Abstract
Objective
Currently, there is limited evidence comparing robot-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) to laparoscopic radical cystectomy (LRC). The purpose of this study is to systematically review the literature and conduct a meta-analysis.
Materials and methods
We conducted a systematic literature search to identify matching publications regarding RARC and LRC for bladder cancer through PubMed/Medline, Embase, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) and Web of Science with no restriction to date and language. The evaluated outcomes include perioperative outcomes (i.e. days to oral intake, operative time, estimated blood loss (EBL), transfusion rates, length of stay (LOS) and complication rates) and oncological outcomes (i.e. positive surgical margin (PSM), lymph node yield, and overall survival (OS)).
Results
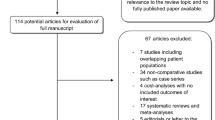
After screening 780 articles, 10 studies were included in the final meta-analysis. We found that there was no significant difference with regard to basic demographic variables, operative time, and PSM. There were statistically significant shorter LOS (MD − 0.63, 95% CI − 1.24, 0.03), fewer complication rates (the risk ratios were 0.74 and 0.49 for Clavien grade 1–2 and Clavien grade 3–5,respectively), more lymph node yield (MD 2.38, 95% CI 1.89–2.87) and less death risk (HR 0.26, 95% CI 0.17–0.39) in RARC group compared with LRC group.
Conclusions
Our findings indicated that patients with RARC may benefit from significantly lower complications, shorter LOS, higher lymph node yield and lower death risk. These data thus showed that RARC might improve the management of patients with muscle invasive or high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424
Teishima J, Hieda K, Inoue S, Goto K, Ikeda K, Ohara S, Kobayashi K, Kajiwara M, Matsubara A (2014) Comparison of initial experiences of robot-assisted radical cystectomy with those of laparoscopic for bladder cancer. Innovations (Phila) 9:322–326
Su S, Gu L, Ma X, Li H, Wang B, Shi T, Zhang X (2019) Comparison of laparoscopic and robot-assisted radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: perioperative and oncologic outcomes. Clin Genitourin Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2019.06.007
Basillote JB, Abdelshehid C, Ahlering TE, Shanberg AM (2004) Laparoscopic assisted radical cystectomy with ileal neobladder: a comparison with the open approach. J Urol 172:489–493
Satkunasivam R, Tallman CT, Taylor JM, Miles BJ, Klaassen Z, Wallis CJD (2019) Robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy: a meta-analysis of oncologic, perioperative, and complication-related outcomes. Eur Urol Oncol 2:443–447
Palazzetti A, Sanchez-Salas R, Capogrosso P, Barret E, Cathala N, Mombet A, Prapotnich D, Galiano M, Rozet F, Cathelineau X (2017) Systematic review of perioperative outcomes and complications after open, laparoscopic and robot-assisted radical cystectomy. Actas Urol Esp 41:416–425
Fonseka T, Ahmed K, Froghi S, Khan SA, Dasgupta P, Shamim KM (2015) Comparing robotic, laparoscopic and open cystectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Ital Urol Androl 87:41–48
Yuh B, Wilson T, Bochner B, Chan K, Palou J, Stenzl A, Montorsi F, Thalmann G, Guru K, Catto JWF, Wiklund PN, Novara G (2015) Systematic review and cumulative analysis of oncologic and functional outcomes after robot-assisted radical cystectomy. Eur Urol 67:402–412
Chade DC, Laudone VP, Bochner BH, Parra RO (2010) Oncological outcomes after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: open versus minimally invasive approaches. J Urol 183:862–869
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement[J]. Ann Intern Med 151:264–269
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien P (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240:205–213
Higgins JP (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of intervensions. Version 5.1.0. London: The Cochrane Collaboration. (Updated March 2011)
Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, Tugwell P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality if nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses[J]. Ottawa Hosp Res Inst. www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Accessed 10 Nov 2019
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5:13
Lijing Y, Guyan W, Yingjie Du, Bingyang Ji, Zhe Z (2014) Remote ischemic preconditioning reduces cardiac troponin I release in cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 28:682–689
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses[J]. BMJ 327:557–560
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis[J]. Stat Med 21:1539–1558
Khan MS, Challacombe B, Elhage O, Rimington P, Coker B, Murphy D, Grieve A, Dasgupta P (2012) A dual-centre, cohort comparison of open, laparoscopic and robotic-assisted radical cystectomy. Int J Clin Pract 66:656–662
Khan MS, Gan C, Ahmed K, Ismail AF, Watkins J, Summers JA, Peacock JL, Rimington P, Dasgupta P (2016) A single-centre early phase randomised controlled three-arm trial of open, robotic, and laparoscopic radical cystectomy (CORAL). Eur Urol 69:613–621
Patel A, Ismail F, Watkins J, O'Brien T, Rimington P, Dasgupta P, Khan MS (2011) 36 initial experience with a randomised controlled trial of open, robotic, and laparoscopic (coral) radical cystectomy: an interim report. Eur Urol Suppl 10(8):543–544
Gan C, Ismail F, Cheung G, Patel A, Watkins J, O’Brien T, Hegarty P, Dasgupta P, Rimington P, Khan MS (2013) A pilot prospective single-centre 3-arm randomised controlled trial of open, robotic and laparoscopic (CORAL) radical cystectomy for bladder cancer[J]. J Urol Suppl 189:e667
Abraham Jose Benito A, Young JL, Box GN, Lee HJ, Deane LA, Ornstein DK (2007) Comparative analysis of laparoscopic and robot-assisted radical cystectomy with ileal conduit urinary diversion. J Endourol 21:1473–1480
Panwar P, Mavuduru RS, Mete UK, Kumar S, Bora GS, Devana SK, Mandal AK, Singh SK, Kakkar N (2018) Perioperative outcomes of minimally invasive versus open radical cystectomy: a single-center experience. Indian J Urol 34:115–121
Kim TH, Sung HH, Jeon HG, Seo S, Jeon SS, Lee HM, Choi HY, Jeong BC (2016) Oncological outcomes in patients treated with radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: comparison between open, laparoscopic, and robot-assisted approaches. J Endourol 30:783–791
Matsumoto K, Tabata K-I, Hirayama T, Shimura S, Nishi M, Ishii D, Fujita T, Iwamura M (2019) Robot-assisted laparoscopic radical cystectomy is a safe and effective procedure for patients with bladder cancer compared to laparoscopic and open surgery: Perioperative outcomes of a single-center experience. Asian J Surg 42:189–196
Witjes JA, Bruins M, Cathomas R, Compérat E, Cowan NC, Gakis G, Hernández V, Lorch A, Ribal MJ, Thalmann GN, van der Heijden AG, Veskimäe E (2019) Guidelines associates. In: Linares Espinós E, Rouanne M, Neuzillet Y (eds) Guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer. European association of urology, The Netherlands. Available from: https://uroweb.org/guideline/bladder-cancer-muscle-invasive-andmetastatic/#7. Accessed 10 Nov 2019
Cohen SA, Mirheydar HS, Parsons JK, Palazzi KL, Liss MA, Chang DC, Kane CJ, Kader AK (2014) Minimally invasive cystectomy is associated with improved perioperative patient safety outcomes compared with open cystectomy in a national cohort[J]. Urology 84:314–319
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed1000097
Funding
The study was supported by the 1.3.5 project for disciplines of excellence, West China Hospital, Sichuan University (ZY2016104) and Pillar Program from Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (2018SZ0219).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DCF: project development, data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing; SZL: data collection, data analysis; YT: data collection; WRW: data management; YBY: data management, data analysis; PH: manuscript editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical statement
The authors have no ethical conflicts to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Search strategy ((((robot-assisted [Title/Abstract]) OR robotic [Title/Abstract])) AND laparoscopic [Title/Abstract]) AND radical cystectomy [Title/Abstract] 220 records
PubMed/Medline, Embase and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) databases by Ovid (laparoscopic [keyword]) AND (Robot* [keyword]) AND radical cystectomy [keyword] 26 records.
Web of Science (Robot* [subject]) AND (laparoscopic [subject]) AND radical cystectomy[subject] 527 records.
The risk of bias of Patel 2011 [20] and Khan 2016 [19]

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, D., Liu, S., Tang, Y. et al. Comparison of perioperative and oncologic outcomes between robot-assisted and laparoscopic radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: a systematic review and updated meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 52, 1243–1254 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02406-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02406-0