Abstract
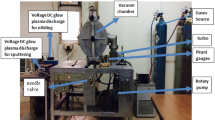
Tribological properties of TiO2 coatings synthesized by micro-arc oxidation (MAO) on the surface of TC4 titanium alloys were investigated at the fretting contact against 440C stainless steel in simulated body fluid (SBF). Fretting experiments were carried out by ball-on-flat contact at various loads for 1 h, with an amplitude of 100 μm and a frequency of 5 Hz. Results show that MAO TiO2 coatings presented good tribological properties with lower friction coefficient in SBF. Less wear volume was observed for MAO TiO2 coatings compared with that for TC4 alloy. At lower load, the wear mechanism of MAO TiO2 coatings was dominated to abrasive wear. With an increase of normal load, however, fretting corrosion increased due to chemical reactions with SBF, and therefore, fretting fatigue coexisting with abrasive wear became the predominant mode.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iwabuchi, A., Lee, J.W., Uchidate, M.: Synergistic effect of fretting wear and sliding wear of Co-alloy and Ti-alloy in Hanks’ solution. Wear 263, 492–500 (2007)
Matsuno, H., Yokoyama, A., Watari, F., Uo, M., Kawasaki, T.: Biocompatibility and osteogenesis of refractory metal implants, titanium, hafnium, niobium, tantalum and rhenium. Biomaterials 22, 1253–1262 (2001)
Khan, M.A., Williams, R.L., Williams, D.F.: Conjoint corrosion and wear in titanium alloys. Biomaterials 20, 765–772 (1999)
Willert, H.G., Semlitsch, M.: Reactions of the articular capsule to wear products of artificial joint prostheses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 11, 157–164 (1977)
Brown, S.A., Merritt, K.: Fretting corrosion in saline and serum. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 15, 479–488 (1981)
Langkamer, V.G., Case, C.P., Watt, I., Palmer, M., Atkins, R.M.: Aggressive wear-debris pseudotumor following total hip replacement. Orthopedics 22, 353–355 (1999)
Uo, M., Watari, F., Yokoyama, A., Matsuno, H., Kawasaki, T.: Visualization and detectability of elements rarely contained in soft tissue by X-ray scanning analytical microscopy and electron-probe micro analysis. Biomaterials 22, 1787–1794 (2001)
Liu, X.Y., Chu, P.K., Ding, C.X.: Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Mat. Sci. Eng. R 47, 49–121 (2004)
Choubey, A., Basu, B., Balasubramaniam, R.: Tribological behaviour of Ti-based alloys in simulated body fluid solution at fretting contacts. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 379, 234–239 (2004)
Bailey, L.O., Lipplatt, S., Biancanello, F.S., Ridder, S.D., Washburn, N.R.: The quantification of cellular viability and inflammatory response to stainless steel alloys. Biomaterials 26, 5296–5302 (2005)
Merritt, K., Brown, S.A.: Metal sensitivity reactions to orthopedic implants. Int. J. Dermatol. 20, 89–94 (1981)
Schuh, A., Thomas, P., Kachler, W., Goske, J., Wagner, L., Holzwarth, U., Forst, R.: Allergic potential of titanium implants. Orthopade 34, 327–333 (2005)
Ning, C.Q., Zhou, Y.: In vitro bioactivity of a biocomposite fabricated from HA and Ti powders by powder metallurgy method. Biomaterials 23, 2909–2915 (2002)
Karanjai, M., Kumar, B.V.M., Sundaresan, R., Basu, B., Mohan, T.R.R., Kashyap, B.P.: Fretting wear study on Ti-Ca-P biocomposite in dry and simulated body fluid. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 475, 299–307 (2008)
Navaneethakrishnan, P., Raman, S.G.S., Pathak, S.D., Gnanamoorthy, R., Ravi, N.: Fretting wear studies on diamond-like carbon coated Ti-6Al-4 V. Surf. Coat. Technol. 203, 1205–1212 (2009)
Budzynski, P., Youssef, A.A., Sielanko, J.: Surface modification of Ti-6Al-4V alloy by nitrogen ion implantation. Wear 261, 1271–1276 (2006)
Dong, Q., Chen, C.Z., Wang, D.G., Ji, Q.M.: Research status about surface modification of biomedical Ti and its alloys by micro-arc oxidation. Surf. Rev. Lett. 13, 35–43 (2006)
Lee, Y.K.: Effects of electrical parameters on titania film grown by micro-arc oxidation. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 23, 2035–2040 (2009)
Santos, A., Lidizio, L.R., Cruz, T.S., Sena, L.A., Damasceno, C.J., Achete, A.C.: Influence of electrolyte composition and time deposition on TiO2 films produced by micro-arc oxidation. Key Eng. Mater. 396–398, 349–352 (2009)
Jiang, Z.H., Sun, X.T., Li, Y.P., Wang, F.P., Lu, Y.D.: Effect of the oxidation time on properties of ceramic coatings produced on Ti-6Al-4V by micro-arc oxidation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 21, 281–284 (2005)
Li, Y., Lee, I.S., Cui, F.Z., Choi, S.H.: The biocompatibility of nanostructured calcium phosphate coated on micro-arc oxidized titanium. Biomaterials 29, 2025–2032 (2008)
Yu, S.R., Yang, X.Z., Yang, L., Liu, Y.H., Yu, Y.J.: Novel technique for preparing Ca- and P-containing ceramic coating on Ti-6Al-4V by micro-arc oxidation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 83B, 623–627 (2007)
Wang, Y.M., Zhang, P.F., Guo, L.X., Ouyang, J.H., Zhou, Y., Jia, D.C.: Effect of microarc oxidation coating on fatigue performance of Ti-Al-Zr alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 8616–8623 (2009)
Sun, X.T., Jiang, Z.H., Xin, S.G., Yao, Z.P.: Composition and mechanical properties of hard ceramic coating containing alpha-Al2O3 produced by microarc oxidation on Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Thin Solid Films 471, 194–199 (2005)
Guo, B.G., Liang, J., Tian, J., Liu, H.W., Xu, T.: Structure and composition of surface and interface of micro-arc oxide ceramic layer on Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 34, 1897–1900 (2005)
Wei, Z.S., Wang, M., Zhang, M., Ding, W.J.: Study on fretting fatigue behavior of TC4 titanium alloy. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 35, 1050–1052 (2006)
Merhej, R., Fouvry, S.: Contact size effect on fretting wear behavior: application to an AISI 52100/AISI 52100 interface. Lubr. Sci. 21, 83–102 (2009)
Johnson, L.: Contact Mechanics, pp. 50–55. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1989)
Zhou, G.H., Zhang, Y., Ding, H.Y.: Negative synergism between corrosion and wear of Nickel-free austenitic stainless steel in artificial body solution. Mater. Sci. Forum 610–613, 1183–1187 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Jiangsu Province Friction of Materials Key Laboratory under Grant No. 07kjmcx003. The authors would like to acknowledge Mr. Li Dong for his assistance on SEM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, G., Ding, H., Zhang, Y. et al. Fretting Wear Study on Micro-Arc Oxidation TiO2 Coating on TC4 Titanium Alloys in Simulated Body Fluid. Tribol Lett 40, 319–326 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-010-9665-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-010-9665-6