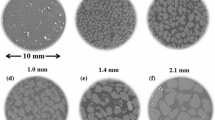
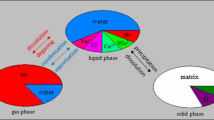
Abstract
The impact of salt precipitation, within or on top of porous media, on water evaporation from the media is an important issue with practical implications for agricultural practices, civil engineering and construction materials, the food industry and more. Even though the evaporation of saline solutions from porous media has been widely studied in recent years, there are still many uncertainties about the associated physical and chemical mechanisms. Moreover, most studies have focused on the impact of efflorescent salt precipitation on evaporation. This work focuses on subflorescent salt precipitation and its connection to evaporation from porous media. The different impacts of subflorescent and efflorescent salt precipitation on porous media evaporation are discussed, and the results of experiments that measured and quantified the impact of crystallization patterns on evaporation and porous media hydraulic conductivity are presented. A simple model was used to better understand the limiting factors that control liquid transport within porous media, with and without crystallized salts. The experimental results showed a major impact of efflorescent salt crust on evaporation, while for the subflorescent salt precipitation, the measured evaporation rates were similar to those measured for salt-free conditions. The model indicated that even though subflorescent-precipitated salt reduced the hydraulic conductivity of the medium by several orders of magnitude, it was not the limiting factor for evaporation as the diffusive vapor transport between the matrix surface and atmosphere was the slowest transport mechanism in the system, thus controlling evaporation rates.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benavente, D.: Role of pore structure in salt crystallisation in unsaturated porous stone. J. Cryst. Growth. 260, 532–544 (2004)
Cardell, C., Benavente, D., Rodríguez-Gordillo, J.: Weathering of limestone building material by mixed sulfate solutions. Characterization of stone microstructure, reaction products and decay forms. Mater. Charact. 59, 1371–1385 (2008)
Cochrane, T.T., Cochrane, T.A.: Osmotic potential properties of solutes common in the soil-plant solution continuum. Soil Sci. 170, 433–444 (2005)
Cussler, E.W.: Diffusion: mass transfer in fluid systems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1997)
Eloukabi, H., Sghaier, N., Ben Nasrallah, S., Prat, M.: Experimental study of the effect of sodium chloride on drying of porous media: The crusty–patchy efflorescence transition. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 56, 80–93 (2013)
Fisher, E.A.: Some factors affecting the evaporation of water from soil. J. Agric. Sci. 13, 121–143 (1923)
Fujimaki, H., Shimano, T., Inoue, M., Nakane, K.: Effect of a salt crust on evaporation from a bare saline soil. Vadose Zo. J. 5, 1246 (2006)
Garcia-Vallés, M., Vendrell-Saz, M., Molera, J., Blazquez, F.: Interaction of rock and atmosphere: patinas on Mediterranean monuments. Environ. Geol. 36(1–2), 137–149 (1998)
Gran, M., Carrera, J., Olivella, S., Saaltink, M.W.: Modeling evaporation processes in a saline soil from saturation to oven dry conditions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 15, 2077–2089 (2011)
Gupta, S., Huinink, H.P., Pel, L., Kopinga, K.: How ferrocyanide influences NaCl crystallization under different humidity conditions. 14(4), 4–12 (2014)
Hillel, D.: Introduction to environmental soil physics. Elsevier, New York (2004)
Ho, C.K., Webb, S.W.: Gas transport in porous media. Springer, Netherlands (2006)
Kasenow, M.: Determination of hydraulic conductivity from grain size analysis. Water Resources Publication, New York (2002)
Last, W.M., Schweyen, T.H.: Sedimentology and geochemistry of saline lakes of the Great Plains. Hydrobiologia 105, 245–263 (1983)
Leij, F.J., Alves, W.J., van Genuchten, M.T., Williams, J.R.: The UNSODA unsaturated hydraulic database. Cincinnati (1996)
Lide, R.D. (ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. CRC, Boca Raton (2007)
Mansoureh, N.R., Shokri, N.: Effects of grain angularity on NaCl precipitation in porous media during evaporation. Water Resour. Res. 50(11), 9020–9030 (2014)
Mualem, Y.: A new model of predicting hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 12, 513–522 (1976)
Nachshon, U., Ireson, A., van der Kamp, G., Wheater, H.: Sulfate salt dynamics in the glaciated plains of North America. J. Hydrol. 499, 188–199 (2013)
Nachshon, U., Ireson, A.M., Vanderkamp, G., Davies, R., Wheater, H.: Impacts of climate variability on wetland salinization in the North American prairies. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 18, 1–13 (2014)
Nachshon, U., Shahraeeni, E., Or, D., Dragila, M., Weisbrod, N.: Infrared thermography of evaporative fluxes and dynamics of salt deposition on heterogeneous porous surfaces. Water Resour. Res. 47, 1–16 (2011a)
Nachshon, U., Weisbrod, N., Dragila, M.I., Grader, A.: Combined evaporation and salt precipitation in homogeneous and heterogeneous porous media. Water Resour. Res. 47, W03513 (2011b)
Or, D., Lehmann, P., Shahraeeni, E., Shokri, N.: Advances in soil evaporation physics—a review. Vadose Zo. J. 12, (2013)
Rad, N.M., Shokri, N., Sahimi, M.: Pore-scale dynamics of salt precipitation in drying porous media. Phys. Rev. E. 88, 032404 (2013)
Rengasamy, P.: World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J. Exp. Bot. 57(5), 1017–1023 (2006)
Rodriguez-Navarro, C., Benning, L.G.: Control of crystal nucleation and growth by additives. Elements 9, 203–209 (2013)
Rodriguez-Navarro, C., Doehne, E.: Salt weathering: influence of evaporation rate, supersaturation and crystallization pattern. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 24, 191–209 (1999)
Ruiz-Agudo, E., Mees, F., Jacobs, P., Rodriguez-Navarro, C.: The role of saline solution properties on porous limestone salt weathering by magnesium and sodium sulfates. Environ. Geol. 52, 269–281 (2006)
Shahidzadeh-Bonn, N., Rafaï, S., Bonn, D., Wegdam, G.: Salt crystallization during evaporation: impact of interfacial properties. Langmuir 24, 8599–8605 (2008)
Van Genuchten, M.T.: A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44, 892–898 (1980)
Veran-Tissoires, S., Prat, M.: Evaporation of a sodium chloride solution from a saturated porous medium with efflorescence formation. J. Fluid Mech. 749, 701–749 (2014)
Weisbrod, N., Nachshon, U., Dragila, M.I., Grader, A.: Micro-CT analysis to explore salt precipitation impact on porous media permeability. In: Mercury, L., Tas, N., Zilberbrand, M. (eds.) Transp. React. Solut. Confined Hydrosyst., pp. 231–241. Springer, Netherlands (2014)
Wesson, J.A., Worcester, E.M., Wiessner, J.H., Mandel, N.S., Kleinman, J.G.: Control of calcium oxalate crystal structure and cell adherence by urinary macromolecules. Kidney Int. 53, 952–957 (1998)
Zhang, C., Li, L., Lockington, D.: Numerical study of evaporation-induced salt accumulation and precipitation in bare saline soils: mechanism and feedback. Water Resour. Res. 50, 8084–8106 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nachshon, U., Weisbrod, N. Beyond the Salt Crust: On Combined Evaporation and Subflorescent Salt Precipitation in Porous Media. Transp Porous Med 110, 295–310 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-015-0514-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-015-0514-9