Abstract
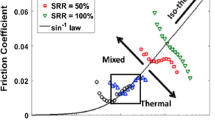
The effects of nanoscale ripple texture on the film thickness and friction in elastohydrodynamically lubricated (EHL) contacts were investigated through ball-on-disc experiments and numerical simulations of line contacts. The texturing was produced by femtosecond LASER irradiations and the ripple texture was in the form of sinusoidal waviness with nanoscale amplitudes and wavelengths. The experimental and numerical results indicate that the orientation of the ripples with respect to the entrainment direction has little to no effect on their capability to form a lubricating film. In the EHL regime, the ripples were found to reduce the central and minimum film thickness by half of their peak-to-peak amplitude as compared to a smooth contact. The transition from EHL to mixed lubrication regime was attributed to micro-EHL effects although the subsequent friction increase was found to be largely due to the onset of asperity contacts. In the mixed lubrication regime, the coefficient of friction was mainly determined by surface roughness and its value increased with an increase in the ripple amplitude.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(a\) :
-
Contact radius
- \(A\) :
-
Waviness/ripple amplitude
- \(A_{\text{d}}\) :
-
Waviness/ripple deformed amplitude
- \(d\) :
-
Groove depth
- \(h,H\) :
-
Film thickness
- \({H_0}\) :
-
Distance between ball and disc neglecting elastic deformation
- \({h_{{\text{av}}}}\) :
-
Average central film thickness
- \({h_{\text{c}}},{H_{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Central film thickness
- \({h_{\text{m}}},{H_{\text{m}}}\) :
-
Minimum film thickness
- \(p,P\) :
-
Pressure
- \({p_{\text{h}}}\) :
-
Maximum Hertzian pressure
- \({p_{{\text{m}},{\text{Hertz}}}}\) :
-
Mean Hertzian pressure
- \({p_{\text{m}}}\) :
-
Mean contact pressure
- \({R_{\text{q}}}\) :
-
RMS roughness
- \({R_{\text{x}}}\) :
-
Reduced curvature radius
- \({\text{SRR}}\) :
-
\({\text{Sliding}}/{\text{rolling ratio}}=100\% \cdot {u_{\text{s}}}/{u_{\text{e}}}\)
- \(t,T\) :
-
Time
- \({\Delta}T\) :
-
Time step
- \(TE\) :
-
Temperature
- \({u_1}\) :
-
Disc speed
- \({u_2}\) :
-
Ball speed
- \({u_{\text{e}}}\) :
-
\({\text{Entrainment speed}}=({u_1}+{u_2})/2\)
- \({u_s}\) :
-
Sliding speed \(={u_1} - {u_2}\)
- \(W\) :
-
Load
- \(w\) :
-
Groove width
- \(x,X\) :
-
Position along the contact
- \({\varvec{\Delta}}X\) :
-
Mesh spacing
- \({\Lambda}_{\text{T}}\) :
-
Tallian parameter
- \(\varepsilon\) :
-
Cavitation penalty parameter
- \({\eta _0}\) :
-
Ambient viscosity
- \(\eta ,\bar {\eta }\) :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- \(\dot {\gamma }\) :
-
Shear rate
- \(\lambda\) :
-
Groove/waviness/ripple wavelength
- \(\mu\) :
-
Friction coefficient
- \({\rho _0}\) :
-
Ambient density
- \(\rho ,\bar {\rho }\) :
-
Density
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Composite RMS roughness
- \(\tau\) :
-
Shear stress
- \(\theta\) :
-
Ripple orientation
- \(\mathcal{H}\) :
-
Modified Hersey number
References
Stachowiak, G.W., Batchelor, A.W.: Engineering Tribology. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2013)
Jackson, A., Cameron, A.: An interferometric study of the EHL of rough surfaces. ASLE Trans. 19(1), 50–56 (1976)
Wedeven, L.D., Cusano, C.: Elastohydrodynamic film thickness measurements of artificially produced surface dents and grooves. ASLE Trans. 22(4), 369–381 (1979)
Mourier, L., Mazuyer, D., Lubrecht, A.A., Donnet, C.: Transient increase of film thickness in micro-textured EHL contacts. Tribol. Int. 39, 1745–1756 (2006)
Touche, T., Cayer-Barrioz, J., Mazuyer, D.: Friction of textured surfaces in EHL and mixed lubrication: effect of the groove topography. Tribol. Lett. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0713-8
Yang, P., Cui, J., Kaneta, M., Nishikawa, H.: Influence of a surface bump or groove on the lubricating performance and dimple phenomena in simple sliding point EHL contacts. J. Tribol. 126(3), 466–472 (2004)
Sperka, P., Krupka, I., Hartl, M.: The effect of surface grooves on film breakdowns in point contacts. Tribol. Int. 102, 249–256 (2016)
Cusano, C., Wedeven, L.D.: The influence of surface dents and grooves on traction in sliding ehd point contacts. ASLE Trans. 26(3), 306–310 (1983)
Touche, T., Woloszynski, T., Podsiadlo, P., Stachowiak, G.W., Cayer-Barrioz, J., Mazuyer, D.: Numerical simulations of groove topography effects on film thickness and friction in EHL regime. Tribol. Lett. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-017-0896-7
Lubrecht, A.A., Ten Napel, W.E., Bosma, R.: Influence of longitudinal and transverse roughness on the elastohydrodynamic lubrication of circular contacts. J. Tribol. 110(3), 421–426 (1988)
Venner, C.H., Lubrecht, A.A.: Numerical analysis of the influence of waviness on the film thickness of a circular EHL contact. J. Tribol. 118(1), 153–161 (1996)
Ehret, P., Dowson, D., Taylor, C.M.: Time-dependent solutions with waviness and asperities in EHL point contacts. Tribol. Ser. 32, 313–324 (1997)
Kweh, C.C., Evans, H.P., Snidle, R.W.: Micro-elastohydrodynamic lubrication of an elliptical contact with transverse and three-dimensional sinusoidal roughness. J. Tribol. 111(4), 577–584 (1989)
Ehret, P., Dowson, D., Taylor, C.M.: Waviness orientation in EHL point contact. Tribol. Ser. 31, 235–244 (1996)
Kaneta, M., Yamada, T., Wang, J.: Micro-elastohydrodynamic lubrication of simple sliding elliptical contacts with sinusoidal roughness. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 222(3), 395–405 (2008)
Seabra, J., Berthe, D.: Elastohydrodynamic point contacts part ii: influence of surface speeds, surface waviness and load on the contact behaviour. Wear 130(2), 319–335 (1989)
Holmes, M.J.A., Evans, H.P., Snidle, R.W.: Analysis of mixed lubrication effects in simulated gear tooth contacts. J. Tribol. 127(1), 61–69 (2005)
Evans, H.P., Snidle, R.W.: A model for elastohydrodynamic film failure in contacts between rough surfaces having transverse finish. J. Tribol. 118(4), 847–857 (1996)
Venner, C.H., Lubrecht, A.A.: Transient analysis of surface features in an EHL line contact in the case of sliding. J. Tribol. 116(2), 186–193 (1994)
Guegan, J., Kadiric, A., Spikes, H.: A study of the lubrication of EHL point contact in the presence of longitudinal roughness. Tribol. Lett. 59, 22 (2015)
Venner, C.H., Couhier, F., Lubrecht, A.A., Greenwood, J.A.: Amplitude reduction of waviness in transient ehl line contacts. Tribol Ser. 32, 103–112 (1997)
Lubrecht, A.A., Graille, D., Venner, C.H., Greenwood, J.A.: Waviness amplitude reduction in EHL line contacts under rolling-sliding. J. Tribol. 120, 705–709 (1998)
Sperka, P., Krupka, I., Hartl, M.: The behaviour of surface roughness in EHL contacts under small slide to roll ratios. Tribol. Lett. 47, 357 (2012)
De Silva, S., Anderson, J.C., Leather, J.A.: Model rough surfaces in elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Thin Solid Films 96, 1 (1982)
Hooke, C.J.: Surface roughness modification in EHL line contacts—the effect of roughness wavelength, orientation and operating conditions. Tribol. Ser. 36 (1999)
Chang, L., Jackson, A., Webster, M.N.: Effects of 3-d surface topography on the EHL film thickness and film breakdown. Tribol. Trans. 37, 435 (1994)
Patching, M.J., Evans, H.P., Snidle, R.W.: Micro-EHL analysis of ground and superfinished steel discs used to simulate gear tooth contacts. Tribol. Trans. 39, 595 (1996)
Kaneta, M., Sakai, T., Nishikawa, H.: Effects of surface roughness on point contact EHL. STLE Tribol. Trans. 36(4), 605–612 (1993)
Kaneta, M., Tani, N., Nishikawa, H.: Optical interferometric observations of the effect of moving transverse asperities on point contact EHL films. Tribol. Ser. 41, 101–109 (2002)
Ali, F., Kaneta, M., Krupka, I., Hartl, M.: Experimental and numerical investigation on the behavior of transverse limited micro-grooves in EHL point contacts. Tribol. Trans. 84, 81–89 (2015)
Leamy, H.J., Rozgonyi, G.A., Sheng, T.T., Celler, G.K.: Periodic regrowth phenomena produced by laser annealing of ion-implanted silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 32, 535 (1978)
Ernesto, A., Mazuyer, D., Cayer-Barrioz, J.: The combined role of soot aggregation and surface effect on the friction of a lubricated contact. Tribol. Lett. 55, 329–341 (2014)
Diew, M., Ernesto, A., Cayer-Barrioz, J., Mazuyer, D.: Stribeck and traction curves under moderate contact pressure: from friction to interfacial rheology. Tribol. Lett. 57, 8 (2015)
Cross, M.M.: Polymer rheology: inuence of molecular weight and polydispersity. J. Appl. Polym Sci. 13, 765 (1969)
Roelands, C.J.A.: Correlational aspects of the viscosity-temperature-pressure relationship of the lubricating oils. PhD thesis, University of Technology Delft, The Netherlands (1966)
Braun, M.J., Hannon, W.M.: Cavitation formation and modelling for fluid film bearings: a review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. J. 224, 839–863 (2010)
Nijenbanning, G., Venner, C.H., Moes, H.: Film thickness in elastohydrodynamically lubricated elliptic contacts. Wear 176, 217–229 (1994)
Moes, H.: Optimum similarity analysis with applications to elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Wear 159, 57–66 (1992)
Venner, C.H.: Multilevel solution of the EHL line and point contact problems. University of Twente, The Netherlands, PhD thesis (1991)
Mourier, L.: Optimisation des contacts elastohydrodynamiques par la micro-texturation de surface. Ecole Centrale de Lyon, France, PhD thesis (2007) (in French)
Mazuyer, D., Ernesto, A., Cayer-Barrioz, J.: Theoretical modelling of film-forming mechanisms under transient conditions: application to deceleration and experimental validation. Tribol. Lett. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0801-9
Schipper, D.J.: Transitions in the lubrication of concentred contacts. University of Twente, The Netherlands, PhD thesis (1966)
Emmens, W.C.: Tribology of flat contacts and its application in deep drawing. University of Twente, The Netherlands, PhD thesis (1997)
Tallian, T.E.: On competing failure modes in rolling contact. ASLE Trans. 10, 418 (1967)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the School of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, Curtin University for the support of this study and acknowledge IREIS Company (France) for active collaboration and fabricating surface textures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woloszynski, T., Touche, T., Podsiadlo, P. et al. Effects of Nanoscale Ripple Texture on Friction and Film Thickness in EHL Contacts. Tribol Lett 67, 16 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-018-1130-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-018-1130-y