Abstract
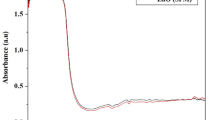
This study proposes the tenacious vitality for biomass production and eco-friendly, cost-effective, renewable silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) biosynthesis approach for beneficial utilization. For the first time, halogen dried callus biomass obtained from petioles of Centella asiatica L. (CA) was utilized for biosynthesis of AgNPs through process optimization using face-centered central composite design. Non-embryogenic, whitish-yellow callus propagated on B5 medium augmented with 2,4-D (1.00 µM) and TDZ (0.50 µM) was utilized for the synthesis of AgNPs. Qualitative and quantitative phytochemical estimation indicated the presence of active ingredients such as total phenolic, flavonoids, tannins, saponins, and terpenoids in aqueous callus extract. The characterization techniques reinforced each other and affirmed the ability of CA callus extract to fabricate AgNPs with an average size of 32.9 nm and maximum absorbance at 443 nm. Also, the presence of elemental Ag, spherical shape, and crystalline nature was confirmed by SEM and EDX, TEM, and XRD analysis respectively. FTIR and phytochemical screening confirmed the presence of bioactive functional groups in CA callus AgNPs. Both callus extract and AgNPs exhibited potential antioxidant activity in a dose-dependent manner.
Key message
The callus culture obtained from agricultural residue of Centella asiatica served as a novel source for statistical optimization and biosynthesis of spherical and crystalline silver nanoparticles possessing potent antioxidative property.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
Centella asiatica L.
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- AgNPs:
-
Silver nanoparticles
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- B5:
-
Gamborg’s B5 medium
- BAP:
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- CCD:
-
Face Centred Central Composite design
- DDW:
-
Double distilled water
- DLS:
-
Dynamic light scattering
- DPPH:
-
1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl
- EDX:
-
Energy dispersive X-ray
- FTIR:
-
Fourier-transform infrared
- F value:
-
Fisher’s statistical test
- Kn:
-
Kinetin
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog medium
- P value:
-
Probability value
- RSM:
-
Response surface methodology
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
- TDZ:
-
Thidiazuron
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- XRD:
-
Powder X-ray diffraction
- Zn:
-
Zeatin
- R2 value:
-
Coefficient of determination
- IC 50:
-
Half maximal inhibitory concentration
References
Anjum S, Abbasi BH (2016) Thidiazuron-enhanced biosynthesis and antimicrobial efficacy of silver nanoparticles via improving phytochemical reducing potential in callus culture of Linum usitatissimum L. Int J Nanomed 11:715–728. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S102359
Arpita Roy LK et al (2018) Qualitative and quantitative phytochemical analysis of Centella asiatica. Nat Prod Chem Res 06:4–7. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-6836.1000323
Belwal T, Andola HC, Atanassova MS et al (2019) Gotu Kola (Centella asiatica). Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-812491-8.00038-2
Blois MS (1958) Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical. Nat Microbiol 182:800–801. https://doi.org/10.2307/3280933
Botcha S, Prattipati SD (2020) Callus extract mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles, their characterization and cytotoxicity evaluation against MDA-MB-231 and PC-3 Cells. Bionanoscience 10:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-019-00683-3
Brinkhaus B, Lindner M, Schuppan D, Hahn EG (2000) Chemical, pharmacological and clinical profile of the East Asian medical plant Centella asiatica. Phytomedicine 7:427–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0944-7113(00)80065-3
Chang C-C, Yang M-H, Wen HM (2002) Estimation of total flavonoid content in propolis by two complementary colorimetric methods. J Food Drug Anal 10:178–182
Eze FN, Tola AJ, Nwabor OF, Jayeoye TJ (2019) Centella asiatica phenolic extract-mediated bio-fabrication of silver nanoparticles: characterization, reduction of industrially relevant dyes in water and antimicrobial activities against foodborne pathogens. RSC Adv 9:37957–37970. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra08618h
Fard SE, Tafvizi F, Torbati MB (2018) Silver nanoparticles biosynthesised using Centella asiatica leaf extract: apoptosis induction in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. IET Nanobiotechnol 12:994–1002. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2018.5069
Flores-López LZ, Espinoza-Gómez H, Somanathan R (2019) Silver nanoparticles: electron transfer, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress, beneficial and toxicological effects. Mini review. J Appl Toxicol 39:16–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3654
Gallego A, Ramirez-Estrada K, Vidal-Limon HR et al (2014) Biotechnological production of centellosides in cell cultures of Centella asiatica (L.) urban. Eng Life Sci 14:633–642. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201300164
Gray NE, Alcazar Magana A, Lak P et al (2018) Centella asiatica: phytochemistry and mechanisms of neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement. Phytochem Rev 17:161–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-017-9528-y
Gupta S, Mao AA, Sarma S (2020) Effects of thidiazuron (TDZ) on direct shoot organogenesis of Gymnocladus assamicus: a threatened and critically endangered species from Northeast India. Natl Acad Sci Lett 43:85–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40009-019-00801-5
Hamid AA, Shah ZM, Muse R, Mohamed S (2002) Characterisation of antioxidative activities of various extracts of Centella asiatica (L.) urban. Food Chem 77:465–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(01)00384-3
Hammond JB, Kruger NJ (1988) Chapter 2 The Bradford Met hod for Protein Quantitation. In: Walk JM (ed) Humana Press vol 10, pp 0–89603
Huang F, Long Y, Liang Q et al (2019) Safed Musli (Chlorophytum borivilianum L.) callus-mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of their antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity against human colon cancer cells. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2418785
Huo C, Khoshnamvand M, Liu P et al (2008) Eco-friendly approach for biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Citrus maxima peel extract and their characterization, catalytic, antioxidant and antimicrobial characteristics. Mater Res Express Accept. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aae34c
Iyer RI, Panda T (2016) Biosynthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles with anti-microbial activity by callus cultures of Michelia champaca L. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 16:7345–7357. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2016.12406
Iyer RI, Panda T (2018) Biosynthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using extracts of callus cultures of pumpkin (Cucurbita maxima). J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18:5341–5353. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2018.15378
Jain A, Jain R, Jain S (2020) Basic techniques in biochemistry, microbiology and molecular biology principles and techniques, 1st edn. Springer, New York
Jayappa MD, Ramaiah CK, Kumar MAP et al (2020) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from the leaf, stem and in vitro grown callus of Mussaenda frondosa L.: characterization and their applications. Appl Nanosci 10:3057–3074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01382-2
Jemal K, Sandeep BV, Pola S (2017) Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of the antibacterial activity of Allophylus serratus Leaf and leaf derived callus extracts mediated silver nanoparticles. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4213275
Kalia A, Manchanda P, Bhardwaj S, Singh G (2020) Biosynthesized silver nanoparticles from aqueous extracts of sweet lime fruit and callus tissues possess variable antioxidant and antimicrobial potentials. Inorg Nano-Metal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2020.1735420
Karhan Ö, Ceran ÖB, Şara ON, Şimşek B (2017) Response surface methodology based desirability function approach to investigate optimal mixture ratio of silver nanoparticles synthesis process. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:8180–8189. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b01150
Kim OT, Kim MY, Huh SM et al (2004) Effect of growth regulators on asiaticoside production in whole plant cultures of Centella asiatica (L.) urban. J Plant Biol 47:361–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03030552
Kshirsagar PR, Mohite A, Suryawanshi S et al (2020) Plant regeneration through direct and indirect organogenesis, phyto-molecular profiles, antioxidant properties and swertiamarin production in elicitated cell suspension cultures of Swertia minor (Griseb.) Knobl. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01962-8
Kumar S, Mitra A, Halder D (2017) Centella asiatica leaf mediated synthesis of silver nanocolloid and its application as filler in gelatin based antimicrobial nanocomposite film. LWT-Food Sci Technol 75:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.06.061
Lalegani Z, Seyyed Ebrahimi SA (2020) Optimization of synthesis for shape and size controlled silver nanoparticles using response surface methodology. Colloids Surf A 595:124647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124647
Lansdown R (2019) Centella asiatica. IUCN Red List Threat Species 2019 eT168725A88308182. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T168725A88308182.en
Mathews P (2005) Design of experiments with MINITAB. ASQ Quality Press, Milwaukee
Mehring A, Haffelder J, Chodorski J et al (2020) Establishment and triterpenoid production of Ocimum basilicum cambial meristematic cells. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 143:573–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01942-y
Mude N, Ingle A, Gade A, Rai M (2009) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using callus extract of Carica papaya—a first report. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 18:83–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03263300
Nath Tiwari K, Chandra Sharma N, Tiwari V, Deo Singh B (2000) Micropropagation of Centella asiatica “L”. A valuable medicinal herb. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 63:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010690603095
Netala VR, Kotakadi VS, Nagam V et al (2015) First report of biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous callus extract of Centella asiatica and their antimicrobial activity. Appl Nanosci 5:801–807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-014-0374-6
Osibe DA, Chiejina NV, Ogawa K, Aoyagi H (2018) Stable antibacterial silver nanoparticles produced with seed-derived callus extract of Catharanthus roseus. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46:1266–1273. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1367927
Patra A, Rai B, Rout GR, Das P (1998) Successful plant regeneration from callus cultures of Centella asiatica (Linn.) urban. Plant Growth Regul 24:13–16. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005932313180
Prieto P, Pineda M, Aguilar M (1999) Spectrophotometric quantitation of antioxidant capacity through the formation of a phosphomolybdenum complex: specific application to the determination of vitamin E. Anal Biochem 269:337–341. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0037168
Rao KP, Rao SSSM (1999) Tissue culture studies of Centella asiatica. Indian J Pharm Sci 61(6):392–394
Rashmi V, Sanjay KR (2016) Green synthesis, characterisation and bioactivity of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using Decalepis hamiltonii root extract. IET Nanobiotechnol 11:247–254. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2016.0018
Rashmi V, Kumar JP, Sanjay KR (2020) Mathematical modelling and optimization studies of photo-mediated green synthesis of 2 hydroxy 4 methoxybenzaldehyde conjugated silver nanoparticles using Decalepis hamiltonii: a note on antioxidant and nano-catalytic activi. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.833
Sabaragamuwa R, Perera CO, Fedrizzi B (2018) Centella asiatica (Gotu kola) as a neuroprotectant and its potential role in healthy ageing. Trends Food Sci Technol 79:88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.07.024
Shkryl YN, Veremeichik GN, Kamenev DG et al (2018) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using transgenic Nicotiana tabacum callus culture expressing silicatein gene from marine sponge Latrunculia oparinae. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46:1646–1658. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1388248
Singleton VL, Rossi J (1965) Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am J Enol Vitic 16:144–158. https://doi.org/10.12691/ijebb-2-1-5
Toshio M, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Xia QH, Zheng LP, Zhao PF, Wang JW (2017) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Artemisia annua callus for inhibiting stem-end bacteria in cut carnation flowers. IET Nanobiotechnol 11:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2015.0125
Acknowledgements
Authors gratefully acknowledge the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India for the financial support in the form of Senior Research Fellowship under the SRF-Direct Program to Ms. Rashmi Venkatasubbaiah (8/584 (0002)/18EMR-1) The authors also acknowledge JSS STU, Mysuru; VTU, Belagavi; SAIF-IIT Bombay for HR-TEM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RV performed tissue culture, conducted all the experiments, data analysis, and interpretation, conceptualization, and wrote the original and revised draft manuscript. HBP supervised tissue culture, review, and correction of the manuscript. KRS supervised, conceptualization, data analysis, review, and correction of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Ranjith Pathirana.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rashmi, V., Prabhushankar, H.B. & Sanjay, K.R. Centella asiatica L. callus mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles, optimization using central composite design, and study on their antioxidant activity. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 146, 515–529 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02086-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-021-02086-3