Abstract
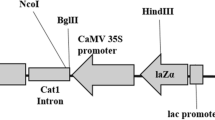
Transgenic plants of hyacinth (Hyacinthus orientalis L.) cvs. Edisson and Chine Pink have been obtained by Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Leaf explants of the both hyacinth cultivars regenerated shoots on MS medium containing 2.2 μM BAP and 0.3 μM NAA at a frequency of 95%. A. tumefaciens strain CBE21 carrying binary vector pBIThau35 was used for transformation. Plasmid pBIThau35 has been produced by cloning preprothaumatin II cDNA into pBI121 instead of uidA gene. Inoculated leaf explants formed calli and shoots at high frequency on selective medium with 100 mg l−1 kanamycin. Four hyacinth transgenic lines of cv. Chine Pink and one line of cv. Edisson have been selected on medium containing 200 mg l−1 kanamycin. The insertion of thaumatin II gene into hyacinth genome has been confirmed by PCR-analysis. All transgenic plants expressed substantial amounts of thaumatin II (between 0.06 and 0.28% of the total soluble protein). Hyacinth transgenic lines were assayed for resistance to the pathogenic fungi Fusarium culmorum and Botrytis cinerea. There were no significant differences between nontransformed control and transgenic leaves of both cultivars. At the same time the bulbs of the transgenic line Н7401 cv. Chine Pink showed the higher level of resistance to B. cinerea, the bulbs of the transgenic line Н7404 were more resistant to F. culmorum. In both cases the signs of the fungal disease were developed more slowly. The resistance of the bulbs cv. Edisson line to these fungi was not changed. All transgenic hyacinth plant were successfully transferred to soil for further evaluation.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAP:
-
6-benzylaminopurine
- CaMV:
-
Cauliflower mosaic virus
- IBA:
-
3-indolebutyric acid
- NAA:
-
Naphthaleneacetic acid
- uidA :
-
β-glucuronidase gene
References
Bach A (1992) Micropropagation of hyacinth (Hyacinthus orientalis L.). In: Bajaj YPS (ed) Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry, vol 4. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 144–159
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chen WP, Chen PD, Liu DJ, Kynast R, Friebe B, Velazhahan R, Muthukrishnan S, Gill BS (1999) Development of wheat scab symptoms is delayed in transgenic wheat plants that constitutively express a rice thaumatin-like protein gene. Theor Appl Genet 99:755–760
Datta K, Velazhan R, Oliva N, Ona I, Mew T, Khush GS, Muthukrishnan S, Datta SK (1999) Over-expression of the cloned rice thaumatin-like protein (PR-5) gene in transgenic rice plants enhances environmental friendly resistance to Rhizoctonia solani causing sheath blight disease. Theor Appl Genet 98:1138–1145
Davies C, Robinson SP (2000) Differential screening indicates a dramatic change in mRNA profiles duting grape berry ripening. Cloning and characterization of cDNA encoding putative cell wall and stress response proteins. Plant Physiol 122:803–812
Dellaporta SL, Woods J, Hicks JB (1984) Maize DNA miniprep. In: Malmberg R, Messing J, Sussex I (eds) Molecular biology of plants: a laboratory course manual. Cold Spring Harbor Press, pp 36–37
Edens L, Heslinga L, Klok R, Ledeboer AM, Maat J, Toonen MY, Visser C, Verrips CT (1982) Cloning of cDNA encoding the sweet-tasting plant protein thaumatin and its expression in Escherichia coli. Gene 18:1–12
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Kaneko R, Kitabatake N (2001) Structure–sweetness relationship in thaumatin: importance of lysine residues. Chem Senses 26:167–177
Li R, Wu N, Fan Y, Song B (1999) Transgenic potato plants expressing osmotin gene inhibits fungal development in inoculated leaves. Chin J Biotechnol 15:71–75
Li Q, Lawrence C, Xing H, Babbitt R, Bass W, Maiti I, Everett N (2001) Enhanced disease resistance conferred by expression of an antimicrobial magainin analog in transgenic tobacco. Planta 212:635–639
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Revenkova EV, Kraev AS, Skryabin KG (1993) Construction of a disarmed derivative of the supervirulent Ti plasmid pTiBo542. In: Skryabin KG (ed) Plant biotechnology and molecular biology. Pushchino Research Centre, Moscow, pp 67–76
Sage D, Hammatt N (2002) Somatic embryogenesis and transformation in Narcissus pseudonarcissus cultivars. Acta Horticult 570:247–249
Salzman RA, Tikhonova I, Bordelon BP, Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA (1998) Coordinate accumulation of antifungal proteins and hexoses constitutes a developmentally controlled defense response during fruit ripening in grape. Plant Physiol 117:465–472
Schestibratov KA, Dolgov SV (2005) Transgenic strawberry plants expressing a thaumatin II gene demonstrate enhanced resistance to Botrytis cinerea. Sci Horticult 106:177–189
Selitrennikoff CP (2001) Antifungal proteins. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2883–2894
Selitrennikoff CP, Wilson SJ, Clemons KV, Stevens DA (2000) Zeamatin, an antifungal protein. Curr Opin Anti-Infect Invest Drugs 2:368–374
Suzuki S, Nakano M (2002) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in Liliaceous ornamental plants. JARQ 36:119–127
Szwacka M, Krzymowska M, Malepszy S, Altman A, Ziv M, Izhar S (1999) Thaumatin expression in transgenic cucumber plants. In: Altman A, Ziv M, Izhar S (eds) Plant biotechnology and in vitro biology in the 21st century. Proceedings of the IXth international congress of the international association of plant tissue culture and biotechnology, pp 609–612
Szwacka M, Krzymowska M, Osuch A, Kowalczyk ME, Malepszy S (2002) Variable properties of transgenic cucumber plants containing the thaumatin II gene from Thaumatococcus daniellii. Acta Physiol Plant 24:173–185
Trudel J, Grenier J, Potvin C, Asselin A (1998) Several thaumatinlike proteins bind to b-1,3-glucans. Plant Physiol 118:1431–1438
Tukavin GB (2007) Biotehnologicheskie osnovi selekcionnoy tehnologii morkovi (Biotechnological bases of carrot breeding technology (Daucus carota L.)). Dissertation, All-Russia Research Institute of Agricultural Biotechnology, Moscow
Yun D, Ibeas J, Lee H, Coca M, Narasimhan M, Uesono Y, Hasegawa P, Pardo J, Bressan R (1998) Osmotin, a plant antifungal protein, subverts signal transduction to enhance fungal cell susceptibility. Mol Cell 1:807–817
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. A.M. Ledeboer for kindly provided pUR528:thaumatin II and Dr. V.S. Golubeva (Central botanical garden NАS of Belarus) for fungal cultures and help with fungal infection assays.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popowich, E.A., Firsov, A.P., Mitiouchkina, T.Y. et al. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Hyacinthus orientalis with thaumatin II gene to control fungal diseases. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 90, 237–244 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-007-9254-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-007-9254-z