Abstract
Objectives
The purpose was to investigate the role of immunophilin ligands in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced germ cell apoptosis in the rat.
Materials and methods
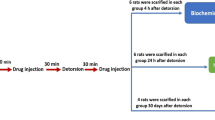
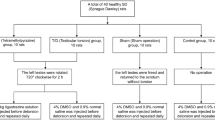
Sprague–Dawley rats were divided into five groups with ten animals in each. In animals undergoing torsion/detorsion, right testes were rotated 720º for 1 h. A baseline group was for basal normal values. The sham-operated group served as a control group. The TD group underwent torsion/detorsion surgery alone; the cyclosporine-A group (TD-CsA) received intravenous cyclosporine injection (5 mg/kg) at the time of detorsion, and the FK-506 group (TD-FK) received intravenous FK-506 (3.5 mg/kg) at the time of detorsion. For measurement of lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities, the right testes of five animals in each group were excised after 4-h reperfusion. Germ cell apoptosis indices were determined 24 h following detorsion in the right testes of the remaining five animals in each group.
Results
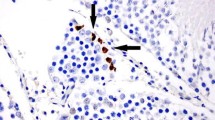
Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in the TD group were significantly higher compared to control and baseline groups. Moreover, testicular MDA values in TD-CsA and TD-FK groups were significantly lower than in TD. There were also significant decreases in catalase and superxide dismutase activities in the TD group compared to control and baseline groups. These values in TD-CsA and TD-FK groups were significantly higher than in TD. The mean germ cell apoptosis scores were significantly higher in TD animals compared to control and baseline groups; however, CsA and FK-506 treatment significantly reduced the apoptosis compared with the TD group.
Conclusion
We have shown that administration of immunophilin ligands in testicular torsion decreases ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) cellular damage. The results of biochemical studies suggest that reduction of oxidative stress along with attenuated neutrophil accumulation by immunophilin ligands may have a major role in their cytoprotective effects.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williamson RC (1985) The continuing conundrum of testicular torsion. Br J Surg 72:509–510. doi:10.1002/bjs.1800720702
Lysiak JJ, Nguyen QA, Turner TT (2002) Peptide and nonpeptide reactive oxygen scavengers provide partial rescue of the testis after torsion. J Androl 23:400–409
Ghazinezami B, Rahimpour S, Gholipour T et al (2007) Pharmacologic preconditioning of random-pattern skin flap in rats using local cyclosporine and FK-506: interaction with nitric oxide system. Ann Plast Surg 59:435–440
Perrea DN, Moulakakis KG, Poulakou MV et al (2006) Correlation between oxidative stress and immunosuppressive therapy in renal transplant recipients with an uneventful postoperative course and stable renal function. Int Urol Nephrol 38:343–348. doi:10.1007/s11255-006-0054-x
Vanrenterghem Y (1998) Tacrolimus (FK 506) in kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc 30:2171–2173. doi:10.1016/S0041-1345(98)00578-8
Singh D, Lawen J, Alkhudair W (2005) Does pretransplant obesity affect the outcome in kidney transplant recipients? Transplant Proc 37:717–720. doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2004.12.033
Hemenway CS, Heitman J (1999) Calcineurin. Structure, function, and inhibition. Cell Biochem Biophys 30:115–151. doi:10.1007/BF02737887
Halestrap AP, McStay GP, Clarke SJ (2002) The permeability transition pore complex: another view. Biochimie 84:153–166. doi:10.1016/S0300-9084(02)01375-5
Hausenloy D, Wynne A, Duchen M et al (2004) Transient mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening mediates preconditioning-induced protection. Circulation 109:1714–1717. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000126294.81407.7D
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Beheshtian A, Salmasi AH, Payabvash S et al (2008) Role of endogenous cannabinoids in ischemia/reperfusion injury following testicular torsion in rats. Int J Urol 15:449–454. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2042.2008.02018.x
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Payabvash S, Ghahremani MH, Goliaei A et al (2006) Nitric oxide modulates glutathione synthesis during endotoxemia. Free Radic Biol Med 41:1817–1828. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.09.010
Paoletti F, Mocali A (1990) Determination of superoxide dismutase activity by purely chemical system based on NAD(P)H oxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:209–220. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(90)86110-H
Turner TT, Bang HJ, Lysiak JL (2004) The molecular pathology of experimental testicular torsion suggests adjunct therapy to surgical repair. J Urol 172:2574–2578. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000144203.30718.19
Barlas M, Hatiboglu C (2002) The effect of nitric oxide in testicular ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int Urol Nephrol 34:81–86. doi:10.1023/A:1021311029572
Savas C, Dindar H, Aras T et al (2002) Pentoxifylline improves blood flow to both testes in testicular torsion. Int Urol Nephrol 33:81–85. doi:10.1023/A:1014469323448
Beheshtian A, Salmasi AH, Payabvash S et al (2008) Protective effects of sildenafil administration on testicular torsion/detorsion damage in rats. World J Urol 26:197–202. doi:10.1007/s00345-008-0243-6
Jaeschke H, Farhood A, Smith CW (1990) Neutrophils contribute to ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat liver in vivo. FASEB J 4:3355–3359
Poggetti RS, Moore FA, Moore EE et al (1992) Liver injury is a reversible neutrophil-mediated event following gut ischemia. Arch Surg 127:175–179
Baggiolini M, Walz A, Kunkel SL (1989) Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest 84:1045–1049. doi:10.1172/JCI114265
Payabvash S, Kiumehr S, Tavangar SM et al (2008) Ethyl pyruvate reduces germ cell-specific apoptosis and oxidative stress in rat model of testicular torsion/detorsion. J Pediatr Surg 43:705–712. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2007.12.063
Ozturk H, Dokucu AI (2008) The role of cell adhesion molecules in ischemic epididymal injury. Int Urol Nephrol 40:137–142. doi:10.1007/s11255-007-9243-5
Watanabe K, Suematsu M, Iida M et al (1992) Effect of rat CINC/gro, a member of the interleukin-8 family, on leukocytes in microcirculation of the rat mesentery. Exp Mol Pathol 56:60–69. doi:10.1016/0014-4800(92)90023-5
Watanabe K, Kinoshita S, Nakagawa H (1989) Purification and characterization of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant produced by epithelioid cell line of normal rat kidney (NRK-52E cell). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 161:1093–1099. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(89)91355-7
Pazderka F, Enns J, Batiuk TD et al (1996) The functional consequences of partial calcineurin inhibition in human peripheral blood mononuclear leucocytes. Transpl Immunol 4:23–31. doi:10.1016/S0966-3274(96)80029-3
Puglisi RN, Strande L, Santos M et al (1996) Beneficial effects of cyclosporine and rapamycin in small bowel ischemic injury. J Surg Res 65:115–118. doi:10.1006/jsre.1996.0352
Suzuki S, Toledo-Pereyra LH, Rodriguez FJ et al (1993) Neutrophil infiltration as an important factor in liver ischemia and reperfusion injury. Modulating effects of FK506 and cyclosporine. Transplantation 55:1265–1272
Adams DH, Wang LF, Neuberger JM et al (1990) Inhibition of leukocyte chemotaxis by immunosuppressive agents. Specific inhibition of lymphocyte chemotaxis by cyclosporine. Transplantation 50:845–850
Weinbaum DL, Kaplan SS, Zdziarski U et al (1984) Human polymorphonuclear leukocyte interaction with cyclosporine A. Infect Immun 43:791–794
Borel JF, Feurer C, Gubler HU et al (1976) Biological effects of cyclosporin A: a new antilymphocytic agent. Agents Actions 6:468–475. doi:10.1007/BF01973261
Kawai M, Nishikomori R, Jung EY et al (1995) Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits intercellular adhesion molecule-1 biosynthesis induced by cytokines in human fibroblasts. J Immunol 154:2333–2341
Ohtsuka T, Kubota A, Hirano T et al (1996) Glucocorticoid-mediated gene suppression of rat cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant CINC/gro, a member of the interleukin-8 family, through impairment of NF-kappa B activation. J Biol Chem 271:1651–1659. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.3.1651
Suthanthiran M, Morris RE, Strom TB (1996) Immunosuppressants: cellular and molecular mechanisms of action. Am J Kidney Dis 28:159–172. doi:10.1016/S0272-6386(96)90297-8
Fruman DA, Burakoff SJ, Bierer BE (1994) Immunophilins in protein folding and immunosuppression. FASEB J 8:391–400
Shatrov VA, Lehmann V, Chouaib S (1997) Sphingosine-1-phosphate mobilizes intracellular calcium and activates transcription factor NF-kappa B in U937 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 234:121–124. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6598
Kanno T, Siebenlist U (1996) Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB via T cell receptor requires a Raf kinase and Ca2+ influx. Functional synergy between Raf and calcineurin. J Immunol 157:5277–5283
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by a research grant provided by the Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nezami, B.G., Rahimpour, S., Gholipour, T. et al. Protective effects of immunophilin ligands on testicular torsion/detorsion damage in rats. Int Urol Nephrol 41, 93–99 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-008-9453-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-008-9453-5