Abstract
Objective
Kidney transplantation from a living donor nephrectomy (LDN) is the best treatment for end-stage renal disease, but decrease in donor renal function is often revealed. The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between preoperative factors and postoperative estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and test a predictive model to estimate postoperative eGFR, 1 year after LDN.
Patients and methods
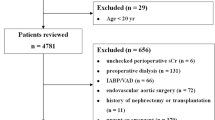
We reviewed 226 records of consecutive patients who underwent laparoscopic live donor nephrectomy between 2006 and 2014 in a single tertiary center. Of these, complete data on 202 patients were analyzed. A training (2/3 of the whole population) and a validation set (1/3) were randomized. A multivariate regression model was used to identify predictors and a formula to estimate of 1-year postoperative eGFR in the training set, using the CKD-EPI formula. Then, the formula was subjected to internal validation using the validation set using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
Results
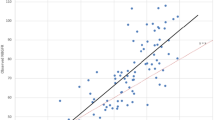
Two hundred and two LLDN were evaluated with a mean preoperative eGFR of 94.1 ± 15.5 ml/min/1.73 m2 and postoperative eGFR of 64.6 ± 14.5 ml/min/1.73 m2 (p < 0.0001). In multivariable analysis, age and preoperative eGFR were independent predictors of postoperative eGFR in the training set. A formula to estimate postoperative eGFR was generated with Pearson r = 0.70 in the training cohort and 0.65 in the validation cohort (both p < 0.0001). Area under the ROC curve of the formula was 0.89 in the training cohort and 0.83 in the validation cohort (both p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
Preoperative eGFR and age are predictors of postoperative eGFR after LDN. The internally validated predictive model of postoperative eGFR developed could be an accurate tool to improve the selection of LDN candidates.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- LDN:
-
Living donor nephrectomy (LDN)
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- ASA:
-
American Society of Anaesthesiologists
- CKD-EPI:
-
Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration Formula
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating curves
- AUC:
-
Areas under the curve
References
Collins AJ, Foley R, Herzog C, Chavers B, Gilbertson D, Ishani A et al (2008) Excerpts from the United States renal data system 2007 annual data report. Am J Kidney Dis 51:S1–S320
Horvat LD, Shariff SZ, Garg AX (2009) Donor nephrectomy outcomes research N. Global trends in the rates of living kidney donation. Kidney Int 75:1088–1098
Groth CG (2003) Presidential address 2002: organ transplantation as a patient service worldwide. Transplantation 75:1098–1100
Park YH, Min SK, Lee JN, Lee HH, Jung WK, Lee JS et al (2004) Comparison of survival probabilities for living-unrelated versus cadaveric renal transplant recipients. Transpl Proc 36:2020–2022
Ross LF, Thistlethwaite JR Jr (2009) Long-term consequences of kidney donation. New Engl J Med 360:2371
Krohn AG, Ogden DA, Holmes JH (1966) Renal function in 29 healthy adults before and after nephrectomy. JAMA 196:322–324
Ibrahim HN, Foley R, Tan L, Rogers T, Bailey RF, Guo H et al (2009) Long-term consequences of kidney donation. New Engl J Med 360:459–469
Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY (2004) Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. New Engl J Med 351:1296–1305
Hu JC, Liu CH, Treat EG, Ernest A, Veale J, Carter S et al (2014) Determinants of laparoscopic donor nephrectomy outcomes. Eur Urol 65:659–664
Levey HR, Rais-Bahrami S, Richstone L, Kavoussi LR (2011) Laparoscopic live donor nephrectomy: a technical road map. J Endourol/Endourol Soc 25:201–208
Wolters U, Wolf T, Stutzer H, Schroder T (1996) ASA classification and perioperative variables as predictors of postoperative outcome. Br J Anaesth 77:217–222
National Kidney F (2002) K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 39:S1–S266
Rook M, Hofker HS, van Son WJ, Homan van der Heide JJ, Ploeg RJ, Navis GJ (2006) Predictive capacity of pre-donation GFR and renal reserve capacity for donor renal function after living kidney donation. Am J Transpl. 6:1653–1659
Huang WC, Levey AS, Serio AM, Snyder M, Vickers AJ, Raj GV et al (2006) Chronic kidney disease after nephrectomy in patients with renal cortical tumours: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol 7:735–740
Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Greene T, Zhang YL, Beck GJ, Froissart M et al (2010) Comparative performance of the CKD Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) and the modification of diet in renal disease (MDRD) study equations for estimating GFR levels above 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Am J Kidney Dis 56:486–495
Matsushita K, Tonelli M, Lloyd A, Levey AS, Coresh J, Hemmelgarn BR et al (2012) Clinical risk implications of the CKD epidemiology collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation compared with the modification of diet in renal disease (MDRD) study equation for estimated GFR. Am J Kidney Dis 60:241–249
Matsushita K, Mahmoodi BK, Woodward M, Emberson JR, Jafar TH, Jee SH et al (2012) Comparison of risk prediction using the CKD-EPI equation and the MDRD study equation for estimated glomerular filtration rate. JAMA 307:1941–1951
Saito T, Uchida K, Ishida H, Tanabe K, Nitta K (2015) Changes in glomerular filtration rate after donation in living kidney donors: a single-center cohort study. Int Urol Nephrol 47:397–403
Kasiske BL, Anderson-Haag T, Israni AK, Kalil RS, Kimmel PL, Kraus ES et al (2015) A prospective controlled study of living kidney donors: three-year follow-up. American J Kidney Dis 66:114–124
Yakoubi R, Autorino R, Kassab A, Long JA, Haber GP, Kaouk JH (2013) Does preserved kidney volume predict 1 year donor renal function after laparoscopic living donor nephrectomy? Int J Urol 20:931–934
Muzaale AD, Massie AB, Wang MC, Montgomery RA, McBride MA, Wainright JL et al (2014) Risk of end-stage renal disease following live kidney donation. JAMA 311:579–586
Toyoda M, Yamanaga S, Kawabata C, Hidaka Y, Inadome A, Arakane F et al (2014) Long-term safety of living kidney donors aged 60 and older. Transpl Proc 46:318–320
Yoon YE, Choi KH, Lee KS, Kim KH, Yang SC, Han WK (2015) Impact of metabolic syndrome on postdonation renal function in living kidney donors. Transpl Proc 47:290–294
Touijer K, Jacqmin D, Kavoussi LR, Montorsi F, Patard JJ, Rogers CG et al (2010) The expanding role of partial nephrectomy: a critical analysis of indications, results, and complications. Eur Urol 57:214–222
Dulabon LM, Lowrance WT, Russo P, Huang WC (2010) Trends in renal tumor surgery delivery within the United States. Cancer 116:2316–2321
Vergho D, Burger M, Schrammel M, Brookman-May S, Gierth M, Hoschke B et al (2015) Matched-pair analysis of renal function in the immediate postoperative period: a comparison of living kidney donors versus patients nephrectomized for renal cell cancer. World J Urol 33:725–731
Timsit MO, Nguyen KN, Rouach Y, Elie C, Loupy A, Fournier C et al (2012) Kidney function following nephrectomy: similitude and discrepancies between kidney cancer and living donation. Urol Oncol 30:482–486
Hew MN, Opondo D, Cordeiro ER, van Donselaar-van der Pant KA, Bemelman FJ, Idu MM et al (2014) The 1-year decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) after radical nephrectomy in patients with renal masses and matched living kidney donors is the same. BJU Int 113:E49–E55
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI et al (2009) A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 150:604–612
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional review board and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benoit, T., Game, X., Roumiguie, M. et al. Predictive model of 1-year postoperative renal function after living donor nephrectomy. Int Urol Nephrol 49, 793–801 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1559-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1559-1