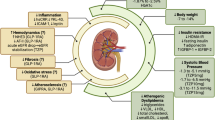
Abstract
Non-diabetic glomerulonephritis is a frequent cause of end-stage renal disease. The use of renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system blockers is a fundamental therapeutic approach. However, converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE-is) and angiotensin receptor blockers do not always achieve the desired target of proteinuria. The induction of the prorenin and renin up-regulation is a possible explanation. Aliskiren is the first drug acting as direct inhibitor of plasmatic renin activity, also able to interfere with the prorenin and renin profibrotic escape. We aimed at reviewing the literature for the assessment of potential efficacy and safety of aliskiren in the treatment of non-diabetic glomerulonephritis. The data on this topic are limited; however, we concluded for a possible usefulness of aliskiren. The renal safety profile appears potentially acceptable in non-diabetic patients although extreme carefulness, particularly with respect to long-term renal and cardiovascular tolerability, is recommended.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moranne O, Watier L, Rossert J, Stengel B (2008) Group GN-PS: primary glomerulonephritis: an update on renal survival and determinants of progression. QJM 101(3):215–224
Chiurchiu C, Remuzzi G, Ruggenenti P (2005) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and renal protection in nondiabetic patients: the data of the meta-analyses. J Am Soc Nephrol 16(Suppl 1):S58–S63
Frampton JE, Curran MP (2007) Aliskiren: a review of its use in the management of hypertension. Drugs 67(12):1767–1792
Krebs C, Hamming I, Sadaghiani S, Steinmetz OM, Meyer-Schwesinger C, Fehr S, Stahl RA, Garrelds IM, Danser AH, van Goor H et al (2007) Antihypertensive therapy upregulates renin and (pro)renin receptor in the clipped kidney of Goldblatt hypertensive rats. Kidney Int 72(6):725–730
Veniant M, Menard J, Bruneval P, Morley S, Gonzales MF, Mullins J (1996) Vascular damage without hypertension in transgenic rats expressing prorenin exclusively in the liver. J Clin Invest 98(9):1966–1970
Nguyen G, Danser AH (2008) Prorenin and (pro)renin receptor: a review of available data from in vitro studies and experimental models in rodents. Exp Physiol 93(5):557–563
Paul M (2006) Poyan Mehr A, Kreutz R: physiology of local renin-angiotensin systems. Physiol Rev 86(3):747–803
Moon JY (2013) Recent update of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Electrolyte Blood Press 11(2):41–45
Ichihara A, Hayashi M, Kaneshiro Y, Suzuki F, Nakagawa T, Tada Y, Koura Y, Nishiyama A, Okada H, Uddin MN et al (2004) Inhibition of diabetic nephropathy by a decoy peptide corresponding to the “handle” region for nonproteolytic activation of prorenin. J Clin Invest 114(8):1128–1135
Simeoni M, Cianfrone P, Comi N, Gentile I, Fabiano FF, Piraina V, Talarico R, Lucisano G, Rivoli L, Andreucci M et al (2015) Is it feasible to improve the duration and the efficiency of Ramipril anti-proteinuric response? G Ital Nefrol 32(1)
Tylicki L, Lizakowski S, Rutkowski B (2012) Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade for nephroprotection: current evidence and future directions. J Nephrol 25(6):900–910
Nguyen G, Delarue F, Burckle C, Bouzhir L, Giller T, Sraer JD (2002) Pivotal role of the renin/prorenin receptor in angiotensin II production and cellular responses to renin. J Clin Invest 109(11):1417–1427
Huang Y, Noble NA, Zhang J, Xu C, Border WA (2007) Renin-stimulated TGF-beta1 expression is regulated by a mitogen-activated protein kinase in mesangial cells. Kidney Int 72(1):45–52
Prieto-Carrasquero MC, Kobori H, Ozawa Y, Gutierrez A, Seth D, Navar LG (2005) AT1 receptor-mediated enhancement of collecting duct renin in angiotensin II-dependent hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289(3):F632–F637
Danser AH, Derkx FH, Schalekamp MA, Hense HW, Riegger GA, Schunkert H (1998) Determinants of interindividual variation of renin and prorenin concentrations: evidence for a sexual dimorphism of (pro)renin levels in humans. J Hypertens 16(6):853–862
Miyata K, Satou R, Inui D, Katsurada A, Seth D, Davis A, Urushihara M, Kobori H, Mitchell KD, Navar LG (2014) Renoprotective effects of direct renin inhibition in glomerulonephritis. Am J Med Sci 348(4):306–314
Huang J, Siragy HM (2009) Glucose promotes the production of interleukin-1beta and cyclooxygenase-2 in mesangial cells via enhanced (Pro)renin receptor expression. Endocrinology 150(12):5557–5565
Advani A, Kelly DJ, Cox AJ, White KE, Advani SL, Thai K, Connelly KA, Yuen D, Trogadis J, Herzenberg AM et al (2009) The (Pro)renin receptor: site-specific and functional linkage to the vacuolar H+-ATPase in the kidney. Hypertension 54(2):261–269
Nguyen G, Delarue F, Berrou J, Rondeau E, Sraer JD (1996) Specific receptor binding of renin on human mesangial cells in culture increases plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 antigen. Kidney Int 50(6):1897–1903
Huang Y, Border WA, Noble NA (2007) Functional renin receptors in renal mesangial cells. Curr Hypertens Rep 9(2):133–139
Huang Y, Wongamorntham S, Kasting J, McQuillan D, Owens RT, Yu L, Noble NA, Border W (2006) Renin increases mesangial cell transforming growth factor-beta1 and matrix proteins through receptor-mediated, angiotensin II-independent mechanisms. Kidney Int 69(1):105–113
Kaneshiro Y, Ichihara A, Sakoda M, Takemitsu T, Nabi AH, Uddin MN, Nakagawa T, Nishiyama A, Suzuki F, Inagami T et al (2007) Slowly progressive, angiotensin II-independent glomerulosclerosis in human (pro)renin receptor-transgenic rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 18(6):1789–1795
Sanoski CA (2009) Aliskiren: an oral direct renin inhibitor for the treatment of hypertension. Pharmacotherapy 29(2):193–212
Riccioni G (2011) Aliskiren in the treatment of hypertension and organ damage. Cardiovasc Ther 29(1):77–87
Feldman DL, Jin L, Xuan H, Contrepas A, Zhou Y, Webb RL, Mueller DN, Feldt S, Cumin F, Maniara W et al (2008) Effects of aliskiren on blood pressure, albuminuria, and (pro)renin receptor expression in diabetic TG(mRen-2)27 rats. Hypertension 52(1):130–136
Ferri N, Greco CM, Maiocchi G, Corsini A (2011) Aliskiren reduces prorenin receptor expression and activity in cultured human aortic smooth muscle cells. JRAAS 12(4):469–474
McMurray JJ, Abraham WT, Dickstein K, Kober L, Massie BM, Krum H (2012) Aliskiren, ALTITUDE, and the implications for atmosphere. Eur J Heart Fail 14(4):341–343
Kelly DJ, Zhang Y, Moe G, Naik G, Gilbert RE (2007) Aliskiren, a novel renin inhibitor, is renoprotective in a model of advanced diabetic nephropathy in rats. Diabetologia 50(11):2398–2404
Lizakowski S, Tylicki L, Rutkowski B (2013) Direct renin inhibition–a promising strategy for renal protection? Med Sci Monit 19:451–457
Gross O, Girgert R, Rubel D, Temme J, Theissen S, Muller GA (2011) Renal protective effects of aliskiren beyond its antihypertensive property in a mouse model of progressive fibrosis. Am J Hypertens 24(3):355–361
Li SY, Chen YT, Yang WC, Tarng DC, Lin CC, Yang CY, Liu WS (2012) Effect of add-on direct renin inhibitor aliskiren in patients with non-diabetes related chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol 13:89
Wu MT, Tung SC, Hsu KT, Lee CT (2014) Aliskiren add-on therapy effectively reduces proteinuria in chronic kidney disease: an open-label prospective trial. JRAAS 15(3):271–277
Moriyama T, Tsuruta Y, Kojima C, Itabashi M, Sugiura H, Takei T, Ogawa T, Uchida K, Tsuchiya K, Nitta K (2012) Beneficial effect of aliskiren combined with olmesartan in reducing urinary protein excretion in patients with chronic kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol 44(3):841–845
Lopez V, Martin M, Cobelo C, Aranda P, Cabello M, Sola E, Gutierrez C, Burgos D, Martinez D, Hernandez D (2010) Renin-angiotensin system dual blockade using angiotensin receptor plus aliskiren decreases severe proteinuria in kidney transplant recipients. Transpl Proc 42(8):2883–2885
Parving HH, Brenner BM, McMurray JJ, de Zeeuw D, Haffner SM, Solomon SD, Chaturvedi N, Persson F, Desai AS, Nicolaides M et al (2012) Cardiorenal end points in a trial of aliskiren for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 367(23):2204–2213
Li PK, Leung CB, Chow KM, Cheng YL, Fung SK, Mak SK, Tang AW, Wong TY, Yung CY, Yung JC et al (2006) Hong Kong study using valsartan in IgA nephropathy (HKVIN): a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Kidney Dis 47(5):751–760
Cheng J, Zhang X, Zhang W, He Q, Tao X, Chen J (2009) Efficacy and safety of glucocorticoids therapy for IgA nephropathy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Nephrol 30(4):315–322
Ballardie FW, Roberts IS (2002) Controlled prospective trial of prednisolone and cytotoxics in progressive IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 13(1):142–148
Coppo R, Peruzzi L, Amore A, Piccoli A, Cochat P, Stone R, Kirschstein M, Linne T (2007) IgACE: a placebo-controlled, randomized trial of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in children and young people with IgA nephropathy and moderate proteinuria. JASN 18(6):1880–1888
Chan LY, Leung JC, Tang SC, Choy CB, Lai KN (2005) Tubular expression of angiotensin II receptors and their regulation in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 16(8):2306–2317
Mann JF, Schmieder RE, McQueen M, Dyal L, Schumacher H, Pogue J, Wang X, Maggioni A, Budaj A, Chaithiraphan S et al (2008) Renal outcomes with telmisartan, ramipril, or both, in people at high vascular risk (the ONTARGET study): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet 372(9638):547–553
Messerli FH (2009) The sudden demise of dual renin-angiotensin system blockade or the soft science of the surrogate end point. J Am Coll Cardiol 53(6):468–470
Tang SC, Lin M, Tam S, Au WS, Ma MK, Yap DY, Ho YW, Lai KN (2012) Aliskiren combined with losartan in immunoglobulin A nephropathy: an open-labeled pilot study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27(2):613–618
Woo KT, Choong HL, Wong KS, Tan HK, Foo M, Fook-Chong S, Lee EJ, Anantharaman V, Lee GS, Chan CM (2014) Aliskiren and losartan trial in non-diabetic chronic kidney disease. JRAAS 15(4):515–522
Szeto CC, Kwan BC, Chow KM, Leung CB, Li PK (2013) The safety and short-term efficacy of aliskiren in the treatment of immunoglobulin a nephropathy–a randomized cross-over study. PLoS ONE 8(5):e62736
Wasserstein AG (1997) Membranous glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 8(4):664–674
Polanco N, Gutierrez E, Covarsi A, Ariza F, Carreno A, Vigil A, Baltar J, Fernandez-Fresnedo G, Martin C, Pons S et al (2010) Spontaneous remission of nephrotic syndrome in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(4):697–704
Gupta A, Khaira A, Singh B, Bhowmik DM, Tiwari SC (2009) Aliskiren as an antiproteinuric add-on therapy in primary membranous nephropathy. Clin Exp Nephrol 13(4):402–403
Salgado A, Herrera-Diaz C (2012) Lupus Nephritis: an Overview of Recent Findings. Autoimmune Dis 2012:1–21
Beck L, Bomback AS, Choi MJ, Holzman LB, Langford C, Mariani LH, Somers MJ, Trachtman H, Waldman M (2013) KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis 62(3):403–441
Cheigh JS, Kim H, Stenzel KH, Tapia L, Sullivan JF, Stubenbord W, Riggio RR, Rubin AL (1990) Systemic lupus erythematosus in patients with end-stage renal disease: long-term follow-up on the prognosis of patients and the evolution of lupus activity. Am J Kidney Dis 16(3):189–195
Presta P, Presta P, Fuiano G, Lombardi G, Simeoni M, Rivoli L, Lombardi L, Coppolino G (2015) Successful conception and pregnancy in p-ANCA-associated vasculitis in course of treatment with immunosuppressive drugs and renal replacement therapy. Int J Rheum Dis 18(4):470–472
Yen TH, Yang HY, Yeh YH, Chu PH, Wen CJ, Fu JF, Wang IK, Liang CC, Chang CT, Chen KH et al (2013) Aliskiren attenuates proteinuria in mice with lupus nephritis by a blood pressure-independent mechanism. Lupus 22(2):180–189
Kitiyakara C, Eggers P, Kopp JB (2004) Twenty-one-year trend in ESRD due to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 44(5):815–825
D’Agati V (1994) The many masks of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 46(4):1223–1241
Collins AJ, Kasiske B, Herzog C, Chavers B, Foley R, Gilbertson D, Grimm R, Liu J, Louis T, Manning W et al. (2005) Excerpts from the United States Renal Data System 2004 annual data report: atlas of end-stage renal disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis, 45(1 Suppl 1):A5-7, S1-280
Korbet SM (2003) Angiotensin antagonists and steroids in the treatment of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Semin Nephrol 23(2):219–228
Freiberger V, Amann K, Heemann U, Frank H (2009) Effect of a triple blockade of the renin-angiotensin-system in recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after kidney transplantation. Transpl Int 22(11):1110–1113
Gardenswartz MH, Lerner CW, Seligson GR, Zabetakis PM, Rotterdam H, Tapper ML, Michelis MF, Bruno MS (1984) Renal disease in patients with AIDS: a clinicopathologic study. Clin Nephrol 21(4):197–204
Winston JA, Bruggeman LA, Ross MD, Jacobson J, Ross L, D’Agati VD, Klotman PE, Klotman ME (2001) Nephropathy and establishment of a renal reservoir of HIV type 1 during primary infection. N Engl J Med 344(26):1979–1984
Levin ML, Palella F, Shah S, Lerma E, Butter J, Kanwar YS (2001) Hiv-associated nephropathy occurring before HIV antibody seroconversion. Am J Kidney Dis 37(5):E39
Kumar D, Plagov A, Yadav I, Torri DD, Sayeneni S, Sagar A, Rai P, Adabala M, Lederman R, Chandel N et al (2012) Inhibition of renin activity slows down the progression of HIV-associated nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 303(5):F711–F720
Plagov A, Lan X, Rai P, Kumar D, Lederman R, Rehman S, Malhotra A, Ding G, Chander PN, Singhal PC (2014) Modulation of renin angiotensin system predominantly alters sclerotic phenotype of glomeruli in HIVAN. Histol Histopathol 29(12):1575–1581
Laurinavicius A, Hurwitz S, Rennke HG (1999) Collapsing glomerulopathy in HIV and non-HIV patients: a clinicopathological and follow-up study. Kidney Int 56(6):2203–2213
Kirchner JT (2002) Resolution of renal failure after initiation of HAART: 3 cases and a discussion of the literature. AIDS Read 12(3):103–105, 110–102
Burns GC, Paul SK, Toth IR, Sivak SL (1997) Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in HIV-associated nephropathy. JASN 8(7):1140–1146
Bolignano D, Pisano A, Coppolino G (2015) The DARK SIDE OF BLOCKing RAS in diabetic patients with incipient or manifested nephropathy. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. [Epub ahead of print]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have not to declare any financial conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simeoni, M., Nicotera, R., Colao, M. et al. Direct inhibition of plasmatic renin activity with aliskiren: a promising but under-investigated therapeutic option for non-diabetic glomerulonephritis. Int Urol Nephrol 48, 229–237 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1128-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1128-4