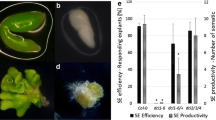
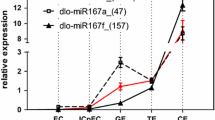
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are single-stranded small, endogenous RNAs that can downregulate gene expression in plants and animals. Plant miRNAs are already known to function in many biological processes during plant development by targeting mRNA for degradation or repression. Somatic embryogenesis is used as a model to investigate miRNAs associated with embryogenesis and also as an important pathway for plant propagation. To determine the roles of miRNAs in Arabidopsis somatic embryogenesis, we analyzed miRNA microarrays representing known miRNAs in embryonic callus before and after somatic embryo (SE) induction. After identifying several differentially expressed miRNAs from the microarray data, we focused on MIR167c encoding miR167 because of its potential involvement in SE induction. Overexpression of miR167 inhibited SE formation, showing that miR167 negatively regulates SE induction. The negative effects of miR167 on SE formation are characterized by the alteration of auxin response and local auxin transport in embryonic callus. Overexpression of miR167 resulted in low levels of auxin response factor 6 (ARF6) and ARF8 transcripts. Genetic analysis revealed that arf6 and arf8 single mutants and the arf6-2 arf8-3/+ sesquimutant displayed SE defects. Our results thus suggest that miR167 regulates somatic embryogenesis through auxin signaling components ARF6 and ARF8. This study provides important information concerning miRNA-mediated somatic embryogenesis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Birnbaum KD, Sanchez Alvarado A (2008) Slicing across kingdoms: regeneration in plants and animals. Cell 132:697–710
Carrington JC, Ambros V (2003) Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science 301:336–338
Chiou TJ (2007) The role of microRNAs in sensing nutrient stress. Plant Cell Environ 30:323–332
Friml J, Vieten A, Sauer M, Weijers D, Schwarz H, Hamann T, Offringa R, Jurgens G (2003) Efflux-dependent auxin gradients establish the apical-basal axis of Arabidopsis. Nature 426:147–153
Gaj MD (2001) Direct somatic embryogenesis as a rapid and efficient system for in vitro regeneration of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 64:39–46
Goetz M, Vivian-Smith A, Johnson SD, Koltunow AM (2006) AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR8 is a negative regulator of fruit initiation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:1873–1886
Gordon SP, Heisler MG, Reddy GV, Ohno C, Das P, Meyerowitz EM (2007) Pattern formation during de novo assembly of the Arabidopsis shoot meristem. Development 134:3539–3548
Gray WM, del Pozo JC, Walker L, Hobbie L, Risseeuw E, Banks T, Crosby WL, Yang M, Ma H, Estelle M (1999) Identification of an SCF ubiquitin-ligase complex required for auxin response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes Dev 13:1678–1691
Gray WM, Kepinski S, Rouse D, Leyser O, Estelle M (2001) Auxin regulates SCF(TIR1)-dependent degradation of AUX/IAA proteins. Nature 414:271–276
Guo HS, Xie Q, Fei JF, Chua NH (2005) MicroRNA directs mRNA cleavage of the transcription factor NAC1 to downregulate auxin signals for arabidopsis lateral root development. Plant Cell 17:1376–1386
Gutierrez L, Bussell JD, Pacurar DI, Schwambach J, Pacurar M, Bellini C (2009) Phenotypic plasticity of adventitious rooting in Arabidopsis is controlled by complex regulation of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR transcripts and microRNA abundance. Plant Cell 21:3119–3132
Hagen G, Guilfoyle T (2002) Auxin-responsive gene expression: genes, promoters, and regulatory factors. Plant Mol Biol 49:373–385
Heisler MG, Ohno C, Das P, Sieber P, Reddy GV, Long JA, Meyerowitz EM (2005) Patterns of auxin transport and gene expression during primordium development revealed by live imaging of the Arabidopsis inflorescence meristem. Curr Biol 15:1899–1911
Huang Z, Xu C, Li Y, Wang P, Li Y, Kang X (2015) Induction of somatic embryogenesis by anther-derived callus culture and plantlet ploidy determination in poplar (Populus × beijingensis). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 120:949–959
Ikeda-Iwai M, Satoh S, Kamada H (2002) Establishment of a reproducible tissue culture system for the induction of Arabidopsis somatic embryos. J Exp Bot 53:1575–1580
Jacobsen SE, Running MP, Meyerowitz EM (1999) Disruption of an RNA helicase/RNAse III gene in Arabidopsis causes unregulated cell division in floral meristems. Development 126:5231–5243
Jenik PD, Gillmor CS, Lukowitz W (2007) Embryonic patterning in Arabidopsis thaliana. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:207–236
Jiménez VM (2005) Involvement of plant hormones and plant growth regulators on in vitro somatic embryogenesis. Plant Growth Regul 47:91–110
Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Bartel B (2006) MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:19–53
Kim J, Jung JH, Reyes JL, Kim YS, Kim SY, Chung KS, Kim JA, Lee M, Lee Y, Narry Kim V, Chua NH, Park CM (2005) MicroRNA-directed cleavage of ATHB15 mRNA regulates vascular development in Arabidopsis inflorescence stems. Plant J 42:84–94
Li XM, Sang YL, Zhao XY, Zhang XS (2013) High-throughput sequencing of small RNAs from pollen and silk and characterization of miRNAs as candidate factors involved in pollen-silk interactions in maize. PLoS One 8:e72852. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072852
Liscum E, Reed JW (2002) Genetics of Aux/IAA and ARF action in plant growth and development. Plant Mol Biol 49:387–400
Liu C, Xu Z, Chua NH (1993) Auxin polar transport is essential for the establishment of bilateral symmetry during early plant embryogenesis. Plant Cell 5:621–630
Luo YC, Zhou H, Li Y, Chen JY, Yang JH, Chen YQ, Qu LH (2006) Rice embryogenic calli express a unique set of microRNAs, suggesting regulatory roles of microRNAs in plant post-embryogenic development. FEBS Lett 580:5111–5116
Mahdavi-Darvari F, Noor NM, Ismanizan I (2015) Epigenetic regulation and gene markers as signals of early somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue OrgAN Cult 120:407–422
Mallory AC, Bartel DP, Bartel B (2005) MicroRNA-directed regulation of Arabidopsis AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR17 is essential for proper development and modulates expression of early auxin response genes. Plant Cell 17:1360–1375
Mayer KF, Schoof H, Haecker A, Lenhard M, Jurgens G, Laux T (1998) Role of WUSCHEL in regulating stem cell fate in the Arabidopsis shoot meristem. Cell 95:805–815
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nagpal P, Ellis CM, Weber H, Ploense SE, Barkawi LS, Guilfoyle TJ, Hagen G, Alonso JM, Cohen JD, Farmer EE, Ecker JR, Reed JW (2005) Auxin response factors ARF6 and ARF8 promote jasmonic acid production and flower maturation. Development 132:4107–4118
Nodine MD, Bartel DP (2010) MicroRNAs prevent precocious gene expression and enable pattern formation during plant embryogenesis. Genes Dev 24:2678–2692
Rademacher EH, Möller B, Lokerse AS, Llavata-Peris CI, van den Berg W, Weijers D (2011) A cellular expression map of the Arabidopsis AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR gene family. Plant J 68:597–606
Rhoades MW, Reinhart BJ, Lim LP, Burge CB, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002) Prediction of plant microRNA targets. Cell 110:513–520
Schauer SE, Jacobsen SE, Meinke DW, Ray A (2002) DICER-LIKE1: blind men and elephants in Arabidopsis development. Trends Plant Sci 7:487–491
Schlereth A, Moller B, Liu W, Kientz M, Flipse J, Rademacher EH, Schmid M, Jurgens G, Weijers D (2010) MONOPTEROS controls embryonic root initiation by regulating a mobile transcription factor. Nature 464:913–916
Schwab R, Palatnik JF, Riester M, Schommer C, Schmid M, Weigel D (2005) Specific effects of microRNAs on the plant transcriptome. Dev Cell 8:517–527
Shiota H, Satoh R, Watabe K, Harada H, Kamada H (1998) C-ABI3, the carrot homologue of the Arabidopsis ABI3, is expressed during both zygotic and somatic embryogenesis and functions in the regulation of embryo-specific ABA-inducible genes. Plant Cell Physiol 39:1184–1193
Sieburth LE, Meyerowitz EM (1997) Molecular dissection of the AGAMOUS control region shows that cis elements for spatial regulation are located intragenically. Plant Cell 9:355–365
Su YH, Zhao XY, Liu YB, Zhang CL, O’Neill SD, Zhang XS (2009) Auxin-induced WUS expression is essential for embryonic stem cell renewal during somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 59:448–460
Talapatra S, Ghoshal N, Raychaudhuri SS (2014) Molecular characterization, modeling and expression analysis of a somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase (SERK) gene in Momordica charantia L. during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue OrgAN Cult 116:271–283
Thomson JM, Parker J, Perou CM, Hammond SM (2004) A custom microarray platform for analysis of microRNA gene expression. Nat Methods 1:47–53
Wang XJ, Reyes JL, Chua NH, Gaasterland T (2004) Prediction and identification of Arabidopsis thaliana microRNAs and their mRNA targets. Genome Biol 5:R65
Wang JW, Wang LJ, Mao YB, Cai WJ, Xue HW, Chen XY (2005) Control of root cap formation by MicroRNA-targeted auxin response factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:2204–2216
Wang Z, Hu H, Huang H, Duan K, Wu Z, Wu P (2009) Regulation of OsSPX1 and OsSPX3 on expression of OsSPX domain genes and Pi-starvation signaling in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 51:663–674
Willmann MR, Mehalick AJ, Packer RL, Jenik PD (2011) MicroRNAs regulate the timing of embryo maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 155:1871–1884
Wójcikowska B, Gaj MD (2015) LEAFY COTYLEDON2-mediated control of the endogenous hormone content: implications for the induction of somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Tissue OrgAN Cult 121:255–258
Wójcikowska B, Jaskóla K, Gasiorek P, Meus M, Nowak K, Gaj MD (2013) LEAFY COTYLEDON2 (LEC2) promotes embryogenic induction in somatic tissues of Arabidopsis, via YUCCA-mediated auxin biosynthesis. Planta 238:425–440
Wu G, Poethig RS (2006) Temporal regulation of shoot development in Arabidopsis thaliana by miR156 and its target SPL3. Development 133:3539–3547
Wu MF, Tian Q, Reed JW (2006) Arabidopsis microRNA167 controls patterns of ARF6 and ARF8 expression, and regulates both female and male reproduction. Development 133:4211–4218
Wu XM, Liu MY, Ge XX, Xu Q, Guo WW (2011) Stage and tissue-specific modulation of ten conserved miRNAs and their targets during somatic embryogenesis of Valencia sweet orange. Planta 233:495–505
Xing S, Salinas M, Hohmann S, Berndtgen R, Huijser P (2010) miR156-targeted and nontargeted SBP-box transcription factors act in concert to secure male fertility in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 22:3935–3950
Zhu S, Wang J, Ye J, Zhu A, Guo W, Deng X (2014) Isolation and characterization of LEAFY COTYLEDON 1-LIKE gene related to embryogenic competence in Citrus sinensis. Plant Cell Tissue OrgAN Cult 119:1–13
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91217308, 31170272).
Authors contribution
Conceived and designed the experiments: X.S. Zhang, Y.H. Su. Performed the experiments: Y.H. Su, Y.B. Liu, C. Zhou, X.M. Li. Analyzed the microarray data: X.S. Zhang, Y.H. Su, C. Zhou. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: Y.H. Su, Y.B. Liu, C. Zhou, X.M. Li. Wrote the paper: X.S. Zhang, Y.H. Su.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Ying Hua Su, Yu Bo Liu and Chao Zhou have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Y.H., Liu, Y.B., Zhou, C. et al. The microRNA167 controls somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis through regulating its target genes ARF6 and ARF8 . Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 124, 405–417 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0903-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0903-3