Abstract
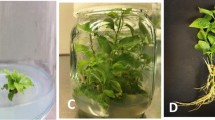
Olive tree harbors several viruses affecting the yield and quality of fruit worldwide. Application of virus-free planting materials is one of the main strategies to counteract virus diseases. The elimination of Arabis mosaic virus (ArMV), Cherry leaf roll virus (CLRV), Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) and Strawberry latent ringspot virus (SLRSV) by different regimes of electrotherapy followed by 1 mm shoot tip culture was investigated in a native Iranian olive cultivar Meshkat. The results showed that survival, regrowth and proliferation rates were dependent on the therapy regime and shoot tip type. Apical shoot tips showed more significant proliferation rate compared to axillary ones under 30 min treatment of electric current. In addition, apical shoot tips represented higher survival and regrowth rate under 30 min of electrotherapy, 54 and 46% respectively compared to 15 min of therapy. Interestingly, the regrowth rate in the virus mixed-infected cv. Meshkat was notably increased by increasing the electrotherapy duration from 13 min to 10% to 40 min and 46% in axillary and apical shoot tips respectively. The traditional method of shoot tip culture has not been able to eradicate the viruses in question. However, ArMV, CLRV, CMV and SLRSV were completely eradicated by electrotherapy treatment (35 mA, 100 V, 30 min) and the therapy efficiency index (TEI) was 54 for all studied viruses. Moreover, electrotherapy treatment (35 mA, 100 V, 15 min) eradicated only ArMV (62.5%) and CLRV (50%) with TEI of 31.25 and 25 respectively. The results concluded that the combination of electrotherapy with shoot tip culture can be successfully used as a virus elimination method for producing virus-free olive plants.
Key message
ArMV, CLRV, CMV, and SLRSV have been for the first time eradicated from olive cv. Meshkat shoot tip cultures using electrotherapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- ArMV:
-
Arabis mosaic virus
- CLRV:
-
Cherry leaf roll virus
- CMV:
-
Cucumber mosaic virus
- SLRSV:
-
Strawberry latent ring spot virus
- 2iP:
-
6-(γ,γ-Dimethylallylamino) purine
- BAP:
-
6-benzylaminopurine
- IBA:
-
L-indole-3-butyric acid
- LN:
-
Liquid nitrogen
- FeEDDHA:
-
Ethylenediamine di-2-hydroxyphenyl acetate ferric
- MgCl2 :
-
Magnesium chloride
- OM:
-
Olive medium
- TEI:
-
Therapy efficiency index
- mA:
-
Milliampers
- NaCl:
-
Sodium chloride
- M-MuLV:
-
Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus
- dNTPs:
-
Deoxynucleotide triphosphates
- RT:
-
Reverse transcription
- PCRs:
-
Polymerase chain reactions
- Nad5 :
-
Plant mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase gene subunit 5
References
Adil S, Singh V, Anjum A, Quraishi A (2022) A mini-review on electrotherapeutic strategy for the plant viral elimination. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 125:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-022-02265-w
Al Abdullah A, El Beaino T, Saponari M, Hallak H et al (2005) Preliminary evaluation of the status of olive-infecting viruses in Syria. EPPO Bull 35:249–252. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2338.2005.00818.x
Alabdullah A, Minafra A, Elbeaino T, Saponari M, Savino V et al (2010) Complete nucleotide sequence and genome organization of Olive latent virus-3, a new putative member of the family Tymoviridae. Virus Res 152:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2010.05.010
Alabi OJ, Diaz-Lara A, Erickson TM, Al Rwahnih M (2021) Olea europaea Geminivirus is present in a germplasm repository and in California and Texas olive (Olea europaea L.) groves. ArchVirol 166:3399–3404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-021-05218-4
Albanese G, Faggioli F, Ferretti L, Sciarroni R, La Rosa R et al (2003) Sanitary status evaluation of olive cultivars in Calabria and Sicily. J Plant Pathol 85:304
Albanese G, Saponari M, Faggioli F (2012) Phytosanitary certification. In: Muzzalupo I (ed) Olive germplasm: the olive cultivation, table olive and olive oil industry in Italy. InTechopen, pp. 107–132. https://doi.org/10.5772/51722
Asadi MR, Torkaman G (2014) Bacterial inhibition by electrical stimulation. Adv Wound Care 3. https://doi.org/10.1089/wound.2012.0410.:91– 7
Badarau CL, Chiru N, Guta IC (2014) The effect of some therapies on Potato virus Y and Potato virus X infected Solanum tuberosum L. plantlets (cv.‘Roclas’). Analele Univ din Oradea Fasc Biol 21:24–32
Bayati S, Shams-Bakhsh M, Moini A (2011) Elimination of Grapevine virus A (GVA) by cryotherapy and electrotherapy. J Agric Sci 3:442–450
Bertolini E, Olmos A, Martı́nez MC, Gorris MT et al (2001) Single-step multiplex RT-PCR for simultaneous and colourimetric detection of six RNA viruses in olive trees. J Virol Methods 96:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-0934(01)00313-5
Besnard G, El Bakkali A, Haouane H, Baali-Cherif D et al (2013) Population genetics of Mediterranean and Saharan olives: geographic patterns of differentiation and evidence for early generations of admixture. Ann Bot 112:1293–1302. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mct196
Besnard G, Terral JF, Cornille A (2018) On the origins and domestication of the olive: a review and perspectives. Ann Bot 121:385–403. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcx145
Bettoni JC, Costa MD, Gardin JP, Kretzschmar AA et al (2016) Cryotherapy: a new technique to obtain grapevine plants free of viruses. Rev Bras Frutic 38. https://doi.org/10.1590/0100-29452016833
Bettoni JC, Souza JA, Volk GM, Dalla Costa M et al (2019) Eradication of latent viruses from apple cultivar ‘Monalisa’ shoot tips using droplet-vitrification cryotherapy. Sci Hortic 250:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.02.033
Bettoni JC, Fazio G, Carvalho Costa L, Hurtado-Gonzales OP et al (2022) Thermotherapy followed by shoot tip cryotherapy eradicates latent viruses and Apple hammerhead viroid from in vitro apple rootstocks. Plants 11:582. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11050582
Bettoni JC, Wang MR, Li JW, Fan X et al (2024) Application of biotechniques for in vitro virus and viroid elimination in pome fruit crops. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-07-23-0232-KC. Phytopathol
Bhat AI, Rao GP (2020) Virus elimination by meristem-tip culture. In: Bhat AI, Rao GP (eds) Characterization of plant viruses: methods and protocols. Humana, Springer Nature, pp 465–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0334-5
Byrne PF, Volk GM, Gardner C, Gore MA et al (2018) Sustaining the future of plant breeding: the critical role of the USDA-ARS National Plant Germplasm System. Crop Sci 58:451–468. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2017.05.0303
Çaglayan K, Faggioli F, Barba M (2011) Viruses, phytoplasmas and diseases of unknown etiology of olive trees. In: Hadidi A, Barba M, Candresse T, Jelkmann W (eds) Virus and virus-like diseases of pome and stone fruits, The American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, Minnesota, USA, pp 289–297. https://doi.org/10.1094/9780890545010.fm
Campos MD, Zellama MS, Varanda C, Materatski P et al (2019) Establishment of a sensitive qPCR methodology for detection of the olive-infecting viruses in Portuguese and Tunisian orchards. Front Plant sci 10:694. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00694
Chiumenti M, Greco C, De Stradis A, Loconsole G et al (2021) Olea europaea Geminivirus: anovel bipartite geminivirid infecting olive trees. Viruses 13:481. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030481
Emami MD, Mozafari J, Babaeiyan N, Rahimian H (2011) Application of electrotherapy for the elimination of potato potyviruses. J Agr Sci Tech 13:921–927. http://jast.modares.ac.ir/article-23-12294-en.html
Fadel C, Digiaro M, Choueiri E, El Beaino T et al (2005) On the presence and distribution of olive viruses in Lebanon. EPPO Bull 35:33–36. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2338.2005.00776.x
Faggioli F, Ferretti L, Albanese G, Sciarroni R et al (2005) Distribution of olive tree viruses in Italy as revealed by one-step RT-PCR. J Plant Pathol 87:49–55. https://www.jstor.org/stable/41998207
Farhadi-Tooli S, Ghanbari A, Jafarkhani Kermani M, Zeinalabedini M et al (2022) Droplet-vitrification cryotherapy and thermotherapy as efficient tools for the eradication of Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus and Apple stem grooving virus from virus infected quince in vitro cultures. Eur J Plant Pathol 162: 31–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-021-02400-x
Felix MDR, Varanda CMR, Clara MIE (2012) Biology and molecular characterization of necroviruses affecting Olea europaea L: a review. Eur J Plant Pathol 133:247–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-011-9907-y
Ferreti L, Faggioli G, Pasquini G, Sciarroni R et al (2002) Strawberry latent ringspot virus (SLRSV) cause of differentiation among Raggiola and Frantoio olive cultivars. J Plant Pathol 84171200
Godena S, Bendini A, Giambanelli E, Cerretani L et al (2012) Cherry Leafroll virus: impact on olive fruit and virgin olive oil quality. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 114:535–541. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.201100277
Gong H, Igiraneza C, Dusengemungu L (2019) Major in vitro techniques for potato virus elimination and post eradication detection methods. A review. Am J Potato Res 96:379–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-019-09720-z
Grieco F, Alkowni R, Saponari M, Savino V, Martelli G (2000) Molecular detection of olive viruses. EPPO Bull 30:469–473. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2338.2000.tb00931.x
Guta IC, Buciumeanu EC, Gheorghe RN, Teodorescu A (2010) Solutions to eliminate Grapevine leafroll associated virus serotype 1 + 3 from V. Vinifera L. Cv. Ranai Magaraci. Rom Biotechnol Lett 15:72–78
Henriques MI, Rei FT, Leitão FA, Serrano JF et al (1992) Virus diseases in Olea europaea L. cultivars. I. Immunodiagnosis of Strawberry latent ringspot nepovirus. Phytopathol Mediterr 31:127–132. https://www.jstor.org/stable/42685831
Henry G, Thonart P, Ongena M (2012) PAMPs, MAMPs, DAMPs and others: an update on the diversity of plant immunity elicitors. Biotechnol Agron Soc Environ 16:257–268
Hernandez R, Bertrand H, Lepoivre P, Gonzalez JE et al (2002) Diagnosis and elimination of Banana streak virus (BSV) in Musa Spp. Cent Agric 29:42–47
Hernández PR, Fontanella J, Noa JC, Pichardo T et al (1997) Electrotherapy; a novel method for eliminating viruses from garlic. Hortic Argent 16:68–71
Herrbach E, Chesnais Q (2021) Vector transmission of plant viruses. In: Bamford DH, Zuckerman M (eds) Encyclopedia of virology (4th edn), Academic Press, pp 106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809633-8.21349-6
Hormozi-Nejad MH, Mozafari J, Rakhshandehroo F (2010) Elimination of Bean common mosaic virus using an electrotherapy technique. J Plant Dis Prot 117:201–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356361
Hosseini-Mazinani M, Torkzaban B, Arab J (2013) Iranian olive catalogue: morphological and molecular characterization of Iranian olive germplasm. NIGEB, Tehran, Iran
Hosseini-Mazinani M, Mariotti R, Torkzaban B, Sheikh-Hassani M et al (2014) High genetic diversity detected in olives beyond the boundaries of the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 9:e93146. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093146
Hu G, Dong Y, Zhang Z, Fan X et al (2015) Virus elimination from in vitro apple by thermotherapy combined with chemotherapy. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 121:435–443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0714-6
Igarza-Castro J, Hernández PR, Castellanos BC (2001) Electrotherapy as an alternative for elimination of the Dasheen mosaic virus in Tania. Span Manejo Integrado De Plagas 60:57–60
Jimenez-Diaz RM, Cirulli M, Bubici G, Jimenez-Gasco MDM et al (2012) Verticillium wilt, a major threat to olive production: current status and future prospects. Plant Dis 96:304–329. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-06-11-0496
Kazemi N, Nahandi FZ, Habashi AA, Masoomi-Aladizgeh F (2020) Comparing the efficiency of conventional and novel methods of virus elimination using molecular techniques. Eur J Plant Pathol 157:887–897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-020-02048-z
King AMQ, Adams MJ, Carstens EB, Lefkowitz EJ (2011) Virus taxonomy, ninth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of viruses. Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam
Koscak L, Lamovsek J, Dermic E, Tegli S et al (2023) Identification and characterization of Pseudomonas savastanoi Pv. Savastanoi as the causal agent of olive knot disease in Croatian, Slovenian and Portuguese olive (Olive Euroaea L.) orchards. Plants 12:307. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12020307
Loconsole G, Saponari M, Faggioli F, Albanese G et al (2010) Inter-laboratory validation of PCR‐based protocol for detection of olive viruses. EPPO bull 40:423–428. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2338.2010.02416.x
Lozoya-Saldaña H, Abello J, García GDL (1996) Electrotherapy and shoot tip culture eliminate Potato virus X in potatoes. Am Potato J 73:149–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02853073
Luigi M, Godena S, Đermić E, Barba M et al (2011) Detection of viruses in olive trees in Croatian Istria. Phytopathol Mediterr 50:150–153. https://doi.org/10.14601/Phytopathol_Mediterr-8398
Magyar-Tábori K, Mendler-Drienyovszki N, Hanász A, Zsombik L et al (2021) Phytotoxicity and other adverse effects on the in vitro shoot cultures caused by virus elimination treatments: reasons and solutions. Plants 10:670. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040670
Maliogka VI, Martelli GP, Fuchs M, Katis NI (2015) Control of viruses infecting grapevine. Adv Virus Res 91:175–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.aivir.2014.11.002
Marte M, Gadani F, Savino V, Rugini E (1986) Strawberry latent ringspot virus associated with a new disease of olive in Central Italy. Plant Dis 70:171–172. https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-70-171
Martelli GP (1999) Infectious diseases and certification of olive: an overview. EPPO Bull 29. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2338.1999.tb00806.x.:127– 33
Martelli GP (2013) A brief outline of infectious diseases of olive. Palest Tech Unive Res J 1:10. https://digitalcommons.aaru.edu.jo/ptuk/vol1/iss1/10
Martelli GP, Salerno M, Savino V, Prota U (2002) An appraisal of diseases and pathogens of olive. Acta Hortic 586:701–708. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2002.586.150
Mathew L, Tiffin H, Erridge Z, McLachlan A et al (2021) Efficiency of eradication of raspberry bushy dwarf virus from infected raspberry (Rubus idaeus) by in vitro chemotherapy, thermotherapy and cryotherapy and their combinations. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 144:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01829-y
Mathioudakis MM, Saponari M, Hasiow-Jaroszewska B, Elbeaino T et al (2020) The detection of viruses in olive cultivars in Greece, using a rapid and effective RNA extraction method, for certification of virus-tested propagation material. Phytopathol Mediterr 59:203–211. https://doi.org/10.36253/phyto-11033
Menzel W, Jelkmann W, Maiss E (2002) Detection of four apple viruses by multiplex RT-PCR assays with coamplification of plant mRNA as internal control. J Virol Methods 99:81–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-0934(01)00381-0
Mirzaei L, Yadollahi A, Kermani MJ, Naderpour M et al (2021) Evaluation of genetic stability in olive callus-induced and meristem-induced shoots using flow cytometry and amplified fragment length polymorphism techniques. Plant Methods 17:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-021-00724-7
Mirzaei L, Yadollahi A, Kermani MJ, Naderpour M et al (2022) Stability investigation of air-dried olive ribo nucleic acids for metavirome studies. Plant Methods 18:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-022-00846-6
Montemurro C, Simeone R, Blanco A, Saponari M et al (2008) Sanitary selection and molecular characterization of olive cultivars grown an Apulia. Acta Hortic 791:603–609. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2008.791.93
Montes-Osuna N, Mercado-Blanco J (2020) Verticillium wilt of olive and its control: what did we learn during the last decade? Plants 9:735. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9060735
Montilon V, Potere O, Susca L, Bottalico G (2023) Phytosanitary rules for the movement of olive (Olea europaea L.) propagation material into the European Union. Plants 12:669. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12040699
Morelli M, Garcia-Madero JM, Jos A, Saldarelli P et al (2021) Xylella fastidiosa in olive: a review of control attempts and current management. Microorganisms 9:1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081771
Motamedifar M, Nekooeian AA, Moatari A (2007) The effect of hydroalcoholic extract of olive leaves against herpes simplex virus type 1. Iran J Med Sci 32:4
Naderpour M, Shahbazi R, Sadeghi L, Maddah-Arefi H (2013) Simultaneous detection of Arabis mosaic virus, Cherry Leafroll virus and Cucumber mosaic virus with coamplification of plant mRNA as internal control for olive certification programs. Iran J Virol 8:7–12. https://doi.org/10.21859/isv.8.1.7
Nerway ZA, Duhoky MM, Kassim NA (2020) In vitro elimination of Dahlia mosaic virus by using meristem culture, electrotherapy and chemotherapy. Iraqi J Agric Sci 51:665–674. https://doi.org/10.36103/ijas.v51i2.994
Owen CA, Bita EC, Banilas G, Hajjar SE et al (2005) AFLP reveals structural details of genetic diversity within cultivated olive germplasm from the Eastern Mediterranean. Theor Appl Genet 110:1169–1176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1861-z
Padilla IM, Vidoy I, Encina CL (2009) Influence of indole-butyric acid and electro-pulse on in vitro rooting and development of olive (Olea Europea L.) microshoots. Plant Cell Rep 28:1411–1420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-009-0740-0
Pazhouhande M (2001) In vitro development of potato virus-free germplasm. Master Thesis, Tarbiat Modarres University, Iran
Rakosy-Tican L, Aurori CM, Morariu VV (2005) Influence of near null magnetic field on in vitro growth of potato and wild solanum species. Bioelectromagnetics 26:548–557. https://doi.org/10.1002/bem.20134
Roschetti A, Ferretti L, Muzzalupo I, Pellegrini F et al (2009) Evaluation of the possibile effect of virus infections on olive propagation. Petria 19:18–28
Rubino L, Martelli GP (2008) Necrovirus. In: Brian WJM, Van Regenmortel MHV (eds) Encyclopedia of virology, 3rd edn. Academic, pp 403–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012374410-4.00448-9.
Rugini E (1984) In vitro propagation of some olive (Olea europaea Sativa L.) cultivars with different root-ability, and medium development using analytical data from developing shoots and embryos. Sci Hortic 24:123–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4238(84)90143-2
Rugini E, Cristofori V, Silvestri C (2016) Genetic improvement of olive (Olea europaea L.) by conventional and in vitro biotechnology methods. Biotechnol Adv 34:687–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.03.004
Sastry KS, Zitter TA (2014) Management of virus and viroid diseases of crops in the tropics. In: Sastry KS, Zitter TA (eds) Plant virus and viroid diseases in the tropics. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 149–480
Savino V, Barba M, Gallitelli G, Martelli G (1979) Two nepoviruses isolated from olive in Italy. Phytopathol Medit 18135142
Singh B, Kaur A (2016) In vitro production of PLRV and PSTVd-free plants of potato using electrotherapy. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 19:285–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-016-0028-1
Szabo LK, Desiderio F, Kirilla Z, Hegedus A et al (2024) A mini-review on in vitro methods for virus elimination from Prunus sp. fruit trees. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 156:42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-023-02670-9
Tourang S, Shams-Bakhsh M, Moeini A (2016) Elimination of Cucumber mosaic virus from gladiolus by meristem tip culture, thermotherapy and electrotherapy. Agric Biotechnol J 7:35–50
Triolo E, Materazzi A, Toni S (1996) An isolate of Tobacco mosaic tobamovirus fromOlea europaea L. Adv Hortic Sci 10:39–45. https://www.jstor.org/stable/42881490
Varanda C, Cardoso JM, do Rosário Félix M, Oliveira S et al (2010) Multiplex RT-PCR for detection and identification of three necroviruses that infect olive trees. Eur J Plant Pathol 127:161–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-010-9593-1
Vivek M, Modgil M (2018) Elimination of viruses through thermotherapy and meristem culture in apple cultivar ‘Oregon Spur-II’. Virus Dis 29:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13337-018-0437-5
Waigmann E, Lucas WJ, Citovsky V, Zambryski P (1994) Direct functional assay for Tobacco mosaic virus cell-to-cell movement protein and identification of a domain involved in increasing plasmodesmal permeability. Proc Natl Acad Sci 91:1433–1437. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.4.1433
Walkey DG (1972) Production of apple plantlets from axillary-bud meristems. Canad J Plant Sci 52:1085–1087. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjps72-186
Walkey DGA (1980) Production of virus-free plants by tissue culture. In: Ingrain DS, Helgeson JP (eds) Tissue culture methods for plant pathologists. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, pp 109–117
Wang Q, Valkonen JP (2009) Cryotherapy of shoot tips: novel pathogen eradication method. Trends Plant Sci 14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2008.11.010.:119– 22
Wang MR, Cui ZH, Li JW, Hao XY et al (2018) In vitro thermotherapy-based methods for plant virus eradication. Plant Methods 14:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-018-0355-y
Wang M-R, Bi W-L, Bettoni JC, Zhang D et al (2022) Shoot tip cryotherapy for plant pathogen eradication. Plant Pathol 71:1241–1254. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.13565
Ward RG (1996) The influence of electric currents on the growth of tomato plants. Acta Physiol Plant 18:121–127
Watanabe M, Bessho H, Suzuki A, Komori S (2006) Seasonal changes of IAA and cytokinin in shoots of columnar type apple trees. In XXVII Intl Hortic Cong, International Symposium on Endogenous and Exogenous Plant Bioregulators 774: 75–80. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2008.774.8
Wu H, Qu X, Dong Z, Luo L et al (2020) WUSCHEL triggers innate antiviral immunity in plant stem cells. Science 370:227–231
Xylogianni E, Margaria P, Knierim D, Sareli K et al (2021) Virus surveys in olive orchards in Greece identify Olive virus T, a novel member of the genus Tepovirus. Pathogens 10:574. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050574
Zare Khafri A, Zarghami R, Naderpour M, Ahmadi B et al (2024) Assessment of virus eradication methods from infected in vitro–grown apricot cultures. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 156:52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-023-02621-4
Zellama MS, Varanda CM, Materatski P, Nabi N et al (2019) An integrated approach for understanding the high infection rates of olive viruses in Tunisia. Eur J Plant Pathol 153:1043–1054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-01620-y
Zhao M (2009) Electrical fields in wound healing—an overriding signal that directs cell migration. Semin cell Dev Biol 20:674–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2008.12.009
Zhao L, Wang MR, Cui ZH, Chen L et al (2018) Combining thermotherapy with cryotherapy for efficient eradication of Apple stem grooving virus from infected in-vitro-cultured apple shoots. Plant Dis 102:1574-80. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-11-17-1753-RE
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Karim Rocky Salimi for his assistance in proof reading of the manuscript. We would also like to appreciate Maria Kocanova and Dr. Petr Kominek for their assistance in virus detection experiments during the research visit in the Genetic Departement of Mendel University, Czech Republic.
Funding
This research was financially supported by Tarbiat Modares University and Agricultural Biotechnology Research Institute of Iran (Ministry of Science, Research and Technology).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: AY, MJK; Methodology: LM, MN; Software: LM; Validation: MN, AE, MJK; Formal Analysis: AY; Investigation: LM; Resources: AAZ, MN, AE; Data Curation: LM; Writing– Original Draft Preparation: LM, MN; Writing– Review, Editing, Revision: MN, LM, ME; Visualization: AE; Supervision: AY, MJK; Project Administration: MJK. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Licenses were obtained from concerned authority to collect the plant sample. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Communicated by Ranjith Pathirana.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mirzaei, L., Yadollahi, A., Naderpour, M. et al. Electrotherapy; a promising therapy to eradicate viruses from infected in vitro olive cv. Meshkat. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 157, 52 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-024-02777-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-024-02777-7