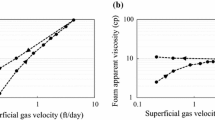
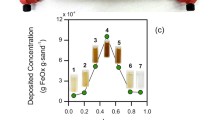
Abstract
Nano-remediation is a promising in situ remediation technology. It consists in injecting reactive nanoparticles (NPs) into the subsurface for the displacement or the degradation of contaminants. However, due to the poor mobility control of the reactive nanoparticle suspension, the application of nano-remediation has some major challenges, such as high mobility of the particles, which may favor override of the contamination, and particle aggregation, which can lead to a limited distance of influence. Previous experimental studies show the potential of combining nano-remediation with foam flooding to overcome these issues. However, in order to design and optimize the process, a model which couples nanoparticle and foam transport is necessary. In this paper, a mechanistic model to describe the transport of NPs with and by a foam is presented. The model considers the delivery of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) and accounts for the processes of aggregation, attachment/detachment, and generation/destruction. Simulations show that when NPs are dispersed in the liquid phase, even in the presence of a foam, they may travel much slower than the NPs carried by the foam bubbles. This is because the nanoparticles in suspension are affected by the attachment onto the rock walls and straining at the pore throats. When the nanoparticle surface is, instead, modified in order to favor their adsorption onto the gas bubbles, NPs are carried by the foam without retardation, except for the small fraction suspended in the liquid phase. Moreover, very stable high-quality foam (\(f_\mathrm{g}\)), i.e., 80–90 vol% of gas, can be attained using properly surface-modified nZVI (i.e., a nanoparticle-stabilized foam), allowing a significant reduction of water for the operation, while increasing the efficiency of nZVI delivery, even in a low-permeability medium within the shallow subsurface.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez, J., Rivas, H., Rossen, W.: A unified model for steady-state foam behavior at high and low foam qualities. In: IOR 1999-10th European Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery. Society of Petroleum Engineers (1999)
Apaydin, O.G., Kovscek, A.R.: Surfactant concentration and end effects on foam flow in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 43(3), 511–536 (2001)
Atmuri, A.K., Henson, M.A., Bhatia, S.R.: A population balance equation model to predict regimes of controlled nanoparticle aggregation. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 436, 325–332 (2013)
Attarakih, M.M., Bart, H.J., Faqir, N.M.: Numerical solution of the spatially distributed population balance equation describing the hydrodynamics of interacting liquid-liquid dispersions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 59(12), 2567–2592 (2004)
Aziz, K.: Petroleum reservoir simulation. Appl. Sci. Publ. (1979)
Azmin, M., Mohamedi, G., Edirisinghe, M., Stride, E.: Dissolution of coated microbubbles: the effect of nanoparticles and surfactant concentration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 32(8), 2654–2658 (2012)
Bayat, A.E., Junin, R., Shamshirband, S., Chong, W.T.: Transport and retention of engineered Al\(_2\) O\(_3\), TiO\(_2\), and SiO\(_2\) nanoparticles through various sedimentary rocks. Sci. Rep. 5 (2015)
Bernard, G.G., Jacobs, W.: Effect of foam on trapped gas saturation and on permeability of porous media to water. SPE J. 5(04), 295–300 (1965)
Binks, B.P.: Particles as surfactants similarities and differences. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 7(1–2), 21–41 (2002)
Binks, B.P., Kirkland, M., Rodrigues, J.A.: Origin of stabilisation of aqueous foams in nanoparticle–surfactant mixtures. Soft Matter 4(12), 2373–2382 (2008)
Bogush, G., Zukoski Iv, C.: Uniform silica particle precipitation: an aggregative growth model. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 142(1), 19–34 (1991)
Carn, F., Colin, A., Pitois, O., Vignes-Adler, M., Backov, R.: Foam drainage in the presence of nanoparticle–surfactant mixtures. Langmuir 25(14), 7847–7856 (2009)
Chang, Y.C., Chen, D.H.: Preparation and adsorption properties of monodisperse chitosan-bound Fe\(_3\)O\(_4\) magnetic nanoparticles for removal of cu (ii) ions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 283(2), 446–451 (2005)
Conn, C.A., Ma, K., Hirasaki, G.J., Biswal, S.L.: Visualizing oil displacement with foam in a microfluidic device with permeability contrast. Lab Chip 14(20), 3968–3977 (2014)
Das, B.M., Sobhan, K.: Principles of Geotechnical Engineering. Cengage Learning, Boston (2013)
de Vries, A.S., Wit, K.: Rheology of gas/water foam in the quality range relevant to steam foam. SPE Reserv. Eng. 5(02), 185–192 (1990)
Ding, Y., Liu, B., Shen, X., Zhong, L., Li, X.: Foam-assisted delivery of nanoscale zero valent iron in porous media. J. Environ. Eng. 139(9), 1206–1212 (2013)
Elimelech, M., Gregory, J., Jia, X.: Particle Deposition and Aggregation: Measurement, Modelling and Simulation. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2013)
Elimelech, M., O’Melia, C.R.: Kinetics of deposition of colloidal particles in porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 24(10), 1528–1536 (1990)
Espinoza, D.A., Caldelas, F.M., Johnston, K.P., Bryant, S.L., Huh, C.: Nanoparticle-stabilized supercritical CO\(_2\) foams for potential mobility control applications. In: SPE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium. Society of Petroleum Engineers (2010)
Falls, A., Hirasaki, G., Patzek, T.E.A., Gauglitz, D., Miller, D., Ratulowski, T.: Development of a mechanistic foam simulator: the population balance and generation by snap-off. SPE Reserv. Eng. 3(03), 884–892 (1988)
Gastone, F., Tosco, T., Sethi, R.: Guar gum solutions for improved delivery of iron particles in porous media (part 1): porous medium rheology and guar gum-induced clogging. J. Contam. Hydrol. 166, 23–33 (2014)
Gauglitz, P.A., Friedmann, F., Kam, S.I., Rossen, W.R.: Foam generation in homogeneous porous media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 57(19), 4037–4052 (2002)
Ghosh, S., Jiang, W., McClements, J.D., Xing, B.: Colloidal stability of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: influence of natural organic matter and synthetic polyelectrolytes. Langmuir 27(13), 8036–8043 (2011)
Hirasaki, G., Miller, C., Szafranski, R., Tanzil, D., Lawson, J., Meinardus, H., Jin, M., Londergan, J., Jackson, R., Pope, G., et al.: Field demonstration of the surfactant/foam process for aquifer remediation. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Society of Petroleum Engineers (1997)
Hirasaki, G., Lawson, J.: Mechanisms of foam flow in porous media: apparent viscosity in smooth capillaries. SPE J. 25(02), 176–190 (1985)
Hoefner, M., Evans, E., Buckles, J., Jones, T., et al.: CO\(_2\) foam: results from four developmental field trials. SPE Reserv. Eng. 10(04), 273–281 (1995)
Hogg, R., Healy, T.W., Fuerstenau, D.W.: Mutual coagulation of colloidal dispersions. Trans. Faraday Soc. 62, 1638–1651 (1966)
Hsu, D.: Transport and development of microemulsion-and surfactant stabilized iron nanoparticles for in situ remediation. Ph.D. thesis (2017)
Jiemvarangkul, P., Zhang, W.X., Lien, H.L.: Enhanced transport of polyelectrolyte stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in porous media. Chem. Eng. J. 170(2–3), 482–491 (2011)
Johnson, R.L., Nurmi, J., Johnson, R., Shi, Z., Tratnyek, P., Phenrat, T., Lowry, G.: Injection of nano zero-valent iron for subsurface remediation: a controlled field-scale test of transport. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Remediation of Chlorinated and Recalcitrant Compounds. Battelle, Monterey, CA (2010)
Kam, S.I.: Improved mechanistic foam simulation with foam catastrophe theory. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 318(1), 62–77 (2008)
Kam, S., Rossen, W.: A model for foam generation in homogeneous media. SPE J. 8(04), 417–425 (2003)
Kam, S.I., Nguyen, Q.P., Li, Q., Rossen, W.R.: Dynamic simulations with an improved model for foam generation. SPE J. 12(01), 35–48 (2007)
Kaptay, G.: On the equation of the maximum capillary pressure induced by solid particles to stabilize emulsions and foams and on the emulsion stability diagrams. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 282, 387–401 (2006)
Karn, B., Kuiken, T., Otto, M.: Nanotechnology and in situ remediation: a review of the benefits and potential risks. Environ. Health Perspect. 117(12), 1813 (2009)
Khatib, Z., Hirasaki, G., Falls, A.: Effects of capillary pressure on coalescence and phase mobilities in foams flowing through porous media. SPE Reserv. Eng. 3(03), 919–926 (1988)
Kim, J., Grate, J.W.: Single-enzyme nanoparticles armored by a nanometer-scale organic/inorganic network. Nano Lett. 3(9), 1219–1222 (2003)
Klinkenberg, L., et al.: The permeability of porous media to liquids and gases. In: Drilling and production practice. American Petroleum Institute (1941)
Kocur, C.M., O’Carroll, D.M., Sleep, B.E.: Impact of nZVI stability on mobility in porous media. J. Contam. Hydrol. 145, 17–25 (2013)
Kovscek, A., Patzek, T., Radke, C.: A mechanistic population balance model for transient and steady-state foam flow in Boise sandstone. Chem. Eng. Sci. 50(23), 3783–3799 (1995)
Kumar, S., Ramkrishna, D.: On the solution of population balance equations by discretizationi. A fixed pivot technique. Chem. Eng. Sci. 51(8), 1311–1332 (1996)
Lake, L.: Enhanced Oil Recovery. Prentice Hall, New Jersey (1989)
Lawson, J.B., Reisberg, J.: Alternate slugs of gas and dilute surfactant for mobility control during chemical flooding. In: SPE/DOE Enhanced Oil Recovery Symposium. Society of Petroleum Engineers (1980)
Li, R.F., Yan, W., Liu, S., Hirasaki, G., Miller, C.A., et al.: Foam mobility control for surfactant enhanced oil recovery. SPE J. 15(04), 928–942 (2010)
Li, Z., Kessel, J., Grünewald, G., Kind, M.: Coupled cfd-pbe simulation of nucleation in fluidized bed spray granulation. Dry. Technol. 31(15), 1888–1896 (2013)
Lv, Q., Li, Z., Li, B., Li, S., Sun, Q.: Study of nanoparticle–surfactant–stabilized foam as a fracturing fluid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54(38), 9468–9477 (2015)
Ma, K., Ren, G., Mateen, K., Morel, D., Cordelier, P., et al.: Literature review of modeling techniques for foam flow through porous media. In: SPE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium. Society of Petroleum Engineers (2014)
Maire, J., Coyer, A., Fatin-Rouge, N.: Surfactant foam technology for in situ removal of heavy chlorinated compounds-DNAPLS. J. Hazard. Mater. 299, 630–638 (2015)
Mannhardt, K., Novosad, J.J.: Adsorption of foam-forming surfactants for hydrocarbon-miscible flooding at high salinities. Adv. Chem. Ser. 242, 259–259 (1994)
Martinez, A.C., Rio, E., Delon, G., Saint-Jalmes, A., Langevin, D., Binks, B.P.: On the origin of the remarkable stability of aqueous foams stabilised by nanoparticles: link with microscopic surface properties. Soft Matter 4(7), 1531–1535 (2008)
MathWorks: Matlab R2014b (2014). http://www.mathworks.com/
Mohammadi, S., Coombe, D., Stevenson, V., et al.: Test of steam-foam process for mobility control in south Casper creek reservoir. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 32(10), 49–54 (1993)
Nutt, M.O., Hughes, J.B., Wong, M.S.: Designing pd-on-au bimetallic nanoparticle catalysts for trichloroethene hydrodechlorination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39(5), 1346–1353 (2005)
O’Carroll, D., Sleep, B., Krol, M., Boparai, H., Kocur, C.: Nanoscale zero valent iron and bimetallic particles for contaminated site remediation. Adv. Water Resour. 51, 104–122 (2013)
Peng, X., Li, Y., Luan, Z., Di, Z., Wang, H., Tian, B., Jia, Z.: Adsorption of 1, 2-dichlorobenzene from water to carbon nanotubes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 376(1–2), 154–158 (2003)
Phenrat, T., Saleh, N., Sirk, K., Tilton, R.D., Lowry, G.V.: Aggregation and sedimentation of aqueous nanoscale zerovalent iron dispersions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41(1), 284–290 (2007)
Phenrat, T., Saleh, N., Sirk, K., Kim, H.J., Tilton, R.D., Lowry, G.V.: Stabilization of aqueous nanoscale zerovalent iron dispersions by anionic polyelectrolytes: adsorbed anionic polyelectrolyte layer properties and their effect on aggregation and sedimentation. J. Nanoparticle Res. 10(5), 795–814 (2008)
Prigiobbe, V., Worthen, A.J., Johnston, K.P., Huh, C., Bryant, S.L.: Transport of nanoparticle-stabilized co\(_2\) 2-foam in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 111(1), 265–285 (2016)
Pugh, R.J.: Bubble and Foam Chemistry. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2016)
Quinn, J., Geiger, C., Clausen, C., Brooks, K., Coon, C., O’Hara, S., Krug, T., Major, D., Yoon, W.S., Gavaskar, A., Holdsworth, T.: Field demonstration of DNAPL dehalogenation using emulsified zero-valent iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39(5), 1309–1318 (2005)
Randolph, A.: Theory of Particulate Processes. Academic Press, Cambridge (1988)
Ransohoff, T., Radke, C.: Mechanisms of foam generation in glass-bead packs. SPE Reserv. Eng. 3(02), 573–585 (1988)
Rossen, W.R.: Theory of mobilization pressure gradient of flowing foams in porous media: I. Incompressible foam. J Colloid Interface Sci. 136(1), 1–16 (1990)
Rossen, W.R.: Foams in enhanced oil recovery. Foams: Theory Measure. Appl. 57, 413–464 (1996)
Sa, J., Agüera, C.A., Gross, S., Anderson, J.A.: Photocatalytic nitrate reduction over metal modified TiO\(_2\). Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 85(3–4), 192–200 (2009)
Saleh, N., Sirk, K., Liu, Y., Phenrat, T., Dufour, B., Matyjaszewski, K., Tilton, R.D., Lowry, G.V.: Surface modifications enhance nanoiron transport and NAPL targeting in saturated porous media. Environ. Eng. Sci. 24(1), 45–57 (2007)
Schrick, B., Hydutsky, B.W., Blough, J.L., Mallouk, T.E.: Delivery vehicles for zerovalent metal nanoparticles in soil and groundwater. Chem. Mater. 16(11), 2187–2193 (2004)
Scott, W.T.: Analytic studies of cloud droplet coalescence I. J. Atmos. Sci. 25(1), 54–65 (1968)
Shen, X., Zhao, L., Ding, Y., Liu, B., Zeng, H., Zhong, L., Li, X.: Foam, a promising vehicle to deliver nanoparticles for vadose zone remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 186(2–3), 1773–1780 (2011)
Smith, A.M., Lee, A.A., Perkin, S.: The electrostatic screening length in concentrated electrolytes increases with concentration. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7(12), 2157–2163 (2016)
Song, W., Justice, R., Jones, C., Grassian, V., Larsen, S.: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption properties of nanocrystalline zsm-5. Langmuir 20(19), 8301–8306 (2004)
Thwala, J.M., Li, M., Wong, M.C., Kang, S., Hoek, E.M., Mamba, B.B.: Bacteria-polymeric membrane interactions: atomic force microscopy and XDLVO predictions. Langmuir 29(45), 13773–13782 (2013)
Tosco, T., Papini, M.P., Viggi, C.C., Sethi, R.: Nanoscale zerovalent iron particles for groundwater remediation: a review. J. Clean. Prod. 77, 10–21 (2014)
Tosco, T., Gastone, F., Sethi, R.: Guar gum solutions for improved delivery of iron particles in porous media (part 2): iron transport tests and modeling in radial geometry. J. Contam. Hydrol. 166, 34–51 (2014)
Tufenkji, N., Elimelech, M.: Correlation equation for predicting single-collector efficiency in physicochemical filtration in saturated porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38(2), 529–536 (2004)
Viota, J., De Vicente, J., Duran, J., Delgado, A.: Stabilization of magnetorheological suspensions by polyacrylic acid polymers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 284(2), 527–541 (2005)
Wang, S., Mulligan, C.N.: An evaluation of surfactant foam technology in remediation of contaminated soil. Chemosphere 57(9), 1079–1089 (2004)
Wang, Z., Choi, F., Acosta, E.: Effect of surfactants on zero-valent iron nanoparticles (nZVI) reactivity. J. Surfactants Deterg. 20(3), 577–588 (2017)
Ward, C.: NAPL Removal Surfactants, Foams, and Microemulsions. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2016)
Wei, Y.T., Wu, S.C., Chou, C.M., Che, C.H., Tsai, S.M., Lien, H.L.: Influence of nanoscale zero-valent iron on geochemical properties of groundwater and vinyl chloride degradation: a field case study. Water Res. 44(1), 131–140 (2010)
Wei, Y.T., Wu, S.C., Yang, S.W., Che, C.H., Lien, H.L., Huang, D.H.: Biodegradable surfactant stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron for in situ treatment of vinyl chloride and 1,2-dichloroethane. J. Hazard. Mater. 211–212, 373–380 (2012)
Worthen, A.J., Bagaria, H.G., Chen, Y., Bryant, S.L., Huh, C., Johnston, K.P.: Nanoparticle-stabilized carbon dioxide-in-water foams with fine texture. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 391, 142–151 (2013)
Worthen, A.J., Bryant, S.L., Huh, C., Johnston, K.P.: Carbon dioxide-in-water foams stabilized with nanoparticles and surfactant acting in synergy. AIChE J. 59(9), 3490–3501 (2013)
Xiang, A., Yan, W., Koel, B.E., Jaffé, P.R.: Poly(acrylic acid) coating induced 2-line ferrihydrite nanoparticle transport in saturated porous media. J. Nanoparticle Res. 15(7), 1705 (2013)
Xiang, A., Zhou, S., Koel, B.E., Jaffé, P.R.: Transport of poly(acrylic acid) coated 2-line ferrihydrite nanoparticles in saturated aquifer sediments for environmental remediation. J. Nanoparticle Res. 16(4), 2294 (2014)
Yao, K.M., Habibian, M.T., O’Melia, C.R.: Water and waste water filtration concepts and applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 5(11), 1105–1112 (1971)
Yin, G., Grigg, R.B., Svec, Y., et al.: Oil recovery and surfactant adsorption during co2-foam flooding. In: Offshore Technology Conference. Society of Petroleum Engineers (2009)
Yu, J., Khalil, M., Liu, N., Lee, R.: Effect of particle hydrophobicity on CO\(_2\) foam generation and foam flow behavior in porous media. Fuel 126, 104–108 (2014)
Zhang, W.X.: Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: an overview. J. Nanoparticle Res. 5(3–4), 323–332 (2003)
Zhao, X., Liu, W., Cai, Z., Han, B., Qian, T., Zhao, D.: An overview of preparation and applications of stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles for soil and groundwater remediation. Water Res. 100, 245–266 (2016)
Zhong, L., Qafoku, N.P., Szecsody, J.E., Dresel, P.E., Zhang, Z.F.: Foam delivery of calcium polysulfide to the vadose zone for chromium (vi) immobilization: a laboratory evaluation. Vadose Zone J. 8(4), 976–985 (2009)
Zhong, L., Szecsody, J.E., Zhang, F., Mattigod, S.V.: Foam delivery of amendments for vadose zone remediation: propagation performance in unsaturated sediments. Vadose Zone J. 9(3), 757–767 (2010)
Zhou, Z., Rossen, W., et al.: Applying fractional-flow theory to foam processes at the limiting capillary pressure. SPE Adv. Technol. Ser. 3(01), 154–162 (1995)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Innovation & Entrepreneurial Fellowship Program at Stevens Institute of Technology and by the American Chemical Society Petroleum Research Fund (ACS-PRF) under the Grant number PRF# 57739-DNI9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Prigiobbe, V. Modeling Nanoparticle Transport in Porous Media in the Presence of a Foam. Transp Porous Med 131, 269–288 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-019-01235-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-019-01235-9