phospholipid asymmetry in blood cells. Blood 89:1121–1132
Morel O, Jesel L, Freyssinet JM, Toti F (2011) Cellular mechanisms underlying the formation of circulating microparticles. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:15–26. https://doi.org/10.1161/atvbaha.109.200956
Bevers EM, Williamson PL (2016) Getting to the outer leaflet: physiology of phosphatidylserine exposure at the plasma membrane. Physiol Rev 96:605–645. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00020.2015
Gao C, Xie R, Yu C, Wang Q, Shi F, Yao C, Xie R, Zhou J, Gilbert GE, Shi J (2012) Procoagulant activity of erythrocytes and platelets through phosphatidylserine exposure and microparticles release in patients with nephrotic syndrome. Thromb Haemost 107:681–689. https://doi.org/10.1160/th11-09-0673
Gyamlani G, Molnar MZ, Lu JL, Sumida K, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kovesdy CP (2017) Association of serum albumin level and venous thromboembolic events in a large cohort of patients with nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 32:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfw227
Barbour SJ, Greenwald A, Djurdjev O, Levin A, Hladunewich MA, Nachman PH, Hogan SL, Cattran DC, Reich HN (2012) Disease-specific risk of venous thromboembolic events is increased in idiopathic glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 81:190–195. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2011.312
Kelddal S, Nykjær KM, Gregersen JW, Birn H (2019) Prophylactic anticoagulation in nephrotic syndrome prevents thromboembolic complications. BMC Nephrol 20:139. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-019-1336-8
Medjeral-Thomas N, Ziaj S, Condon M, Galliford J, Levy J, Cairns T, Griffith M (2014) Retrospective analysis of a novel regimen for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in nephrotic syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9:478–483. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.07190713
Hârza M, Ismail G, Mitroi G, Gherghiceanu M, Preda A, Mircescu G, Sinescu I (2013) Histological diagnosis and risk of renal vein thrombosis, and other thrombotic complications in primitive nephrotic syndrome. Rom J Morphol Embryol 54:555–560
Lin R, McDonald G, Jolly T, Batten A, Chacko B (2020) A Systematic review of prophylactic anticoagulation in nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int Rep 5:435–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2019.12.001
Lee T, Biddle AK, Lionaki S, Derebail VK, Barbour SJ, Tannous S, Hladunewich MA, Hu Y, Poulton CJ, Mahoney SL, Charles Jennette J, Hogan SL, Falk RJ, Cattran DC, Reich HN, Nachman PH (2014) Personalized prophylactic anticoagulation decision analysis in patients with membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int 85:1412–1420. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2013.476
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Glomerulonephritis Work Group (2012) KDIGO clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int Suppl 2:139–274. https://doi.org/10.1038/kisup.2012.20
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Glomerular Diseases Work Group (2021) KDIGO 2021 clinical practice guideline for the management of glomerular diseases. Kidney Int 100:S1-s276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2021.05.021
Hirsh J, Warkentin TE, Shaughnessy SG, Anand SS, Halperin JL, Raschke R, Granger C, Ohman EM, Dalen JE (2001) Heparin and low-molecular-weight heparin: mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, dosing, monitoring, efficacy, and safety. Chest 119:64s–94s. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.119.1_suppl.64s
Derebail VK, Rheault MN, Kerlin BA (2020) Role of direct oral anticoagulants in patients with kidney disease. Kidney Int 97:664–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2019.11.027
Weitz JI (1997) Low-molecular-weight heparins. N Engl J Med 337:688–698. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199709043371007
Matyjek A, Rymarz A, Nowicka Z, Literacki S, Rozmyslowicz T, Niemczyk S (2021) Anti-Xa activity of enoxaparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism in severe nephrotic syndrome-a single center prospective study. J Clin Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10235709
Malhotra OP, Nesheim ME, Mann KG (1985) The kinetics of activation of normal and gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-deficient prothrombins. J Biol Chem 260:279–287
Nelsestuen GL (1976) Role of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. An unusual protein transition required for the calcium-dependent binding of prothrombin to phospholipid. J Biol Chem 251:5648–5656
Kleinow ME, Garwood CL, Clemente JL, Whittaker P (2011) Effect of chronic kidney disease on warfarin management in a pharmacist-managed anticoagulation clinic. J Manag Care Pharm 17:523–30. https://doi.org/10.18553/jmcp.2011.17.7.523
Ganeval D, Fischer AM, Barre J, Pertuiset N, Dautzenberg MD, Jungers P, Houin G (1986) Pharmacokinetics of warfarin in the nephrotic syndrome and effect on vitamin K-dependent clotting factors. Clin Nephrol 25:75–80
Yeh CH, Fredenburgh JC, Weitz JI (2012) Oral direct factor Xa inhibitors. Circ Res 111:1069–1078. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.112.276741
Mazzolai L, Aboyans V, Ageno W, Agnelli G, Alatri A, Bauersachs R, Brekelmans MPA, Büller HR, Elias A, Farge D, Konstantinides S, Palareti G, Prandoni P, Righini M, Torbicki A, Vlachopoulos C, Brodmann M (2018) Diagnosis and management of acute deep vein thrombosis: a joint consensus document from the european society of cardiology working groups of aorta and peripheral vascular diseases and pulmonary circulation and right ventricular function. Eur Heart J 39:4208–4218. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehx003
Ageno W, Gallus AS, Wittkowsky A, Crowther M, Hylek EM, Palareti G (2012) Oral anticoagulant therapy: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: american college of chest physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 141:e44S-e88S. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.11-2292
Mekaj YH, Mekaj AY, Duci SB, Miftari EI (2015) New oral anticoagulants: their advantages and disadvantages compared with vitamin K antagonists in the prevention and treatment of patients with thromboembolic events. Ther Clin Risk Manag 11:967–977. https://doi.org/10.2147/tcrm.S84210
Bauer KA (2013) Pros and cons of new oral anticoagulants. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2013:464–470. https://doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2013.1.464
Mueck W, Schwers S, Stampfuss J (2013) Rivaroxaban and other novel oral anticoagulants: pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects, specific patient populations and relevance of coagulation monitoring. Thromb J 11:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-9560-11-10
Almutairi AR, Zhou L, Gellad WF, Lee JK, Slack MK, Martin JR, Lo-Ciganic WH (2017) Effectiveness and safety of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants for atrial fibrillation and venous thromboembolism: a systematic review and meta-analyses. Clin Ther 39:1456-1478.e36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.05.358
Cuker A, Burnett A, Triller D, Crowther M, Ansell J, Van Cott EM, Wirth D, Kaatz S (2019) Reversal of direct oral anticoagulants: guidance from the anticoagulation forum. Am J Hematol 94:697–709. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.25475
Dupree LH, Reddy P (2014) Use of rivaroxaban in a patient with history of nephrotic syndrome and hypercoagulability. Ann Pharmacother 48:1655–1658. https://doi.org/10.1177/1060028014549349
Shimada Y, Nagaba Y, Nagaba H, Kamata M, Murano J, Kamata F, Okina C, Nonoguchi H, Shimada H, Takeuchi Y (2017) Edoxaban was effective for treating renal vein thrombosis in a patient with nephrotic syndrome. Intern Med 56:2307–2310. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.8742-16
Reynolds ML, Nachman PH, Mooberry MJ, Crona DJ, Derebail VK (2019) Recurrent venous thromboembolism in primary membranous nephropathy despite direct Xa inhibitor therapy. J Nephrol 32:669–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-018-0552-9
Sexton DJ, de Freitas DG, Little MA, McHugh T, Magee C, Conlon PJ, O’Seaghdha CM (2018) Direct-acting oral anticoagulants as prophylaxis against thromboembolism in the nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int Rep 3:784–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2018.02.010
Spiess BD (2008) Treating heparin resistance with antithrombin or fresh frozen plasma. Ann Thorac Surg 85:2153–2160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2008.02.037
Zhang L, Zhang H, Zhang J, Tian H, Liang J, Liu Z (2018) Rivaroxaban for the treatment of venous thromboembolism in patients with nephrotic syndrome and low AT-III: a pilot study. Exp Ther Med 15:739–744. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.5471
Fordyce CB, Hellkamp AS, Lokhnygina Y, Lindner SM, Piccini JP, Becker RC, Berkowitz SD, Breithardt G, Fox KA, Mahaffey KW, Nessel CC, Singer DE, Patel MR (2016) On-treatment outcomes in patients with worsening renal function with rivaroxaban compared with warfarin: insights from ROCKET AF. Circulation 134:37–47. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.116.021890
Böhm M, Ezekowitz MD, Connolly SJ, Eikelboom JW, Hohnloser SH, Reilly PA, Schumacher H, Brueckmann M, Schirmer SH, Kratz MT, Yusuf S, Diener HC, Hijazi Z, Wallentin L (2015) Changes in renal function in patients with atrial fibrillation: an analysis from the RE-LY trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 65:2481–2493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2015.03.577
Acknowledgements
YJT thanks Prof. GDS and BCS for their constant encouragement, suggestions and support throughout.
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TYJ drafted the manuscript. GDS and BCS contributed to draft reviewing and critical modifications. All authors had carefully read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., Sun, B. & Sun, G. Research progress of nephrotic syndrome accompanied by thromboembolism. Int Urol Nephrol 55, 1735–1745 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-023-03474-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-023-03474-8