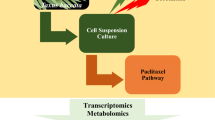
Abstract
Paclitaxel is a highly functionalized diterpenoid that is broadly used for the treatment of several cancer types. This valuable specialized metabolite naturally exists in the inner bark of Taxus species in low amounts. The limited-scale production of paclitaxel in Taxus cell cultures has necessitated the use of several elicitors. Recently, methyl-β-cyclodextrin (CD) and coronatine (COR) have been considered to be highly effective elicitors in producing plant specialized metabolites. Given the limited production of paclitaxel due to the rate limiting enzymes' function, bottleneck removal is conducive to the production of more significant amounts of paclitaxel. In the present study, the full length of DBTNBT coding sequence (CDS), as one of the paclitaxel pathway bottlenecks, was integrated downstream of the CaMV 35S promoter (pCAMBIA1304-DBTNBT) and transiently expressed in Taxus baccata leaves via Agrobacterium tumefaciens and vacuum infiltration method. Paclitaxel production and the expression level of several involved genes were evaluated through different treatments. The transient overexpression of the DBTNBT gene, associated with dual elicitation, resulted in 7.4-fold more paclitaxel production compared with the no-inoculation/no-elicitation control. These ratios were 2.1 and 1.8 in the CD + COR and pCAM treatments, respectively. Among T13αH, T14βH, DBAT, BAPT, DBTNBT, and ABC genes, the most increased expression level belonged to the DBTNBT gene, followed by ABC and BAPT genes. It seems as though in the near future, bottleneck removal could be used on a large scale in Taxus metabolic engineering, resulting in the relative removal of some other bottlenecks and an increase in the final paclitaxel production.
Key message
DBTNBT overexpression associated with CD and COR elicitation led to the much more paclitaxel production and the prevention of feedback repression on the upstream bottleneck genes such as DBAT and BAPT.
AbstractSection Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data generated or analyzed during this study was included in this paper.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- MeJA:
-
Methyl jasmonate
- COR:
-
Coronatine
- CD:
-
Methyl-β-cyclodextrin
- GAPDH :
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- TXS :
-
Taxadiene synthase
- T13αH :
-
Taxane 13α-hydroxylase
- T14βH :
-
Taxane 14β-hydroxylase
- TBT :
-
Taxane-2α-O-benzoyl transferase
- DBAT :
-
10-deacetylbaccatin III-10-O-acetyltransferase
- BAPT :
-
Baccatin III-3-amino 13-phenylpropanoyl- CoA transferase
- DBTNBT :
-
Debenzoyltaxol N-benzoyl transferase
- PAM :
-
Phenylalanine amino mutase
- ABC :
-
ATP-binding cassette
- ORF:
-
Open Reading Frame
- GFP :
-
Green fluorescent protein
- GUS :
-
β- glucuronidase
- OD:
-
Optical Density
- SE:
-
Standard Error
- CRD:
-
Completely Randomized Design
- LSD:
-
Least Significant Difference
- CDS:
-
Coding Sequence
- CaMV 35S Promoter:
-
Cauliflower Mosaic Virus Promoter
- NOS Terminator:
-
Nopaline Synthase Terminator
- cDNA:
-
Complementary DNA
- HPLC:
-
High- Performance Liquid Chromatography
- RP:
-
Reverse Phase
- F:
-
Forward Primer
- R:
-
Reverse Primer
References
Almagro L, Pedreño MÁ (2020) Use of cyclodextrins to improve the production of plant bioactive compounds. Phytochem Rev 19(4):1061–1080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-020-09704-6
Bender CL, Alarcón-Chaidez F, Gross DC (1999) Pseudomonas syringae phytotoxins: mode of action, regulation, and biosynthesis by peptide and polyketide synthetases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63(2):266–292. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.63.2.266-292.1999
Bentebibel S, Moyano E, Palazón J, Cusidó RM, Bonfill M, Eibl R, Pinol MT (2005) Effects of immobilization by entrapment in alginate and scale-up on paclitaxel and baccatin III production in cell suspension cultures of Taxus baccata. Biotechnol Bioeng 89(6):647–655. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.20321
Bru R, Sellés S, Casado-Vela J, Belchí-Navarro S, Pedreño MA (2006) Modified cyclodextrins are chemically defined glucan inducers of defense responses in grapevine cell cultures. J Agric Food Chem 54(1):65–71. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf051485j
Chandran H, Meena M, Barupal T, Sharma K (2020) Plant tissue culture as a perpetual source for production of industrially important bioactive compounds. Biotechnol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2020.e00450
Channuntapipat C, Sedgley M, Collins G (2001) Sequences of the cDNAs and genomic DNAs encoding the S1, S7, S8, and Sf alleles from almond. Prunus Dulcis Theor Appl Genet 103(6–7):1115–1122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220100629
Collin HA (2001) Secondary product formation in plant tissue cultures. Plant Growth Regul 34(1):119–134. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013374417961
Cragg GM, Newman DJ (2005) Plants as a source of anti-cancer agents. J Ethnopharmacol 100(1–2):72–79
Cusido RM, Onrubia M, Sabater-Jara AB, Moyano E, Bonfill M, Goossens A, Pedreño MA, Palazon J (2014) A rational approach to improving the biotechnological production of taxanes in plant cell cultures of Taxus spp. Biotechnol Adv 32(6):1157–1167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.03.002
Exposito O, Syklowska-Baranek K, Moyano E, Onrubia M, Bonfill M, Palazon J, Cusido RM (2010) Metabolic responses of Taxus media transformed cell cultures to the addition of methyl jasmonate. Biotechnol Prog 26(4):1145–1153. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.424
Green R, Rogers EJ (2013) Transformation of chemically competent E. coli. Changes 29:329–336
Ho C-K, Chang S-H, Lung J, Tsai C-J, Chen K-P (2005) The strategies to increase taxol production by using Taxus mairei cells transformed with TS and DBAT genes. Int J Appl Sci Eng 3(3):179–185
Jaziri M, Zhiri A, Guo Y-W, Dupont J-P, Shimomura K, Hamada H, Vanhaelen M, Homès J (1996) Taxus sp. cell, tissue and organ cultures as alternative sources for taxoids production: a literature survey. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 46(1):59–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00039697
Jennewein S, Rithner CD, Williams RM, Croteau RB (2001) Taxol biosynthesis: taxane 13α-hydroxylase is a cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98(24):13595–13600. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.251539398
Kashani K, Jalali Javaran M, Sabet MS, Moieni A (2018) Identification of rate-limiting enzymes involved in paclitaxel biosynthesis pathway affected by coronatine and methyl-β-cyclodextrin in Taxus baccata L. cell suspension cultures. Daru 26(2):129–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40199-018-0217-1
Li F-L, Ma X-J, Hu X-L, Hoffman A, Dai J-G, Qiu D-Y (2011) Antisense-induced suppression of taxoid 14β-hydroxylase gene expression in transgenic Taxus × media cells. Afr J Biotechnol 10(44):8720–8728
Li S-t, Zhang P, Zhang M, Fu C-h, Zhao C-f, Dong Y-s, A-y G, Yu L-j (2012) Transcriptional profile of Taxus chinensis cells in response to methyl jasmonate. BMC Genomics 13(1):295. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-295
Lijavetzky D, Almagro L, Belchi-Navarro S, Martínez-Zapater JM, Bru R, Pedreño MA (2008) Synergistic effect of methyljasmonate and cyclodextrin on stilbene biosynthesis pathway gene expression and resveratrol production in Monastrell grapevine cell cultures. BMC Res Notes 1(1):132. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-1-132
Livak KJ & Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. doi:https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
M. Cusidó R, Palazón J, Bonfill M, Navia-Osorio A, Morales C & Piñol MT, (2002) Improved paclitaxel and baccatin III production in suspension cultures of Taxus media. Biotechnol Prog 18(3):418–423. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp0101583
Malik S, Cusidó RM, Mirjalili MH, Moyano E, Palazón J, Bonfill M (2011) Production of the anticancer drug taxol in Taxus baccata suspension cultures: a review. Process Biochem 46(1):23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2010.09.004
Mubeen S, He C-T, Asad BA, Yang Z-Y (2019) Overview of past and present developments towards biotechnological and molecular approaches to improve taxol production. Front Nat Prod Chem 5(5):95–145
Onrubia M, Moyano E, Bonfill M, Palazon J, Goossens A, Cusido RM (2011) The relationship between TXS, DBAT, BAPT and DBTNBT gene expression and taxane production during the development of Taxus baccata plantlets. Plant Sci 181(3):282–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.06.006
Onrubia M, Cusidó R, Ramirez K, Hernández-Vázquez L, Moyano E, Bonfill M, Palazon J (2013) Bioprocessing of plant in vitro systems for the mass production of pharmaceutically important metabolites: paclitaxel and its derivatives. Curr Med Chem 20(7):880–891. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986713805219064
Onrubia., Moyano E, Bonfill M, Cusido RM, Goossens A & Palazon J, (2013) Coronatine, a more powerful elicitor for inducing taxane biosynthesis in Taxus media cell cultures than methyl jasmonate. J Plant Physiol 170(2):211–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.09.004
Pyo SH, Song BK, Ju CH, Han BH, Choi HJ (2005) Effects of absorbent treatment on the purification of paclitaxel from cell cultures of Taxus chinensis and yew tree. Process Biochem 40(3):1113–1117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.03.004
Rahpeyma SA, Moieni A, Jalali Javaran M (2015) Paclitaxel production is enhanced in suspension-cultured hazel (Corylus avellana L.) cells by using a combination of sugar, precursor, and elicitor. Eng Life Sci 15(2):234–242. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201400115
Ramirez-Estrada K, Osuna L, Moyano E, Bonfill M, Tapia N, Cusido RM, Palazon J (2015) Changes in gene transcription and taxane production in elicited cell cultures of Taxus × media and Taxus globosa. Phytochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2015.06.013
Ramirez-Estrada K, Vidal-Limon H, Hidalgo D, Moyano E, Golenioswki M, Cusidó RM, Palazon J (2016) Elicitation, an effective strategy for the biotechnological production of bioactive high-added value compounds in plant cell factories. Molecules 21(2):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21020182
Sabater-Jara AB, Tudela LR, López-Pérez AJ (2010) In vitro culture of Taxus sp.: strategies to increase cell growth and taxoid production. Phytochem Rev 9(2):343–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-010-9167-z
Sabater-Jara AB, Onrubia M, Moyano E, Bonfill M, Palazón J, Pedreño MA, Cusidó RM (2014) Synergistic effect of cyclodextrins and methyl jasmonate on taxane production in Taxus x media cell cultures. Plant Biotechnol J 12(8):1075–1084. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12214
Sabzehzari M, Naghavi M (2019) Phyto-miRNAs-based regulation of metabolites biosynthesis in medicinal plants. Gene 682:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.09.049
Sah B, Subban K, Jayabaskaran C (2019) Biochemical insights into the recombinant 10-deacetylbaccatin III-10-β-O-acetyltransferase enzyme from the Taxol-producing endophytic fungus Lasiodiplodia theobromae. FEMS Microbiol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnz072
Salehi M, Naghavi MR, Bahmankar M (2019) A review of Ferula species: Biochemical characteristics, pharmaceutical and industrial applications, and suggestions for biotechnologists. Ind Crops Prod 139:111511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111511
Sambrook J & Russell D (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harb Lab Press Cold Spring Harb NY 999
Satish L, Shamili S, Yolcu S, Lavanya G, Alavilli H, Swamy MK (2020) Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites in plants as influenced by different factors Plant-derived Bioactives. Springer, NY, pp 61–100
Singh M, Poddar NK, Singh D, Agrawal S (2020) Foliar application of elicitors enhanced the yield of withanolide contents in Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal (variety, Poshita). Biotech 10(4):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2153-2
Srivastava V, Negi AS, Kumar J, Gupta M, Khanuja SP (2005) Plant-based anticancer molecules: a chemical and biological profile of some important leads. Bioorg Med Chem 13(21):5892–5908
Zamboni A, Gatto P, Cestaro A, Pilati S, Viola R, Mattivi F, Moser C, Velasco R (2009) Grapevine cell early activation of specific responses to DIMEB, a resveratrol elicitor. BMC Genomics 10(1):363. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-10-363
Zhao Y, Thilmony R, Bender CL, Schaller A, He SY, Howe GA (2003) Virulence systems of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato promote bacterial speck disease in tomato by targeting the jasmonate signaling pathway. Plant J 36(4):485–499
Zhu L, Chen L (2019) Progress in research on paclitaxel and tumor immunotherapy. Cell Mol Biol Lett 24(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0164-y
Acknowledgements
All authors gratefully acknowledge the support of Tarbiat Modares University.
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Kimia Kashani performed material preparation, data collection, and analysis. She wrote the first draft of the manuscript and the other authors (Mohammad Sadegh Sabet, Mokhtar Jalali Javaran, and Ahmad Moieni) commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Konstantin V. Kiselev.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kashani, K., Sabet, M.S., Jalali Javaran, M. et al. Bottleneck removal of paclitaxel biosynthetic pathway by overexpression of DBTNBT gene under methyl-β-cyclodextrin and coronatine elicitation in Taxus baccata L.. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 149, 485–495 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-022-02279-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-022-02279-4