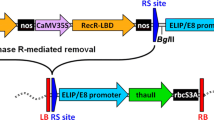
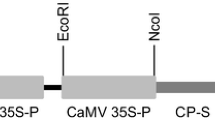
Abstract
Thaumatin represents a unique class of the sweet-tasting plant proteins. Transgenic cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) plants with stable integrated constructs consisting of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter and thaumatin II cDNA were produced. Transformed cucumber plants were obtained using Agrobacterium tumefaciens, with one, two or five integration sites in diploid cucumber and with inheritance confirmed by a 3:1 Mendelian ratio and normal morphologies and viable seeds. Inter- and intra-transformant variabilities in the expression of the thaumatin II gene were observed. The variability was independent of integrated copy number of the T-DNA. Variation in thaumatin II protein accumulation levels in the ripe fruits and the lack of correlation between protein and mRNA levels were observed, suggesting that thaumatin may be controlled at the levels of both transcription and translation. Transgenic fruits accumulating thaumatin II protein exhibited sweet phenotype and positive correation between thaumatin accumulation levels and sweet taste intensity was noticed. Thaumatin II belongs to the pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins family. Some of the T2 progeny plants expressing thaumatin II protein did not exhibit tolerance for pathogenic fungus Pseudoperonospora cubensis. These results, together with previously reported results, suggest no relationship between transgenic protein levels and the increased tolerance phenotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- 2iP:
-
6-(γ,γ-dimethyallylamino)purine
References
Bradford M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding, Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254.
Brink R.A. 1973. Paramutation, Annu. Rev. Genet. 7: 129–152.
Broglie K., Chet I., Holiday M., Cressman R., Biddle P., Knowlton S., Mauvals C.J., Broglie R. 1991. Transgenic plants with enhanced resistance to the fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani, Science 254: 1194–1197.
Burza W., Malepszy S. 1995. Direct plant regeneration from leaf explants in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) is free of stable genetic variation, Plant Breed. 114: 341–345.
Christou P., Swain W.F., Yang N.S., McCabe D.E. 1989. Inheritance and expression of foreign genes in transgenic soybean plants, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 7500–7504.
Christou P., Ford T.L., Kofron M. 1991. Production of transgenic rice (Oryza sativa) from agronomically important Indica and Japonica varieties via electric discharge particle acceleration of exogenous DNA into immature zygotic embryos, Biotechnology 9: 957–962.
Datta S.K., Peterhans A., Datta K., Potrykus I. 1990. Genetically engineered fertile indica-rice recovered from protoplasts, Biotechnology 8: 736–740.
Dellaporta S.L., Wood J., Hicks J.B. 1983. A plant DNA minipreparation: Version II. Plant Mol. Rep. 1: 19–21.
De Vos A.M., Hatada M., Van der Wel H., Kraggendam H., Peerdeman A.F., Kim S.H. 1985. Three-dimensional structure of thaumatin l, an intensely sweet protein, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82: 1406–1409.
Dolgov S.V., Lebedov V.G., Firsov A.P., Shushkova T.V., Tukavin G.B., Taran S.A., 1998. Abstract of the IX International Cong. on Plant Tissue and Cell Culture, Jerusalem, Israel, June 14–19, Kluver Academic Publishers, p. 189.
Edens L., Heslinga L., Klok R., Ledeboer A.M., Maat J., Toonen M.Y., Visser Ch., Verrips C. T. 1982. Cloning of cDNA encoding the sweet-tasting plant protein thaumatin and its expression in Escherichia coli, Gene 18: 1–12.
Goto F., Toki S., Uchimiya H. 1993. Inheritance of a co-tranferred foreign gene in the progenies of transgenic rice plants, Transgenic Res. 2: 302–305.
Hejgaard J., Jacobsen S., Svendsen I. 1991. Two antifungal thaumatin-like proteins from barley grain, FEBS Lett. 291: 127–131.
Higginbotham J.D. 1979. Protein sweeteners. in: C.A.M. Hough, K.J. Parker, A.J. Vlitos (Eds.) Developments in Sweeteners I. Applied Science, London, pp. 87–123
Hilder V.A., Gatehouse A.M.R., Sheerman S.E., Barker R.F., Boutler D. 1987. A novel mechanism of insect resistance engineered into tobacco, Nature (London) 330: 160–163.
Hobbs S.L.A., Warkentin T.D., DeLong C.M.O. 1993. Transgene copy number can be positively or negatively associated with transgene expression, Plant Mol. Biol. 21: 17–26.
Iyengar R.B., Smits P., Van der Ouderaa F., van der Wel H., van Brouvershaven J., Ravestein P., Richters G., van Wassenaar P.D. 1979. The complete amino acid sequence of the sweet protein thaumatin I, Eur. J. Biochem. 96: 193–204.
Kohli A., Gahakawa D., Vain P., Laurie D.A., Christou P. 1999. Transgene expression in rice engineered through particle bombardment: molecular factors controlling stable expression and transgene silencing, Planta 208: 88–97.
Komari T. 1989. Transformation of callus cultures of nine plant species mediated by Agrobacterium, Plant Sci. 60: 223–229.
Komari T. 1990. Genetic characterisation of a double-flowered tobacco plants obtained in a transformation experiment, Theor. Appl. Genet. 80: 167–171.
Linthorst H.J.M., Brederode F.T., van der Does C.H., Bol J.F. 1993. Tabacco proteinase inhibitor I genes are locally, but not systematically induced by stress, Plant Mol. Biol. 21: 985–992.
Malepszy S. 1988. Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.), in: Y.P.S. Bajaj (Ed.), Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry Vol. 6, Crops II, Springer Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp. 277–293.
Michelmore R., Marsh E., Seely S., Landry B. 1987. Transformation of lettuce (Lactuca sativa) mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Plant Cell Rep. 6: 439–442.
Murashige T., Skoog F. 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures, Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497.
Pearson K. 1990. On the criterion that a given system of deviations from the probable in the case of a calculated system of variables is such that it can be reasonably supported to have arisen from random sampling, Philosophical Mag. J. Sci., Fifth series 50, London, Edinburgh, Dublin, pp 157–175.
Pierpoint W.S., Jackson P.J., Evans R.M. 1990. The presence of a thaumatin-like protein, a chitinase and glucanase among the pathogenesis-related proteins of potato (Solanum tuberosum), Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 36: 325–338.
Pröls F., Meyer P. 1992. The methylation patterns of chromosomal integration regions influence gene activity of transferred DNA in Petunia hybrida, Plant J. 2: 465–475.
Puonti-Kaerlas J., Erikson T., Engstrom P. 1990. Production of transgenic pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated gene transfer, Theor. Appl. Genet. 80: 246–252.
Richardson M., Valdes-Rodriguez S., Blanco-Labra A. 1987. A possible function for thaumatin and a TMV-induced protein suggested by homology to a maize inhibitor, Nature (London) 327: 432–434.
Salmeron J.M., Vernooij B. 1998. Transgenic approaches to microbial disease resistance in crop plants, Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 1: 347–352.
Sambrook J., Fritsch E.F., Maniatis T. 1989. Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Spencer T.M., O’Brien J.V., Start W.G., Adams T.R., Gordon-Kamm W.J., Lemaux P.G. 1992. Segregation of transgenes in maize, Plant Mol. Biol. 18: 201–210.
Szwacka M., Morawski M., Burza W. 1996. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated cucumber transformation with thaumatin II cDNA, Genet. Pol. 37A: 126–129.
Szwacka M., Krzymowska M., Malepszy S. 1998. In: A. Altman, M. Ziv, S. Izhar (Eds.) Plant Biotechnology and In Vitro Biology in the 21st Century, Kluver Academic Publishers, pp 609–612.
Tabei Y., Kitade S., Nishizawa Y., Kikuchi N., Kayano T., Hibi T., Akustu K. 1998. Transgenic cucumber plants harboring a nice chitinase gene exhibit enhanced resistance to gray mold Botrytis cinarea, Plant Cell Rep. 17: 159–164.
Van der Wel H., Bel W.J. 1980. Enzymatic properties of the sweet-tasting proteins thaumatin and monellin after partial reduction, Eur. J. Biochem. 104: 413–418.
Van Loon L.C. 1985. Pathogenesis-related proteins, Plant Mol. Biol. 4: 111–116.
Vigers A.J., Roberts W.K., Selitrennikoff C.P. 1991. A new family of plant antifungal proteins, Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 4: 315–323.
Witty M. 1992. Thaumatin II: A sweet marker gene for use in plants, Methods Enzymol. 216: 441–447.
Woloshuk C.P., Meulenhoff J.S., Sela-Buurglage M., van den Elzen P.J.M., Cormelissen B.J.C. 1991. Pathogen-induced proteins with inhibitory activity against Phytophthora infestans, Plant Cell 3: 619–628.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szwacka, M., Krzymowska, M., Osuch, A. et al. Variable properties of transgenic cucumber plants containing the thaumatin II gene from Thaumatococcus daniellii . Acta Physiol Plant 24, 173–185 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-002-0009-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-002-0009-5