Abstract
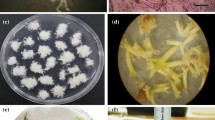
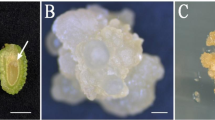
We describe a protocol for somatic embryogenesis of Protea cynaroides, with potential for high frequency production of this important horticultural species. Somatic embryos formed directly on both P. cynaroides mature zygotic embryos and excised cotyledons cultured on MS medium without growth regulators. The addition of growth regulators such as naphthalene acetic acid (NAA) (5; 13 and 27 μM) and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) (5; 11 and 23 μM), in combination with thidiazuron (TDZ) (1 μM), benzylaminopurine (BAP) (1 μM) or kinetin (1 μM) suppressed the formation of somatic embryos. After eight weeks in culture, formation of somatic embryos was observed. Zygotic explants formed the most embryos when cultured in a 12-h photoperiod in comparison to explants cultured in the dark. Up to 83% of these embryos germinated after transferal to the germination medium containing 0.3 μM GA3. Significantly fewer embryos germinated in MS medium with no growth regulators, or supplemented with higher concentrations of GA3, while low germination percentages were also observed in MS media containing casein hydrolysate and coconut water. The germination of normal somatic embryos (two separate cotyledons and a single radicle) was observed only in media containing either no growth regulators, 0.3 μM GA3 or 1 μM GA3. All embryos that germinated in high concentrations of GA3 were malformed.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- BAP:
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- GA3 :
-
Gibberellic acid
- NAA:
-
1-Naphthalene acetic acid
- PAR:
-
Photosynthetic active radiation
- TDZ:
-
Thidiazuron
References
Ammirato PV (1973) Some effects of abscisic acid on the development of embryos from caraway cells in suspension culture. Am J Bot 60(Suppl):22
Ammirato PV (1974) The effects of abscisic acid on the development of somatic embryos from cells of caraway (Carum carvi L.). Bot Gaz 135:328–337
Ammirato PV (1988) Role of ABA in regulation of somatic embryogenesis. HortScience 23:520
Ben-Jaacov J, Jacobs G (1986) Establishing Protea, Leucospermum and Serruria in vitro. Acta Hort 185:39–52
Cheng T-Y, Saka H, Voqui-Dinh TH (1980) Plant regeneration from soybean cotyledonary node segments in culture. Plant Sci Lett 19:91–99
George EF (1993) Plant propagation by tissue culture. Part 1: In Theory. 2nd edn. Exegetics Ltd. Edington, Wilts. BA13 4QG, England
Gingas VM, Lineberger RD (1989) Asexual embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Quercus. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 17:191–203
Hisajima S (1982) Multiple shoot formation from almond embryos. Biol Plant 24:235–238
Kochba J, Button J, Spiegel-Roy P, Bornman CH, Kochba M (1974) Stimulation of rooting of citrus embryoids by gibberellic acid and adenine sulphate. Ann Bot 38:795–802
Lauzer D, Dallaire S, Vincent G (2000) In vitro propagation of reed grass by somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 60:229–234
Lazzeri PA, Hildebrand DF, Collins GB (1987) Soybean somatic embryogenesis: Effects of nutritional, physical and chemical factors. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 10:209–220
Lu C-Y, Vasil IK (1982) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in tissue cultures of Panicum maximum Jacq. Am J Bot 69:77–81
May RA, Trigiano RN (1991) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaves of Dendranthema grandiflora. J Am Soc Hort Sci 116:366–371
Mullins MG, Srinivasan C (1976) Somatic embryos and plantlets from an ancient clone of the grapevine. (cv. Cabernet-Sauvignon) by apoximis in vitro. J Exp Bot 27:1022–1030
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Plata E, Viéitez AM (1990) In vitro regeneration of Camellia reticulata by somatic embryogenesis. J Hort Sci 65:707–714
Rugge BA (1995) Micropropagation of Protea repens. Acta Hort 387:121–127
Rugge BA, van der Merwe P, Jacobs G, Theron K (1989) Light microscopy of somatic embryogenesis from shoots of micropropagated Serruria florida (Proteaceae). Proc Microsc Soc S Afr 19:93–94
Rugini E (1988) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in olive (Olea europaea L.). Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 14:207–214
SAS Institute Inc. (1996) The SAS system for Windows. SAS Institute Inc, SAS Campus drive, Cary, North Carolina, USA
Sharp WR, Sondahl MR, Caldas LS, Maraffa SB (1980) The physiology of in vitro asexual embryogenesis. Hortl Rev 2:268–310
Van Staden J, Choveaux NA, Gilliland MG, McDonald DJ, Davey JE (1981) Tissue culture of South African Proteacea. 1. Callus and proteoid rootlet formation on cotyledonary explants of Protea neriifolia. S Afr J Sci 77:493–495
Wu HC (2006) Improving in vitro propagation of Protea cynaroides L. (King Protea) and the roles of starch and phenolic compounds in the rooting of cuttings. PhD thesis. Department of Plant Production and Soil Science, University of Pretoria, South Africa
Wu HC, du Toit ES (2004) Reducing oxidative browning during in vitro establishment of Protea cynaroides. Sci Hort 100:355–358
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H.C., du Toit, E.S. & Reinhardt, C.F. A protocol for direct somatic embryogenesis of Protea cynaroides L. using zygotic embryos and cotyledon tissues. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 89, 217–224 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-007-9242-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-007-9242-3