Abstract
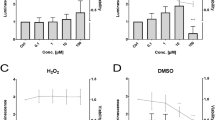
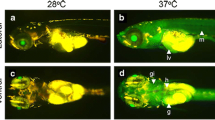
We report a transgenic zebrafish (Danio rerio) designed to respond to heavy metals using a metal-responsive promoter linked to a fluorescent reporter gene (DsRed2). The metallothionein MT-Ia1 promoter containing metal-responsive elements was derived from the Asian green mussel, Perna viridis. The promoter is known to be induced by a broad spectrum of heavy metals. The promoter-reporter cassette cloned into the Tol2 transposon vector was microinjected into zebrafish embryos that were then reared to maturity. A transgene integration rate of 28 % was observed. The confirmed transgenics were mated with wild-type counterparts, and pools of F1 embryos were exposed to sub-lethal doses of Cd2+, Cu2+, Hg2+, Pb2+ and Zn2+. The red fluorescence response of zebrafish embryos was observed 8 h post- exposure to these sub-lethal doses of heavy metals using a fluorescence microscope. Reporter expression estimated by real-time PCR revealed eightfold, sixfold and twofold increase on exposure to highest concentrations of Hg2+, Cd2+ and Cu2+, while Pb2+ and Zn2+ had no effect. This biosensor could be a first-level screening method for confirming aquatic heavy metal bio-toxicity to eukaryotes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida DV, Vaz B, Figueiredo MA, Junior ASV, Marins LF (2014) Fluorescent transgenic zebrafish as a biosensor for growth-related effects of methyl parathion. Aquat Toxicol 152:147151
Baird GS, Zacharias DA, Tsien RY (2000) Biochemistry, mutagenesis, and oligomerization of DsRED, a red fluorescent protein from coral. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11984–11989
Balciunas D, Wangensteen KJ, Wilber A, Bell J, Geurts A, Sivasubbu S, Wang X, Hackett PB, Largaespada DA, Mclvor RS, Ekker SC (2006) Harnessing a high cargo-capacity transposon for genetic applications in vertebrates. PLoS Genet 2(11):e169. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0020169
Bevis BJ, Glick BS (2002) Rapidly maturing variants of the Discosoma red fluorescent protein (DsRed). Nat Biotechnol 20(1):83–87
Blechinger SR, Warren JT Jr, Kuwada JY, Krone PH (2002) Developmental toxicology of cadmium in living embryos of a stable transgenic zebrafish line. Environ Health Perspect 110(10):1041–1046
Breuil P, Di Benedetto D, Poyet JP (1998) On-line analysis of copper and zinc in industrial effluents by UV-visible spectrometry (in French). Analusis 26(8):63–66
Carvan MJ, Dalton TP, Stuart GW, Nebert DW (2000) Transgenic zebrafish as sentinels for aquatic pollution. Ann N Y Acad Sci 919(1):133–147
Chen WY, John JA, Lin CH, Lin HF, Wu SC, Lin CH, Chang CY (2004) Expression of metallothionein gene during embryonic and early larval development in zebrafish. Aquat Toxicol 69(3):215–227
Chen H, Hu J, Yang J, Wang Y, Xu H, Jiang Q, Gong Y, Gu Y, Song H (2010) Generation of a fluorescent transgenic zebrafish for detection of environmental estrogens. Aquat Toxicol 96(1):53–61
Cheng X, Chen X, Jin X, He J, Yin Z (2014) Generation and characterization of gsuα: EGFP transgenic zebrafish for evaluating endocrine-disrupting effects. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 278(1):78–84
Cioci LK, Qiu L, Freedman JH (2000) Transgenic strains of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans as biomonitors of metal contamination. Environ Toxicol Chem 19(8):2122–2129
Clay H, Ramakrishnan L (2005) Multiplex fluorescent in situ hybridization in zebrafish embryos using tyramide signal amplification. Zebrafish 2(2):105–111
Detrich HW, Westerfield M, Zon LI (1998) Overview of the zebrafish system. Method Cell Biol 59:3–10
Driever W, Stemple D, Schier A, Solnica-Krezel L (1994) Zebrafish: genetic tools for studying vertebrate development. Trends Genet 10(5):152–159
Fujimura K, Kocher TD (2011) Tol2-mediated transgenesis in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 319(3):342–346
Gireesh-Babu P, Pawar N, Krishnan P, Kumar AP, Zaidi SGS, Bhartiya D, Kumar N, Sivasubbu S, Rajendran KV, Chaudhari A (2012) Functional characterization of the zebrafish gadd45αb gene promoter and its application as a biosensor. Curr Sci 103(4):388–394
Gutierrez JC, Amaro F, Martín-Gonzalez A (2015) Heavy metal whole-cell biosensors using eukaryotic microorganisms: an updated critical review. Front Microbiol 6:1–8
Jarup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68(1):167–182
Ji C, Jin X, He J, Yin Z (2012) Use of TSHβ: EGFP transgenic zebrafish as a rapid in vivo model for assessing thyroid-disrupting chemicals. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 262(2):149–155
Kawakami K (2007) Tol2: a versatile gene transfer vector in vertebrates. Genome Biol. doi:10.1186/gb-2007-8-S1-S7
Kawakami K, Koga A, Hori H, Shima A (1998) Excision of the Tol2 transposable element of the medaka fish, Oryzias latipes, in zebrafish, Danio rerio. Gene 225(1):17–22
Khoo HW, Patel KH (1999) Metallothionein cDNA, promoter, and genomic sequences of the tropical green mussel, Perna viridis. J Exp Zool 284(4):445–453
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF (1995) Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 203(3):253–310
Kusik BW, Carvan MJ III, Udvadia AJ (2008) Detection of mercury in aquatic environments using EPRE reporter zebrafish. Mar Biotechnol 10(6):750–757
Lagido C, Pettitt J, Porter AJR, Paton GI, Glover LA (2001) Development and application of bioluminescent Caenorhabditis elegans as multicellular eukaryotic biosensors. FEBS Lett 493(1):36–39
Lee HC, Chen YJ, Liu YW, Lin KY, Chen SW, Lin CY, Lu YC, Hsu PC, Lee SC, Tsai HJ (2011) Transgenic zebrafish model to study translational control mediated by upstream open reading frame of human chop gene. Nucleic Acids Res 39(20):e139. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr645
Lee O, Takesono A, Tada M, Tyler CR, Kudoh T (2012a) Biosensor zebrafish provide new insights into potential health effects of environmental estrogens. Environ Health Perspect 120(7):990–996
Lee O, Tyler CR, Kudoh T (2012b) Development of a transient expression assay for detecting environmental oestrogens in zebrafish and medaka embryos. BMC Biotechnol 12(1):32. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-12-32
Lee HC, Lu PN, Huang HL, Chu C, Li HP, Tsai HJ (2014) Zebrafish Transgenic line huORFZ is an effective living bioindicator for detecting environmental toxicants. PLoS ONE 9(3):e90160. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090160
Lele Z, Krone P (1996) The zebrafish as a model system in developmental, toxicological and transgenic research. Biotechnol Adv 14(1):57–72
Liu L, Yan Y, Wang J, Wu W, Xu L (2016) Generation of mt:egfp transgenic zebrafish biosensor for the detection of aquatic zinc and cadmium. Environ Toxicol Chem. doi:10.1002/etc.3362
Ma H, Glenn TC, Jagoe CH, Jones KL, Williams PL (2009) A transgenic strain of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans as a biomonitor for heavy metal contamination. Environ Toxicol Chem 28(6):1311–1318
Mattingly CJ, McLachlan JA, Toscano WA (2001) Green fluorescent protein (GFP) as a marker of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) function in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Health Perspect 109(8):845–849
Misra S, Zafarullah M, Price-Haughey J, Gedamu L (1989) Analysis of stress-induced gene expression in fish cell lines exposed to heavy metals and heat shock. BBA-Gene Struct Expr 1007(3):325–333
OECD (1992) OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. Test No. 203: Fish, Acute Toxicity Test, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris
Park JD, Liu Y, Klaassen CD (2001) Protective effect of metallothionein against the toxicity of cadmium and other metals. Toxicology 163(2):93–100
Putri LSE, Prasetyo AD, Arifin Z (2012) Green mussel (Perna viridis L.) as bioindicator of heavy metals pollution at Kamal estuary, Jakarta Bay, Indonesia. J Environ Res Dev 6(3):389–396
Raja CE, Selvam GS (2011) Construction of green fluorescent protein based bacterial biosensor for heavy metal remediation. Int J Environ Sci Technol 8(4):793–798
Roberto FF, Barnes JM, Bruhn DF (2002) Evaluation of a GFP reporter gene construct for environmental arsenic detection. Talanta 58(1):181–188
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108
Seok SH, Park JH, Baek MW, Lee HY, Kim DJ, Uhm HM, Park JH (2006) Specific activation of the human HSP70 promoter by copper sulfate in mosaic transgenic zebrafish. J Biotechnol 126(3):406–413
Seok SH, Baek MW, Lee HY, Kim DJ, Na YR, Noh KJ, Park SH, Lee HK, Lee BH, Ryu DY, Park JH (2007) Quantitative GFP fluorescence as an indicator of arsenite developmental toxicity in mosaic heat shock protein 70 transgenic zebrafish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 225(2):154–161
Stephanou A, Latchman DS (2011) Transcriptional modulation of heat-shock protein gene expression. Biochem Res Int 2011:1–8. doi:10.1155/2011/238601
Sun L, Xu W, He J, Yin Z (2010) In vivo alternative assessment of the chemicals that interfere with anterior pituitary POMC expression and interrenal steroidogenesis in POMC:EGFP transgenic zebrafish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 248:217–225
The Environmental (Protection) Rules (1986) Ministry of Environment and Forests, India. www.cpcb.nic.in/GeneralStandards.pdf
Tiemann KJ, Gardea-Torresdey JL, Gamez G, Dokken K, Sias S, Renner MW, Furenlid NR (1999) Use of X-ray absorption spectroscopy and esterification to investigate Cr(III) and Ni(II) ligands in alfalfa biomass. Environ Sci Technol 33(1):150–154
Townsend AT, Miller KA, McLean S, Aldous S (1998) The determination of copper, zinc, cadmium and lead in urine by high resolution ICP-MS. J Anal At Spectrom 13(11):1213–1219
Urasaki A, Morvan G, Kawakami K (2006) Functional dissection of the Tol2 transposable element identified the minimal cis-sequence and a highly repetitive sequence in the subterminal region essential for transposition. Genetics 174(2):639–649
Verma N, Singh M (2005) Biosensors for heavy metals. Biometals 18(2):121–129
Viarengo A (1989) Heavy metals in marine invertebrates: mechanisms of regulation and toxicity at the cellular level. Rev Aquat Sci 1(2):295–317
Wan H, Korzh S, Li Z, Mudumana SP, Korzh V, Jiang YJ, Lin S, Gong Z (2006) Analyses of pancreas development by generation of gfp transgenic zebrafish using an exocrine pancreas-specific elastaseA gene promoter. Exp Cell Res 312:1526–1539
Westerfield M (2000) The Zebrafish Book: A guide for the laboratory use of zebrafish (Danio rerio), 4th edn. Univ. of Oregon Press, Eugene
Wu YL, Pan X, Mudumana SP, Wang H, Kee PW, Gong Z (2008) Development of a heat shock inducible gfp transgenic zebrafish line by using the zebrafish hsp27 promoter. Gene 408(1):85–94
Zou J, Beermann F, Wang J, Kawakami K, Wei X (2006) The Fugu tyrp1 promoter directs specific GFP expression in zebrafish: tools to study the RPE and the neural crest-derived melanophores. Pigment Cell Res 19(6):615–627
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi for funding this research project; Dr. Dilip Kumar and Dr. W. S. Lakra, former Directors, ICAR-CIFE, Mumbai and Dr. Gopal Krishna, Director, ICAR-CIFE, Mumbai for providing facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pawar, N., Gireesh-Babu, P., Sabnis, S. et al. Development of a fluorescent transgenic zebrafish biosensor for sensing aquatic heavy metal pollution. Transgenic Res 25, 617–627 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-016-9959-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-016-9959-z