Abstract
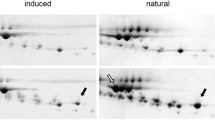
The expression of recombinant proteins of pharmaceutical interest in the milk of transgenic farm animals can result in phenotypes exhibiting compromised lactation performance, as a result of the extraordinary demand placed on the mammary gland. In this study, we investigated differences in the protein composition of milk from control and transgenic goats expressing recombinant human butyrylcholinesterase. In Experiment 1, the milk was characterized by gel electrophoresis and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry in order to identify protein bands that were uniquely visible in the transgenic milk and/or at differing band densities compared with controls. Differences in protein content were additionally evaluated by computer assisted band densitometry. Proteins identified in the transgenic milk only included serum proteins (i.e. complement component 3b, ceruloplasmin), a cytoskeleton protein (i.e. actin) and a stress-induced protein (94 kDA glucose-regulated protein). Proteins exhibiting evident differences in band density between the transgenic and control groups included immunoglobulins, serum albumin, β-lactoglobulin and α-lactalbumin. These results were found to be indicative of compromised epithelial tight junctions, premature mammary cell death, and protein synthesis stress resulting from transgene expression. In Experiment 2, the concentration of α-lactalbumin was determined using the IDRing® assay and was found to be significantly reduced on day 1 of lactation in transgenic goats (4.33 ± 0.97 vs. 2.24 ± 0.25 mg/ml, P < 0.01), but was not different from non-transgenic controls by day 30 (0.99 ± 0.46 vs. 0.90 ± 0.11 mg/ml, P > 0.05). We concluded that a decreased/delayed expression of the α-lactalbumin gene may be the cause for the delayed start of milk production observed in this herd of transgenic goats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldassarre H, Karatzas CN (2004) Advanced assisted reproduction technologies (ART) in goats. Anim Reprod Sci 82–83:255–266. doi:10.1016/j.anireprosci.2004.04.027
Baldassarre H, Wang B, Keefer CL, Lazaris A, Karatzas CN (2004) State of the art in the production of transgenic goats. Reprod Fertil Dev 16:465–470. doi:10.1071/RD04028
Baldassarre H, Rao KM, Neveu N, Brochu E, Begin I, Behboodi E, Hockley DK (2007) Laparoscopic ovum pick-up followed by in vitro embryo production for the reproductive rescue of aged goats of high genetic value. Reprod Fertil Dev 19:612–616. doi:10.1071/RD07024
Baldassarre H, Hockley DK, Dore M, Brochu E, Hakier B, Zhao X, Bordignon V (2008a) Lactation performance of transgenic goats expressing recombinant human butyryl-cholinesterase in the milk. Transgenic Res 17:73–84. doi:10.1007/s11248-007-9137-4
Baldassarre H, Hockley DK, Olaniyan B, Brochu E, Zhao X, Mustafa A, Bordignon V (2008b) Milk composition studies in transgenic goats expressing recombinant human butyrylcholinesterase in the mammary gland. Transgenic Res 17:863–872. doi:10.1007/s11248-008-9184-5
Blum H, Beier H, Gross H (1987) Improved silver staining of plant proteins, RNA and DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 8:93–99. doi:10.1002/elps.1150080203
Burdon T, Wall RJ, Shamay A, Smith GH, Hennighausen L (1991) Over-expression of an endogenous milk protein gene in transgenic mice is associated with impaired mammary alveolar development and a milchlos phenotype. Mech Dev 36:67–74. doi:10.1016/0925-4773(91)90073-F
Burdon TG, Demmer J, Clark AJ, Watson CJ (1994) The mammary factor MPBF is a prolactin-induced transcriptional regulator which binds to STAT factor recognition sites. FEBS Lett 350:177–182. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(94)00757-8
Cudna RE, Dickson AJ (2003) Endoplasmic reticulum signaling as a determinant of recombinant protein expression. Biotechnol Bioeng 81:56–65. doi:10.1002/bit.10445
Doctor BP, Saxena A (2005) Bioscavengers for the protection of humans against organophosphate toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 157–158:167–171. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2005.10.024
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Feather-Stone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Fox PF, McSweeney PLH (1998) Dairy chemistry and biochemistry. Blackie Academic & Professional, London
Fox PF, McSweeney PLH (2002) Advanced dairy chemistry. Plenum Publishing Co, United States
Houdebine LM (2009) Production of pharmaceutical proteins by transgenic animals. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 32(2):107–121
Huang YJ, Huang Y, Baldassarre H, Wang B, Lazaris A, Leduc M, Bilodeau AS, Bellemare A, Cote M, Herskovits P, Touati M, Turcotte C, Valeanu L, Lemee N, Wilgus H, Begin I, Bhatia B, Rao K, Neveu N, Brochu E, Pierson J, Hockley DK, Cerasoli DM, Lenz DE, Karatzas CN, Langermann S (2007) Recombinant human butyrylcholinesterase from milk of transgenic animals to protect against organophosphate poisoning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:13603–13608. doi:10.1073/pnas.0702756104
Keefer CL (2004) Production of bioproducts through the use of transgenic animal models. Anim Reprod Sci 82–83:5–12. doi:10.1016/j.anireprosci.2004.04.010
Koyasu S, Nishida E, Miyata Y, Sakai H, Yahara I (1989) HSP100, a 100-kDa heat shock protein, is a Ca2+-calmodulin-regulated actin-binding protein. J Biol Chem 264:15083–15087
Lenny N, Green M (1991) Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress proteins in COS cells transfected with immunoglobulin mu heavy chain cDNA. J Biol Chem 266:20532–20537
Levieux D, Morgan F, Geneix N, Masle I, Bouvier F (2002) Caprine immunoglobulin G, beta-lactoglobulin, alpha-lactalbumin and serum albumin in colostrum and milk during the early post partum period. J Dairy Res 69:391–399. doi:10.1017/S0022029902005575
Macario AJ, Conway de Macario E (2007a) Molecular chaperones: multiple functions, pathologies, and potential applications. Front Biosci 12:2588–2600. doi:10.2741/2257
Macario AJ, Conway de Macario E (2007b) Chaperonopathies and chaperonotherapy. FEBS Lett 581:3681–3688. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.04.030
McClenaghan M, Springbett A, Wallace RM, Wilde CJ, Clark AJ (1995) Secretory proteins compete for production in the mammary gland of transgenic mice. Biochem J 310(Pt 2):637–641
McFadden TB, Akers RM, Kazmer GW (1987) Alpha-lactalbumin in bovine serum: relationships with udder development and function. J Dairy Sci 70:259–264
Niemann H, Kues WA (2003) Application of transgenesis in livestock for agriculture and biomedicine. Anim Reprod Sci 79:291–317. doi:10.1016/S0378-4320(03)00169-6
Noble MS, Rodriguez-Zas S, Cook JB, Bleck GT, Hurley WL, Wheeler MB (2002) Lactational performance of first-parity transgenic gilts expressing bovine alpha-lactalbumin in their milk. J Anim Sci 80:1090–1096
Ogg SL, Weldon AK, Dobbie L, Smith AJ, Mather IH (2004) Expression of butyrophilin (Btn1a1) in lactating mammary gland is essential for the regulated secretion of milk-lipid droplets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:10084–10089. doi:10.1073/pnas.0402930101
Palmer CA, Lubon H, McManaman JL (2003) Transgenic mice expressing recombinant human protein C exhibit defects in lactation and impaired mammary gland development. Transgenic Res 12:283–292. doi:10.1023/A:1023398926763
Palmer CA, Neville MC, Anderson SM, McManaman JL (2006) Analysis of lactation defects in transgenic mice. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 11:269–282. doi:10.1007/s10911-006-9023-3
Schmidt A, Hall MN (1998) Signaling to the actin cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 14:305–338
Schroder M (2006) The unfolded protein response. Mol Biotechnol 34:279–290. doi:10.1385/MB:34:2:279
Schroder M (2008) Endoplasmic reticulum stress responses. Cell Mol Life Sci 65(6):862–894
Scriven P, Brown NJ, Pockley AG, Wyld L (2007) The unfolded protein response and cancer: a brighter future unfolding? J Mol Med 85:331–341. doi:10.1007/s00109-006-0150-5
Stacey A, Schnieke A, Kerr M, Scott A, McKee C, Cottingham I, Binas B, Wilde C, Colman A (1995) Lactation is disrupted by alpha-lactalbumin deficiency and can be restored by human alpha-lactalbumin gene replacement in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:2835–2839. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.7.2835
Vorbach C, Scriven A, Capecchi MR (2002) The housekeeping gene xanthine oxidoreductase is necessary for milk fat droplet enveloping and secretion: gene sharing in the lactating mammary gland. Genes Dev 16:3223–3235. doi:10.1101/gad.1032702
Watson CJ, Gordon KE, Robertson M, Clark AJ (1991) Interaction of DNA-binding proteins with a milk protein gene promoter in vitro: identification of a mammary gland-specific factor. Nucleic Acids Res 19:6603–6610. doi:10.1093/nar/19.23.6603
Wheeler MB, Walters EM, Clark SG (2003) Transgenic animals in biomedicine and agriculture: outlook for the future. Anim Reprod Sci 79:265–289. doi:10.1016/S0378-4320(03)00168-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldassarre, H., Schirm, M., Deslauriers, J. et al. Protein profile and alpha-lactalbumin concentration in the milk of standard and transgenic goats expressing recombinant human butyrylcholinesterase. Transgenic Res 18, 621–632 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-009-9254-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-009-9254-3