Abstract
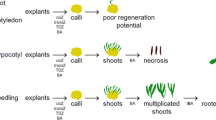
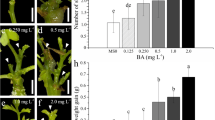
Highly efficient (>90%) protocols were developed for in vitro regeneration from de-embryonated cotyledon explants of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Phytohormone combinations and concentrations, explant source and orientation, period of incubation and the response of genotypes were examined for optimization of the regeneration efficiency. Adventitious shoot primordia could be induced from de-embryonated cotyledon explants when (1) the proximal end of the explant was kept in contact with the shoot induction medium-I supplemented with 5 mg l−1 BAP + 2 mg l−1 2,4-D for 4 weeks, or (2) the distal end was kept in contact with shoot induction medium-II supplemented with only BAP at 20 mg l−1 for the first 2 weeks, followed by subculture in the same medium containing 15 mg l−1 BAP for the next 2 weeks. Orientation of placing the explant on the above media was critical for in vitro regeneration. The factors affecting the morphogenic responses like, repetitive organogenesis, shoot elongation, in vitro flowering and rhizogenesis were examined. Shoot bud formation was genotype independent. Histological studies showed multicellular origin of adventitious shoot primordia. The protocols gave healthy and fertile plants within 4 months.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- BAP:
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- DEC:
-
De-embryonated cotyledon
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog (1962) medium
- NAA:
-
α-naphthalene acetic acid
- SIM-I :
-
Shoot induction medium-I
- SIM-II :
-
Shoot induction medium-II
References
Akasaka Y, Daimon H, Mii M (2000) Improved plant regeneration from cultured leaf segments in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) by limited exposure to thidiazuron. Plant Sci 156:169–175
Baker CM, Wetzstein HY (1998) Leaflet development, induction time, and medium influence somatic embryogenesis in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Cell Rep 17:925–929
Cheng M, His DCH, Phillips GC (1992) In vitro regeneration of valencia-type peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) from cultured petiolules, epicotyl sections and other seedling explants. Peanut Sci 19:82–87
Chengalrayan K, Mhaske VB, Hazra S (1995) In vitro regulation of morphogenesis in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Sci 110:259–268
Desai BB, Kotecha PM, Salunkhe DK (1999) Science and technology of groundnut: biology, production, processing and utilization. Naya Prokash Publ, Calcutta
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Ghewande MP, Desai S, Basu MS (2002) Diagnosis and management of major diseases of groundnut. National Research Centre for Groundnut, Junagadh
Gupta SK, Singh PK, Sawant SV, Chaturvedi R, Tuli R (2000) Effect of light intensity on in vitro multiple shoot induction and regeneration of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. cv Khandawa-2). Indian J Exp Biol 38:399–401
Kanyand M, Peterson CM, Prakash CS (1997) The differentiation of emergences into adventitious shoots in peanut, Arachis hypogaea (L.). Plant Sci 126:87–95
Li Z, Jarret RL, Demski JW (1997) Engineered resistance to tomato spotted wilt virus in transgenic peanut expressing the viral nucleocapsid gene. Transgenic Res 6:297–305
Little LI, Magbanua ZV, Parrott WA (2000) A protocol for repetitive somatic embryogenesis from mature peanut epicotyls. Plant Cell Rep 19:351–357
McKently AH, Moore GA, Gardner FP (1990) In vitro plant regeneration of peanut from seed explants. Crop Sci 30:192–196
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nakajima K, Benfey PN (2002) Signaling in and out: control of cell division and differentiation in the shoot and root. The Plant Cell 14:S265–S276
Narasimhulu SB, Reddy GM (1984) In vitro flowering and pod formation from cotyledons of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Theor Appl Genet 69:87–91
Ozias-Akins P, Anderson WF, Holbrook CC (1992) Somatic embryogenesis in Arachis hypogaea L.: genotype comparison. Plant Sci 83:103–111
Ozias-Akins P, Schnall JA, Anderson WF, Singsit C, Clemente TE, Adang MJ, Weissinger AK (1993) Regeneration of transgenic peanut plants from stably transformed embryogenic callus. Plant Sci 93:185–194
Patil RK, Nadaf HL, Sattigi HN, Hanamaratti NG, Lingappa S, Gopali JB (1995) Effect of groundnut genotypes on biology and development of Spodoptera litura (F.). Crop Improv 22:184–188
Prasad MNR, Gowda MVC (2006) Mechanisms of resistance to tobacco cutworm (Spodoptera litura F.) and their implications to screening for resistance in groundnut. Euphytica 149:387–399
Radhakrishnan T, Murthy TGK, Chandran K, Bandyopadhyay A (2001) Somatic embryogenesis in Arachis hypogaea: revisited. Aust J Bot 49:753–759
Sellars RM, Southward GM, Phillips GC (1990) Adventitious somatic embryogenesis from cultured immature zygotic embryos of peanut and soybean. Crop Sci 30:408–414
Sharma KK, Anjaiah V (2000) An efficient method for the production of transgenic plants of peanut ( Arachis hypogaea L.) through Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation. Plant Sci 159:7–19
Sharma AK, Sharma A (1980) Chromosome techniques; theory and practice. Butterworths, London, pp 71–80
Stalker HT, Moss JP (1987) Speciation cytogenetics, and utilization of Arachis species. Adv Agron 41:1–40
Thorpe TA (1980) Organogenesis in vitro. Structural, physiological, and biochemical aspects. Int Rev Cytol Suppl 11A:71–112
Van KMTT (1981) Control of morphogenesis in in vitro cultures. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 32:291–311
Yang DX, Wet ZM, An HL (2001) Transgenic peanut plants obtained by particle bombardment via somatic embryogenesis regeneration system. Cell Res 11:156–160
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to Dr. K. G. Parmeshwarappa, University of Agricultural Sciences, for providing the peanut germplasm used in the study and Council of Scientific and Industrial Research for funding the study and the fellowship to Mr. Siddharth Tiwari.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiwari, S., Tuli, R. Factors promoting efficient in vitro regeneration from de-embryonated cotyledon explants of Arachis hypogaea L.. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 92, 15–24 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-007-9297-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-007-9297-1