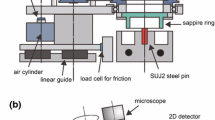
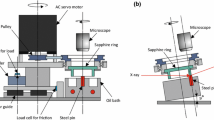
Abstract
Scuffing is a catastrophic failure that causes significant surface damages such as plastic flow and welding with a marked increase in friction, wear, temperature and noise. In this study, variations in the crystal grain structure of a steel surface was analysed in situ during the scuffing process using a synchrotron X-ray diffraction system, combined with a visible camera and a near-infrared thermometer. The in situ observation system was synchronously operated to capture a contact area between a rotating sapphire ring and a stationary bearing steel pin. The Debye–Scherrer ring diffracted from the contact area was captured by a two-dimensional detector. The scuffing behaviour could be classified as either micro scuffing or macro scuffing. During the micro scuffing period, plastic flow occurred intermittently with a significant temperature rise of approximately 1000 °C. During the macro scuffing period, heat was continuously generated over the contact area. When plastic flow occurred, the captured Debye–Scherrer ring indicated the orientation of crystal grains as well as a phase transformation from martensite to austenite. This study constitutes the first in-situ observation of the behaviour of crystal grains in the dynamic recrystallisation process occurring during the scuffing process.
Graphic Abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holmberg, K., Andersson, P., Erdemir, A.: Global energy consumption due to friction in passenger cars. Tribol. Int. 47, 221–234 (2012)
Dyson, A.: Scuffing—a review. Tribol. Int. 8(2), 77–87 (1975a)
Dyson, A.: Scuffing—a review: part 2: the mechanism of scuffing. Tribol. Int. 8(3), 117–122 (1975b)
Scott, D., Smith, A.I., Tait, J., Tremain, G.R.: Materials and metallurgical aspects of piston ring scuffing—a literature survey. Wear 33(2), 293–315 (1975)
Ludema, K.C.: A review of scuffing and running-in of lubricated surfaces, with asperities and oxides in perspective. Wear 100(1–3), 315–331 (1984)
Bowman, W.F., Stachowiak, G.W.: A review of scuffing models. Tribol. Lett. 2(2), 113–131 (1996)
Memorandum on definitions, symbols, and units. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Lubrication and Wear, vol. 4. The Institution of Mechanical Engineers, London (1957)
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development. Glossary of Terms and Definitions in the Field of Friction Wear and Lubrication = Tribology =, Research Group on Wear of Engineering Materials, vol. 53. Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris (1969)
Bowden, F.P., Tabor, D.: The seizure of metals. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 160, 380–383 (1949)
Semenov, A.P.: The phenomenon of seizure and its investigation. Wear 4(1), 1–9 (1960)
Mishina, H., Sasada, T.: Observation of micro-structure in seized portion and mechanism of seizure. Trans. ASME J. Tribol. 108, 28–133 (1986)
Campany, R.G., Wilson, R.W.: The metallurgy of scoring and scuffing failure. In: Dowson, D., Taylor, C.M., Godet, M., Berthe, D. (eds.) Proceedings of the 9th Leeds-Lyon Symposium on Tribology, Tribology of Reciprocating Engines, 201–211. Butterworth & Co Ltd, Guildford (1983)
Wang, Y., Tian, T.: Exploring operation mechanisms of the flexible metal-to-metal face seal: part II—scoring and leakage analysis. Tribol. Trans. 53(5), 649–657 (2010)
Ling, F.F., Saibel, E.: Thermal aspects of galling of dry metallic surfaces in sliding contact. Wear 1(2), 80–91 (1957/58)
Rabinowicz, E.: Friction seizure and galling seizure. Wear 25(3), 357–363 (1973)
Ohmori, T., Kitamura, K., Danno, A., Kawamura, M.: Evaluation of galling prevention properties of cold-forging oils by ball penetration test. Wear 155(1), 183–192 (1992)
Blok, H.: The flash temperature concept. Wear 6(6), 483–494 (1963)
Wojciechowski, Ł, Mathiab, T.G.: Focus on the concept of pressure-velocity-time (pVt) limits for boundary lubricated scuffing. Wear 15, 179–186 (2018)
Castro, J., Seabra, J.: Influence of mass temperature on gear scuffing. Tribol. Int. 119, 27–37 (2018)
Christensen, H.: Failure by collapse of hydrodynamic oil films. Wear 22(3), 359–366 (1972)
Dyson, A.: The failure of elastohydrodynamic lubrication of circumferentially ground discs. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 190, 699–711 (1976)
Enthoven, J., Spikes, H.A.: Infrared and visual study of the mechanisms of scuffing. Tribol. Trans. 39(2), 441–447 (1996)
Batchelor, A.W., Stachowiak, G.W.: Model of scuffing based on the vulnerability of an elastohydrodynamic oil film to chemical degradation catalyzed by the contacting surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 1(4), 349–365 (1995)
Chandrasekaran, M., Batchelor, A.W., Loh, N.L.: Lubricated seizure of stainless observed by X-ray imaging. Wear 243, 68–75 (2000)
Wojciechowski, L., Kubiak, K.J., Mathiad, T.G.: Roughness, and wettability of surfaces in boundary lubricated scuffing wear. Tribol. Int. 93(Part(B)), 593–601 (2016)
O’Donoghue, J.P., Cameron, A.: Temperature at scuffing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 180(Part 3B), 85–94 (1965–66)
Cameron, A.: The role of chemistry in lubrication and scuffing. ASLE Trans. 23(4), 388–392 (1980)
Cutiongco, E.C., Chung, Y.-W.: Prediction of scuffing failure based on competitive kinetics of oxide formation and removal: application to lubricated sliding of AISI 52100 steel on steel. Tribol. Trans. 37(3), 622–628 (1994)
Saeidi, F., Taylor, A.A., Meylan, B., Hoffmann, P., Wasmer, K.: Origin of scuffing in grey cast iron-steel tribo-system. Mater Des. 116(15), 622–630 (2017)
Rogers, M.D.: Metallographic characterisation of transformation phases on scuffed cast-iron diesel engine components. Tribology 2(2), 123–127 (1969)
Rogers, M.D.: The mechanism of scuffing in diesel engines. Wear 15(2), 105–116 (1970)
Torrance, A.A., Cameron, A.: Surface transformations in scuffing. Wear 28(3), 299–311 (1974)
Hershberger, J., Ajayi, O.O., Zhang, J., Yoon, H., Fenske, G.R.: Formation of austenite during scuffing failure of SAE 4340 steel. Wear 256(1–2), 159–167 (2004)
Ajayi, O.O., Hersberger, J.G., Zhang, J., Yoon, H., Fenske, G.R.: Microstructural evolution during scuffing of hardened 4340 steel—implication for scuffing mechanism. Tribol. Int. 38(3), 277–282 (2005)
Yagi, K., Ebisu, Y., Sugimura, J., Kajita, S., Ohmori, T., Suzuki, A.: In situ observation of wear process before and during scuffing in sliding contact. Tribol. Lett. 43(3), 361–368 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-011-9817-3
Li, H., Yagi, K., Sugimura, J., Kajita, S., Shinyoshi, T.: Role of wear particles in scuffing initiation. Tribol. Online 8(5), 285–294 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2474/trol.8.285
Kajita, S., Yagi, K., Izumi, T., Koyamachi, J., Tohyama, M., Saito, K., Sugimura, J.: In situ X-ray diffraction study of phase transformation of steel in scuffing process. Tribol. Lett. 57, 6 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-014-0443-8
Yagi, K., Kajita, S., Izumi, T., Koyamachi, J., Tohyama, M., Saito, K., Sugimura, J.: Simultaneous synchrotron X-ray diffraction, near-infrared, and visible in situ observation of scuffing process of steel in sliding contact. Tribol. Lett. 61, 19 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0636-9
Matsuzaki, Y., Yagi, K., Sugimura, J.: In-situ fast and long observation system for friction surfaces during scuffing of steel. Wear 386, 165–172 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2017.06.013
Izumi, T., Yagi, K., Koyamachi, J., Saito, K., Sanda, S., Yamaguchi, S., Ikehata, H., Yogo, Y., Sugimura, J.: Surface deteriorations during scuffing process of steel and analysis of their contribution to wear using in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction and optical observations. Tribol. Lett. 66, 120 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-018-1062-6
Matsuzaki, Y., Yagi, K., Sugimura, J.: In situ observation of heat generation behaviour on steel surface during scuffing process. Tribol. Lett. 66, 142 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0636-9
Kato, M., Matsuzaki, Y., Yagi, K., Sugimura, J.: Influence of crystal grain structure of steel surface on formation of chemical reaction film derived from engine oil additives. Tribol. Int. 151, 106458 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106458
Cullity, B.D.: Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 2nd edn. Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., Inc., Reading, MA (1978)
Emurlaev, K.I., Bataev, I.A., Lazurenko, D.V., Burov, V.G., Ivanov, I.V., Emurlaeva, Y.Y.: Deformation-induced martensite transformation in AISI 321 stainless steel under dry sliding friction. Mater. Today: Proc. 25(3), 424–427 (2020)
Bataev, I.A., Lazurenko, D.V., Bataev, A.A., Burov, V.G., Ivanov, I.V., Emurlaev, K.I., Smirnov, A.I., Rosenthal, M., Burghammer, M., Ivanov, D.A., Georgarakis, K., Ruktuev, A.A., Ogneva, T.S., Jorge, A.M.J.: A novel operando approach to analyze the structural evolution of metallic materials during friction with application of synchrotron radiation. Acta Mater. 196(1), 355–369 (2020)
Hirose, Y.: TOYOTA beamline BL33XU. In: SPring-8 Research Frontiers 2009. 170 (2010). http://www.spring8.or.jp/pdf/en/res_fro/09/Research_Frontiers_2009_%20web.pdf
Nonaka, T., Dohmae, K., Hayashi, Y., Araki, T., Yamaguchi, S., Nagai, Y., Hirose, Y., Tanaka, T., Kitamura, H., Uruga, T., Yamazaki, H., Yumoto, H., Ohashi, H., Goto, S.: Toyota beamline (BL33XU) at SPring-8. AIP Conf. Proc. 1741, 030043 (2016)
Heilmann, P., Clark, W.A.T., Rigney, D.A.: Orientation determination of subsurface cells generated by sliding. Acta Metall. 31(8), 1293–1305 (1983)
Rainforth, W.M., Stevens, R., Nutting, J.: Deformation structures induced by sliding contact. Philos. Mag. A 66(4), 621–641 (1992)
Hughes, D.A., Dawson, D.B., Korellls, J.S., Weingarten, L.I.: Near surface microstructures developing under large sliding loads. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 3(4), 459–475 (1994)
Rainforth, W.M.: Microstructural evolution at the worn surface: A comparison of metals and ceramics. Wear 245(1–2), 162–177 (2000)
Prasad, S.V., Michael, J.R., Christenson, T.R.: EBSD studies on wear-induced subsurface regions in LIGA nickel. Scripta Mater. 48(3), 255–260 (2003)
Rogers, H.C.: Adiabatic plastic deformation. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 9, 283–311 (1979)
Duffy, A.M.J.: An experimental study of the formation process of adiabatic shear bands in a structural steel. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 36(3), 251–283 (1988)
Meyers, M.A., Nesterenko, V.F., LaSalvia, J.C., Xu, Y.B., Xue, Q.: Observation and modeling of dynamic recrystallization in high-strain, high-strain rate deformation of metals. J. Phys. Fr. 10, Pr9-51-Pr9-56 (2000)
Xue, Q., Gray, G.T., III.: Development of adiabatic shear bands in annealed 316L stainless steel. Part II TEM studies of the evolution of microstructure during deformation localization. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 37, 2447–2457 (2006)
Polyzois, I., Bassim, N.: An examination of the formation of adiabatic shear bands in AISI 4340 steel through analysis of grains and grain deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 631, 18–26 (2015)
Hosseini, S.B., Klement, U., Yao, Y., Ryttberg, K.: Formation mechanisms of white layers induced by hard turning of AISI 52100 steel. Acta Mater. 89(1), 258–267 (2015)
Li, S.-X., Zhao, P.-C., He, Y.-N., Yu, S.-R.: Microstructural evolution associated with shear location of AISI 52100 under high strain rate loading. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 662, 46–53 (2016)
Hossain, R., Pahlevani, F., Witteveen, E., Banerjee, A., Joe, B., Prusty, B.G., Dipenaar, R., Sahajwalla, V.: Hybrid structure of white layer in high carbon steel—formation mechanism and its properties. Sci. Rep. 7, 13288 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The scuffing test was conducted at the Toyota beamline BL33XU of SPring-8 with the approval of the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) (Proposal No. 2014B7021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yagi, K., Izumi, T., Koyamachi, J. et al. In Situ Observation of Crystal Grain Orientation During Scuffing Process of Steel Surface Using Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction. Tribol Lett 68, 115 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-020-01357-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-020-01357-y