Abstract
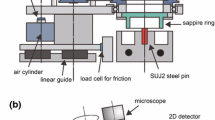
This paper describes an in situ observation of the scuffing process of steel by means of a newly developed system that employs a combination of two-dimensional detector synchrotron X-ray diffraction (XRD), a near-infrared CCD array, and a visible CCD array. In the demonstration of the application of the system, a contact area was produced between a fixed steel pin and a rotating sapphire ring, and the XRD ring, visible image, and near-infrared image of the steel surface of the contact area were synchronously captured at 30 fps under dry conditions. The system visually captured the wear behaviour, significant instantaneous temperature increase, and variation of the grain structure of the steel within the contact area during the scuffing process. The overall wear process was observed to comprise several stages, which were identified with first micro-scuffing, normal wear, second micro-scuffing, and macro-scuffing, respectively. Intermittent plastic flow was observed to occur numerous times with instantaneous heat generation within the contact area during the micro-scuffing processes. The instantaneous heat generation produced an adiabatic boundary condition, which increased the temperature to over 1000°C. The rapid temperature increase and decrease in the contact area also caused repeated phase transformation and reversion between martensite and austenite. The in situ XRD spectrum indicated that the repeated phase transformation and reversion created a definite surface layer that initiated the macro-scuffing process, which caused catastrophic plastic flow.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dyson, A.: Scuffing—a review. Tribol. Int. 8(2), 77–87 (1975)
Dyson, A.: Scuffing—a review: part 2: the mechanism of scuffing. Tribol. Int. 8(3), 117–122 (1975)
Scott, D., Smith, A.I., Tait, J., Tremain, G.R.: Materials and metallurgical aspects of piston ring scuffing —a literature survey. Wear 33(2), 293–315 (1975)
Ludema, K.C.: A review of scuffing and running-in of lubricated surfaces, with asperities and oxides in perspective. Wear 100(1–3), 315–331 (1984)
Bowman, W.F., Stachowiak, G.W.: A review of scuffing models. Tribol. Lett. 2(2), 113–131 (1996)
Memorandum on definitions, symbols and units. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Lubrication and Wear, vol. 4. The Institution of Mechanical Engineers, London (1957)
Glossary of Terms and Definitions in the Field of Friction Wear and Lubrication = Tribology =, Research Group on Wear of Engineering Materials, vol. 53. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris (1969)
Hardy, W.B., Hardy, J.K.: Note on static friction and on the lubricating properties of certain chemical substances. Philos. Mag. Ser. 38(223), 32–48 (1919)
Bowden, F.P., Tabor, D.: The seizure of metals. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 160, 380–383 (1949)
Semenov, A.P.: The phenomenon of seizure and its investigation. Wear 4(1), 1–9 (1960)
Mishina, H., Sasada, T.: Observation of micro-structure in seized portion and mechanism of seizure. Trans. ASME J. Tribol. 108, 28–133 (1986)
Campany, R.G., Wilson, R.W.: The metallurgy of scoring and scuffing failure. In: Dowson, D., Taylor, C.M., Godet, M., Berthe, D. (eds.) Proceedings of the 9th Leeds-Lyon Symposium on Tribology, Tribology of Reciprocating Engines, pp. 201–211. Butterworth & Co Ltd, Guildford (1983)
Wang, Y., Tian, T.: Exploring operation mechanisms of the flexible metal-to-metal face seal: part II—scoring and leakage analysis. Tribol. Trans. 53(5), 649–657 (2010)
Ling, F.F., Saibel, E.: Thermal aspects of galling of dry metallic surfaces in sliding contact. Wear 1(2), 80–91 (1957/58)
Rabinowicz, E.: Friction seizure and galling seizure. Wear 25(3), 357–363 (1973)
Ohmori, T., Kitamura, K., Danno, A., Kawamura, M.: Evaluation of galling prevention properties of cold-forging oils by ball penetration test. Wear 155(1), 183–192 (1992)
Blok, H.: The flash temperature concept. Wear 6(6), 483–494 (1963)
Fein, R.S.: Transition temperatures with four ball machine. ASLE Trans. 3(1), 34–39 (1960)
Fein, R.S.: Effects of lubricants on transition temperature. ASLE Trans. 8(1), 59–68 (1965)
Bell, J.C., Dyson, A.: The effect of some operating factors on the scuffing of hardened steel discs. In: Proceedings of Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication 1972 Symposium, pp. 61–67. The Institution of Mechanical Engineers, London (1972)
Bell, J.C., Dyson, A., Hadley, J.W.: The effects of rolling and sliding speeds on the scuffing of lubricated steel discs. ASLE Trans. 18(1), 62–73 (1975)
Christensen, H.: Failure by collapse of hydrodynamic oil films. Wear 22(3), 359–366 (1972)
Dyson, A.: The failure of elastohydrodynamic lubrication of circumferentially ground discs. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 190, 699–711 (1976)
Enthoven, J., Spikes, H.A.: Infrared and visual study of the mechanisms of scuffing. Tribol. Trans. 39(2), 441–447 (1996)
O’Donoghue, J.P., Cameron, A.: Temperature at scuffing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 180, Part 3B, 85–94 (1965–66)
Cameron, A.: The role of chemistry in lubrication and scuffing. ASLE Trans. 23(4), 388–392 (1980)
Cutiongco, E.C., Chung, Y.-W.: Prediction of scuffing failure based on competitive kinetics of oxide formation and removal: application to lubricated sliding of AISI 52100 steel on steel. Tribol. Trans. 37(3), 622–628 (1994)
Batchelor, A.W., Stachowiak, G.W.: Model of scuffing based on the vulnerability of an elastohydrodynamic oil film to chemical degradation catalyzed by the contacting surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 1(4), 349–365 (1995)
Chandrasekaran, M., Batchelor, A.W., Loh, N.L.: Lubricated seizure of stainless observed by X-ray imaging. Wear 243, 68–75 (2000)
Burwell, J.T., Strang, C.D.: On the empirical law of adhesive wear. J. Appl. Phys. 23(1), 18–28 (1952)
Yagi, K., Ebisu, Y., Sugimura, J., Kajita, S., Ohmori, T., Suzuki, A.: In situ observation of wear process before and during scuffing in sliding contact. Tribol. Lett. 43(3), 361–368 (2011)
Li, H., Yagi, K., Sugimura, J., Kajita, S., Shinyoshi, T.: Role of wear particles in scuffing initiation. Tribol. Online 8(5), 285–294 (2013)
Rogers, M.D.: Metallographic characterisation of transformation phases on scuffed cast-iron diesel engine components. Tribology 2(2), 123–127 (1969)
Rogers, M.D.: The mechanism of scuffing in diesel engines. Wear 15(2), 105–116 (1970)
Torrance, A.A., Cameron, A.: Surface transformations in scuffing. Wear 28(3), 299–311 (1974)
Hershberger, J., Ajayi, O.O., Zhang, J., Yoon, H., Fenske, G.R.: Formation of austenite during scuffing failure of SAE 4340 steel. Wear 256(1–2), 159–167 (2004)
Ajayi, O.O., Hersberger, J.G., Zhang, J., Yoon, H., Fenske, G.R.: Microstructural evolution during scuffing of hardened 4340 steel—implication for scuffing mechanism. Tribol. Int. 38(3), 277–282 (2005)
Hershberger, J., Ajayi, O.O., Zhang, J., Yoon, H., Fenske, G.R.: Evidence of scuffing initiation by adiabatic shear instability. Wear 258(10), 1471–1478 (2005)
Ajayi, O.O., Lorenzo-Martin, C., Erck, R.A., Fenske, G.R.: Scuffing mechanism of near-surface material during lubricated severe sliding contact. Wear 271(9–10), 1750–1753 (2011)
Han, J.M., Zhang, R., Ajayi, O.O., Barber, G.C., Zou, Q., Guessous, L., Schall, D., Alnabulsi, S.: Scuffing behaviour of gray iron and 1080 steel in reciprocating and rotational sliding. Wear 271(9–10), 1854–1861 (2011)
Ajayi, O.O., Lorenzo-Martin, C., Erck, R.A., Fenske, G.R.: Analytical predictive modeling of scuffing initiation in metallic materials in sliding contact. Wear 301(1–2), 57–61 (2013)
Rogers, H.C.: Adiabatic plastic deformation. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 9(1), 283–311 (1979)
Kajita, S., Yagi, K., Izumi, T., Koyamachi, J., Tohyama, M., Saito, K., Sugimura, J.: In situ X-ray diffraction study of phase transformation of steel in scuffing process. Tribol. Lett. 57(1), 1–11 (2015)
Hirose, Y.: TOYOTA beamline BL33XU. In: SPring-8 Research Frontiers 2009. p. 170 (2010)
Nonaka, T., Dohmae, K., Hayashi, Y., Araki, T., Yamaguchi, S., Nagai, Y., Hirose, Y., Tanaka, T., Kitamura, H., Uruga, T., Yamazaki, H., Yumoto, H., Ohashi, H., Goto, S.: Toyota Beamline (BL33XU) at SPring-8. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Synchrotron Radiation Instrumentation (accepted)
Zerwekh, R.P., Wayman, C.M.: On the nature of the α → γ transformation in iron: a study of whiskers. Acta Metall. 13(2), 99–107 (1965)
Apple, C.A., Krauss, G.: The effect of heating rate on the martensite to austenite transformation in Fe-Ni-C alloys. Acta Metall. 20(7), 849–856 (1972)
Ivanisenko, Y., MacLaren, I., Sauvage, X., Valievd, R.Z., Fecht, H.-J.: Shear-induced α → γ transformation in nanoscale Fe–C composite. Acta Mater. 54(6), 1659–1669 (2006)
Welsh, N.C.: Structural changes in rubbed steel surfaces. In: Institute of Mechanical Engineering Proceedings of Conference Lubrication and Wear. pp. 701–706 (1957)
Kawamoto, M., Okabayashi, K.: Wear of cast iron in vacuum and the frictional hardened layer. Wear 17(2), 123–138 (1971)
Yoshida, H., Furuichi, H.: Wear behaviour of a 3% Si steel during repeated frictional contact. Wear 68(2), 219–228 (1981)
Griffiths, B.J., Furze, D.C.: Tribological advantages of white layers produced by machining. Trans. ASME J. Tribol. 109, 338–342 (1987)
Andrade, U., Meyers, M.A., Vecchio, K.S., Chokshi, A.H.: Dynamic recrystallization in high-strain, high-strain-rate plastic deformation of copper. Acta Metall. Mater. 42(9), 3183–3195 (1994)
Cullity, B.D.: Elements of X-ray diffraction, 2nd edn. Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., Inc., Reading, Massachusetts (1978)
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to Dr. Y. Hayashi of Toyota Central R&D Labs., Inc., for his assistance with the acquisition of the XRD data. The test of this study was conducted in the Toyota beamline BL33XU at SPring-8 with the approval of the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) (Proposal No. 2013B7021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yagi, K., Kajita, S., Izumi, T. et al. Simultaneous Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction, Near-Infrared, and Visible In Situ Observation of Scuffing Process of Steel in Sliding Contact. Tribol Lett 61, 19 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0636-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-015-0636-9