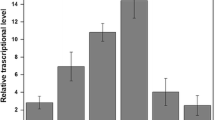
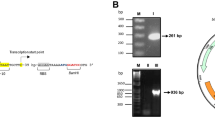
Abstract
Environmental contamination by heavy metals is a worldwide problem. Therefore, it is necessary to develop sensitive, effective and inexpensive methods, which can efficiently monitor and determine the level of hazardous metals in the environment. Conventional techniques to analyze metals, suffer from the disadvantages of high cost. Alternatively, development of simple system for monitoring heavy metals pollution is therefore needed. The present approach is based on the use of bacteria that are genetically engineered so that a measurable signal is produced when the bacteria are in contact with the bioavailable metal ions. Reporter genes are widely used as genetic tools for quantification and detection of specific cell population, gene expression and constructing whole cell biosensors as specific and sensitive devices for measuring biologically relevant concentrations of pollutants. An attempt has been made to construct the reporter gene enhanced green fluorescent protein and was expressed under the control of cadR gene, responsible for cadmium resistance. Recombinant strain Escherichia coli cadR30 was used, that carried cadR gene in pET30b expression vector and cloned. Clones confirmed by the expression of enhanced green fluorescent protein was detected under ultraviolet illumination and separated on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The construction of green fluorescent protein based Escherichia coli bacterial biosensor was developed based on green fluorescent protein expression under the control cadR gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa BC15. The constructed bacterial biosensor is useful and applicable in determining the availability of heavy metals in soil and wastewater.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreazza, R.; Pieniz, S.; Wolf, L.; Lee, M.; Camargo, F. A. O.; Okeke, B. C., (2010). Characterization of copper bioreduction and biosorption by a highly copper resistant bacterium isolated from copper-contaminated vineyard soil. Sci. Total Environ., 408(1), 1501–1507 (7 pages).
APHA; AWWA; WEF, (1992). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 18th edition. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and the Water Environment Federation. Washington DC., USA.
Barker, L. P.; Brooks, D. M.; Small, P. L. C., (1998). The identification of Mycobacterium marinum genes differentially expressed in macrophage phagosomes using promoter fusions to green fluorescent protein. Molecular Microbiol., 29(5), 1167–1177 (11 pages).
Barros, F. C. F.; Sousa, F. W.; Cavalcante, R. M.; Carvalho, T. V.; Dias, F. S.; Queiroz, D. C.; Vasconcellos, L. C. G.; Nascimento, R. F., (2008). Removal of copper, nickel and zinc ions from aqueous solution by chitosan-8-hydroxyquinoline beads. Clean., 36(3), 292–298 (7 pages).
Casper, S.; Holt, C., (1996). Expression of the green fluorescent protein-encoding gene from a tobacco mosaic virus-based vector. Gene., 173(1), 69–73 (5 pages).
Cassidy, M. B.; Leung, K. T.; Lee, H.; Trevors, J. T., (2000). A comparison of enumeration methods for culturable Pseudomonas fluorescens cells marked with green fluorescent protein. J. Microbiol. Mtds., 40(2), 135–145 (11 pages).
Chakraborty, P.; Babu, G.; Alam, A.; Chaudhari, A., (2008). GFP expressing bacterial biosensor to measure lead contamination in aquatic environment. Curr. Sci., 94(6), 800–805 (6 pages).
Chalfie, M.; Tu, Y.; Euskirchen, G.; Ward, W. W.; Prasher, D. C., (1994). Green fluorescent protein as marker for gene expression. Sci., 263(5148), 802–805 (4 pages).
Chien, M. K.; Shih, L. H., (2007). An empirical study of the implementation of green supply chain management practices in the electrical and electronic industry and their relation to organizational performances. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(3), 383–394 (12 pages).
D’Souza, S. F., (2001). Microbial biosensors. Biosen. Bioelec., 16(6), 337–353 (17 pages).
Edward Raja, C.; Selvam, G. S., (2009). Plasmid profile and curing analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as metal resistant. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(2), 259–266 (8 pages).
Giaginis, C.; Gatzidou, E.; Theocharis, S., (2006). DNA repair systems as targets of cadmium toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 213(3), 282–290 (9 pages).
Gronow, M., (1984). Biosensors. Trends Biochem. Sci., 9(8), 336–340 (5 pages).
Gu, M. B.; Mitchell, R. J.; Kim, B. C., (2004). Whole-cell-based biosensors for environmental biomonitoring and application. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotech., 87, 269–305 (37 pages).
Gueu, S.; Yao, B.; Adouby, K.; Ado, G., (2007). Kinetics and thermodynamics study of lead adsorption on to activated carbons from coconut and seed hull of the palm tree. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(1), 11–17 (7 pages).
Il’yasova, D.; Schwartz, G. G., (2005). Cadmium and renal cancer. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 207(2), 179–186 (8 pages).
Ivask, A.; Hakkila, K.; Virta, M., (2001). Detection of organomercurials with sensor bacteria. Analys. Chem., 73(21), 5168–5171 (4 pages).
Karbassi, A. R.; Nouri, J.; Mehrdadi, N.; Ayaz, G. O., (2008). Flocculation of heavy metals during mixing of freshwater with Caspian Sea water. Environ. Geo., 53(8), 1811–1816 (6 pages).
Kopera, E.; Schwerdtle, T.; Hartwig, A.; Bal, W., (2004). Co (II) and Cd (II) substitute for Zn (II) in the zincfinger derived from the DNA repair protein XPA, demonstrating a variety of potential mechanisms of toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol., 17(11), 1452–1458 (7 pages).
Laemmli, U. K., (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685 (6 pages).
Liao, V. H. C.; Chien, M. T.; Tseng, Y. T.; Ou, K. L., (2006). Assessment of heavy metal bioavailability in contaminated sediments and soils using green fluorescent protein based bacterial biosensors. Environ. Poll., 142(1), 17–23 (7 pages).
Liu, J.; Olsson, G.; Mattiasson, B., (2004). Short-term BOD (BODst) as a parameter for on-line monitoring of biological treatment process Part I. A novel design of BOD biosensor for easy renewal of bio-receptor. Biosen. Bioelect., 20(3), 562–570 (9 pages).
Ludin, B.; Doll, T.; Meill, R.; Kaech, S.; Matus, A., (1996). Application of novel vectors for GFP-tagging of proteins to study microtubule-associated proteins. Gene., 173(1), 107–111 (5 pages).
Malakootian, M.; Nouri, J.; Hossaini, H., (2009). Removal of heavy metals from paint industries wastewater using Leca as an available adsorbent. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 6(2), 183–190 (8 pages).
Moss, J. B.; Price, A. L.; Raz, E.; Driever, W.; Rosenthal, N., (1996). Green fluorescent protein marks skeletal muscle in murine cell lines and zebrafish. Gene., 173(1), 89–98 (10 pages).
Mulchandani, A.; Bassi, A. S., (1995). Principles and application of biosensors for bioprocess monitoring and control. Crit. Rev. Biotech., 15(2), 105–124 (20 pages).
Niedenthal, R. K.; Riles, L.; Johnston, M.; Hegemann, J. H., (1996). Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression and subcellular localization in budding yeast. Yeast., 12(8), 773–786 (14 pages).
Nouri, J.; Khorasani, N.; Lorestani, B.; Karami; M. Hassani; Hassani, A. H.; Yousefi, N., (2009). Accumulation of heavy metals in soil and uptake by plant species with phytoremediation potential. Environ. Earth Sci., 59(2); 315–323 (9 pages).
Nouri, J.; Lorestani, B.; Yousefi, N.; Khorasani, N.; Hasani, A. H.; Seif, S.; Cheraghi, M., (2011). Phytoremediation potential of native plants grown in the vicinity of Ahangaran lead-zinc mine (Hamedan, Iran). Environ. Earth Sci., 62(3), 639–644 (6 pages).
Prachayasittikul, V.; Isarankura Na Ayudhaya, C.; Bulow, L., (2001). Lighting E. coli cells as biological sensors for Cd. Biotech. Let., 23(16), 1285–1291 (7 pages).
Roberto, F.; Barnes, J.; Bruhn, D., (2002). Evaluation of a GFP reporter gene construct for environmental arsenic detection. Talanta, 58(1), 181–188 (8 pages).
Samarghandi, M. R.; Nouri, J.; Mesdaghinia, A. R.; Mahvi, A. H.; Nasseri, S.; Vaezi, F., (2007). Efficiency removal of phenol, lead and cadmium by means of UV/TiO2/H2O2 processes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4(1), 19–25 (7 pages).
Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E. F.; Maniatis, T., (). Molecular Cloning: A laboratory manual, 2nd Ed. Cold spring harbour, NY: Cold spring harbour laboratory press.
Selifonova, O.; Burlage, R.; Barkay, T., (1993). Bioluminescent sensors for detection of bioavailable Hg (II) in the environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 59(9), 3083–3090 (8 pages).
Shetty, R.; Ramanathan, S.; Badr, I.; Wolford, J.; Daunert, S., (1999). Green fluorescent protein in the design of a living biosensing system for L-arabinose. Analys. Chem., 71(4), 763–768 (6 pages).
Shetty, R. S.; Deo, S. K.; Shah, P.; Sun, P.; Rosen, B. P.; Daunert, S., (2003). Luminescence based whole cell sensing systems for cadmium and lead using genetically engineered bacteria. Analys. Bioanalys. Chem., 376(1), 11–17 (7 pages).
Stiner, L.; Halverson, L. J., (2002). Development and characterization of a green fluorescent protein based bacterial biosensor for bioavailable toluene and related compounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 68(4), 1962–1971 (10 pages).
Tauriainen, S.; Karp, M.; Chang, W.; Virta, M., (1998). Luminescent bacterial sensor for cadmium and lead. Biosen. Bioelect., 13(9), 931–938 (8 pages).
Townsend, A. T.; Miller, K. A.; Mclean, S.; Aldous, S., (1998). The determination of copper, zinc, cadmium and lead in urine by high resolution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Analys. Atom. Spect., 13, 1213–1219 (7 pages).
Vandeermeer, J. R.; Tropel, D.; Jaspers, M., (2004). Illuminating the detection chain of bacterial bioreporters. Environ. Microbiol., 6(10), 1005–1020 (16 pages).
Wang, S.; Hazelrigg, T., (1994). Implications for bcd mRNA localization from spatial distribution of exu protein in Drosophila oogenesis. Nature, 69, 400–403 (4 pages).
Willardson, M. B. B.; Wilkins, F. J.; Rand, A. T.; Schupp, M. J.; Hill, K. K.; Keim, P.; Jackson, J. P., (1998). Development and testing of a bacterial biosensor for toluene based environmental contaminants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 64(3), 1006–1012 (7 pages).
Yagi, K., (2007). Application of whole cell bacterial sensors in biotechnology and environmental science. Appl. Microbiol. Biotech., 73(6), 1251–1258 (8 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raja, C.E., Selvam, G.S. Construction of green fluorescent protein based bacterial biosensor for heavy metal remediation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 8, 793–798 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326262
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326262