Abstract
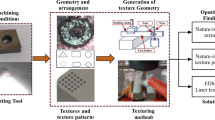
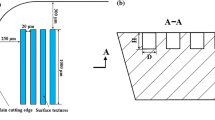
Properly designed micro-scale surface textures can have positive impact on adhesion reduction and lubrication enhancement, which can lead to lower friction and improved performance of a contact interface. The present study aims to utilize this function of textures to reduce the adhesion between a drill and a workpiece. In this study, rectangular surface textures were generated on the margins of drill bits using a diode-pumped Nd:YVO4 picosecond laser with a wavelength of 532 nm. Two designs were created in which the textures covered approximately 10 and 20 % of the margin surface area. Textured drills were tested by drilling a series of holes in a titanium plate while recording cutting forces, and the results were compared with the performance of baseline samples. Thermographic heat profiles and visual inspections of the drills were taken at increments of 5 and 10–15 holes, respectively. The comparison demonstrated an encouraging improvement in drill bit life as judged by the number of holes drilled before failure. Textured drills were found to reduce adhesion of titanium chips on the drill margins. This work has demonstrated the potential of texturing to significantly improve the lifetime of drill bits and similar cutting tools.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, X., Kato, K., Adachi, K., Aizawa, K.: The effect of laser texturing of SiC surface on the critical load for the transition of water lubrication mode from hydrodynamic to mixed. Tribol. Int. 34(10), 703–711 (2001)
Etsion, I., Halperin, G., Brizmer, V., Kligerman, Y.: Experimental investigation of laser surface textured parallel thrust bearings. Tribol. Lett. 17(2), 295–300 (2004)
Lu, X., Khonsari, M.M.: An experimental investigation of dimple effect on the stribeck curve of journal bearings. Tribol. Lett. 27(2), 169–176 (2007)
Tian, H., Saka, N., Suh, N.: Boundary lubrication studies on undulated titanium surfaces. Tribol. Trans. 32(3), 289–296 (1988)
Wakuda, M., Yamauchi, Y., Kanzaki, S., Yasuda, Y.: Effect of surface texturing on friction reduction between ceramic and steel materials under lubricated sliding contact. Wear 254(3–4), 356–363 (2003)
Geiger, M., Popp, U., Engel, U.: Excimer laser micro texturing of cold forging tool surfaces—influence on tool life. Cirp. Ann. Manuf. Technol. 51(1), 231–234 (2002)
Etsion, I.: State of the art in laser surface texturing. J. Tribol. 127(1), 248–253 (2005)
Pettersson, U., Jacobson, S.: Influence of surface texture on boundary lubricated sliding contacts. Tribol. Int. 36(11), 857–864 (2003)
Etsion, I., Halperin, G.: A laser surface textured hydrostatic mechanical seal. Tribol. Trans. 45(3), 430–434 (2002)
Kovalchenko, A., Ajayi, O., Erdemir, A., Fenske, G., Etsion, I.: The effect of laser surface texturing on transitions in lubrication regimes during unidirectional sliding contact. Tribol. Int. 38(3), 219–225 (2005)
Wang, Q.J., Zhu, D., Zhou, R., Hashimoto, F.: Investigating the effect of surface finish on mixed EHL in rolling and rolling-sliding contacts. Tribol. Trans. 51(6), 748–761 (2008)
Nanbu, T., Ren, N., Yasuda, Y., Zhu, D., Wang, Q.J.: Micro-textures in concentrated conformal-contact lubrication: effects of texture bottom shape and surface relative motion. Tribol. Lett. 29(3), 241–252 (2008)
Ren, N., Nanbu, T., Yasuda, Y., Zhu, D., Wang, Q.: Micro textures in concentrated-conformal-contact lubrication: effect of distribution patterns. Tribol. Lett. 28(3), 275–285 (2007)
Tala-Ighil, N., Fillon, M., Maspeyrot, P.: Effect of textured area on the performances of a hydrodynamic journal bearing. Tribol. Int. 44(3), 211–219 (2011)
Shinkarenko, A., Kligerman, Y., Etsion, I.: The effect of surface texturing in soft elasto-hydrodynamic lubrication. Tribol. Int. 42(2), 284–292 (2009)
Ausas, R., Ragot, P., Leiva, J., Jai, M., Bayada, G., Buscaglia, G.C.: The impact of the cavitation model in the analysis of microtextured lubricated journal bearings. J. Tribol. 129(4), 868–875 (2007)
de Kraker, A., van Ostayen, R.A.J., van Beek, A., Rixen, D.J.: A multiscale method modeling surface texture effects. J. Tribol. 129(2), 221–230 (2007)
Sahlin, F., Glavatskih, S.B., Almqvist, T., Larsson, R.: Two-dimensional CFD-analysis of micro-patterned surfaces in hydrodynamic lubrication. J. Tribol. 127(1), 96–102 (2005)
Kawasegi, N., Sugimori, H., Morimoto, H., Morita, N., Hori, I.: Drilling aluminum alloy using small-diameter drills with micro/nanometer-scale textures. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. Part C 76(762), 446–452 (2010)
Sugihara, T., Enomoto, T.: Development of a cutting tool with a nano/micro-textured surface—improvement of anti-adhesive effect by considering the texture patterns. Precis. Eng. 33(4), 425–429 (2009)
Lei, S.T., Devarajan, S., Chang, Z.H.: A study of micropool lubricated cutting tool in machining of mild steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209(3), 1612–1620 (2009)
Neves, D., Diniz, A.E., de Lima, M.S.: Efficiency of the laser texturing on the adhesion of the coated twist drills. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 179(1–3), 139–145 (2006)
Davis, T., Zhou, R., Pallav, K., Beltran, M., Cao, J., Ehmann, K., Wang, Q.J., Xia, C., Talwar, R., Lederich, R.: Experimental friction study of micro-scale laser-textured surfaces. Paper presented at the international workshop on microfactories, Evanston, IL (2009)
Nolte, S., Momma, C., Jacobs, H., Tunnermann, A., Chickov, B.N., Wellegehausen, B., Welling, H.: Ablation of metals by ultrashort laser pulses. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 14(10), 2716–2722 (1997)
Dausinger, F., Hugel, H., Konov, V.I.: Micro-machining with ultrashort laser pulses: from basic understanding to technical applications. In: Heinz P. Weber, Thomas Graf , V.I.K. (eds.) ALT’02 international conference on advanced laser technologies, pp. 106–115, Bellingham WA (2003). SPIE
Nedialkov, N.N., Imamova, S.E., Atanasov, P.A.: Ablation of metals by ultrashort laser pulses. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 37, 638–643 (2004)
Breitling, D., Ruf, A., Dausinger, F.: Fundamental aspects in machining of metals with short and ultrashort laser pulses. In: Photon processing in microelectronics and photonics III, pp. 49–63. San Jose, CA, (2004). SPIE
Ostendorf, A., Kulik, C., Bauer, T., Baersch, N.: Ablation of metals and semiconductors with ultrashort pulsed lasers: improving surface qualities of microcuts and grooves. In: Commercial and biomedical applications of ultrafast lasers IV, pp. 153–163, San Jose, CA (2004). SPIE
Le Harzic, R., Breitling, D., Sommer, S., Fohl, C., Valette, S., Konig, K., Dausinger, F., Audouard, E.: Pulse duration and energy density influence on laser processing of metals with short and ultrashort pulses. In: Photon Processing in microelectronics and photonics IV, pp. 153–163, San Jose, CA (2005), pp. 115-122. SPIE
Hu, W.Q., Shin, Y.C., King, G.B.: Micromachining of metals, alloys, and ceramics by picosecond laser ablation. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME 132(1), 11009–11015 (2010)
Davis, T., Cao, J.: Effect of laser pulse overlap on machined depth. Trans. NAMRI/SME 38, 291–298 (2010)
Meng, F., Zhou, R., Davis, T., Cao, J., Wang, Q.J., Hua, D., Liu, J.: Study on effect of dimples on friction of parallel surfaces under different sliding conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256(9), 2863–2875 (2010)
Zhu, D., Nanbu, N., Ren, N., Yasuda, Y., Wang, Q.: Model-based virtual surface texturing for concentrated conformal-contact lubrication. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J: J. Eng. Tribol. 224(8), 685–696 (2010)
Wang, Q.J., Zhu, D.: Virtual texturing: modeling the performance of lubricated contacts of engineered surfaces. J. Tribol. 127(4), 722–728 (2005)
Xiong, S., Jane Wang, Q.: Steady-state hydrodynamic lubrication modeled with the Payvar–Salant mass conservation model. J. Tribol. 134(3), 031703 (2012)
Payvar, P., Salant, R.F.: A computational method for cavitation in a wavy mechanical seal. J. Tribol. 114(1), 199–204 (1992)
Acknowledgments
Financial support from Ford Motor Company, the Boeing Company, National Science Foundation CMMI-0619284, and the Graduate Research Fellowship Award are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, T.D., Liu, P., Xiong, S. et al. Surface Texturing of Drill Bits for Adhesion Reduction and Tool Life Enhancement. Tribol Lett 52, 113–122 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-013-0198-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-013-0198-7