Abstract
Objectives
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) may have a higher risk of developing chronic kidney (CKD) compared with general population, but the data on this risk are still not well characterized. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to comprehensively investigate this association by reviewing all available studies.
Methods
A systematic review was performed using MEDLINE and EMBASE database from inception to July 2019 to identify all cohort studies that compared the risk of developing CKD after index date among patients with RA versus individuals without RA. Pooled risk ratio and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated using random-effect, generic inverse-variance method of DerSimonian and Laird.
Results
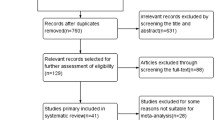
A total of four cohort studies (three retrospective cohort studies and four prospective cohort study) comprising of 1,627,833 participants met the inclusion criteria and were included in the meta-analysis. The overall quality of the included studies was good. The risk of incident CKD was significantly increased among patients with RA with the pooled risk ratio of 1.52 (95% CI 1.28–1.80). The statistical heterogeneity was high with an I2 of 82%.
Conclusions
A significantly increased risk of incident CKD among patients with RA compared with individuals without RA was demonstrated in this study.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kohler BM, Gunther J, Kaudewitz D (2019) Current therapeutic options in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Med 8:E938. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8070938
Deane KD, Holers VM (2019) The natural history of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Ther 41:1256–1269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.04.028
Uhlig T, Moe RH, Kvien TK (2014) The burden of disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics 32:841–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40273-014-0174-6
Malm K, Bergman S, Andersson M et al (2017) Quality of life in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis: a phenomenographic study. SAGE Open Med 5:2050312117713647. https://doi.org/10.1177/2050312117713647
Tobon GJ, Youinou P, Saraux A (2010) The environment, geo-epidemiology, and autoimmune disease: rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun 35:10–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2009.12.009
Crowson CS, Liao KP, Davis JM 3rd et al (2013) Rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular disease. Am Heart J 166:622–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2013.07.010
Cioffi G, Ognilbeni F, Dalbeni A et al (2018) High prevalence of occult heart disease in normotensive patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Cardiol 41:736–743. https://doi.org/10.1002/clc.22926
Ungprasert P, Srivali N, Kittanamongkolchai W (2017) Risk of incident atrial fibrillation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Rheum Dis 20:434–441. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X
Libby P (2002) Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 420:868–874. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01323
Rosenfeld ME (2013) Inflammation in atherosclerosis: direct versus indirect mechanisms. Curr Opin Pharmacol 13:154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2013.01.003
Adcock IM, Mumby S (2017) Glucocorticoids. Handb Exp Pharmacol 237:171–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/164_2016_98
Nakano M, Ueno M, Nishi S et al (1998) Analysis of renal pathology and drug history in 158 Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Nephrol 50:154–160
Helin HJ, Korpela MM, Mustonen JT et al (1995) Renal biopsy findings and clinicopathologic correlations in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38:242–247. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780380213
Hippisley-Cox J, Coupland C (2010) Predicting the risk of chronic kidney disease in men and women in England and Wales: prospective derivation and external validation of QKidney Scores. BMC Fam Pract 11:49. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2296-11-49
Hanaoka R, Kurasawa K, Tanaka A et al (2013) Active rheumatoid arthritis is an independent risk factor of chronic kidney disease. Arthritis Rheum 65(Suppl 10):S164–S165
Hickson LJ, Crowson CS, Gabriel SE et al (2014) Development of reduced kidney function in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Kidney Dis 63:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.08.010
Chiu HY, Huang HL, Li CH et al (2015) Increased risk of chronic kidney disease un rheumatoid arthritis associated with cardiovascular complications—a national population-based cohort study. PLoS One 10:e0136508. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136508
Sihvonen S, Korpela M, Mustonen J et al (2004) Renal disease as a predictor of increased mortality among patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Nephron Clin Pract 96:107–114. https://doi.org/10.1159/000077372
Al-Aly Z, Zeringue A, Fu J et al (2010) Rate of kidney function decline associates with mortality. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1961–1969. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2009121210
Swierkot J, Szechinski J (2006) Methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol Rep 58:473–492
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D et al (2000) The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Accessed 10 July 2019
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trial 7:177–188
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ et al (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Ozyilmaz A, de Jong PE, Gansevoort RT (2012) Screening for chronic kidney disease can be of help to prevent atherosclerotic end-organ damage. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:4046–4052. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfs438
Yang X, Chang Y, Wei W (2016) Endothelial dysfunction and inflammation: immunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Mediat Inflamm 2016:6813016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6813016
Ambrosino P, Lupoli R, Di Minno A et al (2015) Subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A meta-analysis of literature studies. Thromb Haemost 113:916–930. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH14-11-0921
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyzes: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 2009:e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed1000097
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors had access to the data and a role in writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We do not have any financial or non-financial potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raksasuk, S., Ungprasert, P. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis have an increased risk of incident chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int Urol Nephrol 52, 147–154 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02346-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-019-02346-4