Abstract
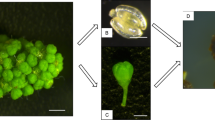
Embryos were obtained using liquid medium culture of sunflower hypocotyl epidermis layers according to the Pélissier et al. (1990) method. In the present work we identified genetic factors controlling somatic embryogenesis and we evidenced the role of ionic channels in embryogenic tissues. Two traits, the number of embryogenic explants (EE) and the number of embryos (EM) were scored in 74 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) from a cross between lines PAC-2 and RHA-266. Analysis of variance indicated the existence of highly significant differences among the parental genotypes and their RILs. Heritability for the somatic embryogenesis traits studied were high (0.64 for EE and 0.77 for EM). Four quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for EE and seven for EM were detected using composite interval mapping. The QTLs for EE explained 48% of the phenotypic variation while the QTLs for EM explained about 89% of the variation, thus revealing several genomic regions related to somatic embryogenesis control in sunflower. In order to study the distribution of ion channels in somatic embryos as compared to zygotic ones, we used a fluorescent-labelled phenylalkylamine, DM-Bodipy PAA, as a probe. Fluorescence labelling was determined by confocal microscopy. The probe intensively labelled the protoderm and epidermis cells in both zygotic and somatic embryos. Callus exhibited labelling on sites where somatic embryos developed. Considering that the location of phenylalkylamine (PAA) binding sites is related to the distribution of ion channels, the high intensity in the protoderm and epidermis of embryos, point to similar properties and functions and their key role in embryo development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EE:
-
embryogenic explants
- EM:
-
number of embryos
- PAA:
-
phenylalkylamine
- QTLs:
-
quantitative trait loci
- RILs:
-
recombinant inbred lines
References
Basten CJ, Weir BS & Zeng ZB (1999) QTL Cartographer Version 1.13: programme in statistical genetics. Department of statistics North Carolina State University.
AR Bolandi M Branchard G Alibert L Gentzbittel A Berville A Sarrafi (2000) ArticleTitleCombining ability analysis of somatic embryogenesis from epidermis layers in sunflower Theor. Appl. Genet. 100 621–624
M Carola T Trabace F Sunseri (1997) ArticleTitleHigh frequency of plant regeneration in sunflower from cotyledon via somatic embryogenesis Plant Cell Rep. 16 295–298
E Flores-Berrios L Gentzbittel G Alibert A Sarrafi (2000) ArticleTitleGenotypic variation and chromosomal location of QTLs for somatic embryogenesis revealed by epidermal layers culture of recombinant inbred lines in sunflower Theor. Appl. Genet. 101 1307–1312
L Gentzbittel S Mouzeyar S Badaoui E Mestries F Vear D Tourvielle Labrouhe Particlede P Nicolas (1998) ArticleTitleCloning of molecular markers for disease resistance in sunflower Theor Appl. Genet. 96 519–525
L Gentzbittel E Mestries S Mouzeyar F Mazeyrat S Badaoui F Vear D Tourvielle Labrouhe Particlede P Nicolas (1999) ArticleTitleA composite map of over expressed sequences and phenotypic traits of the sunflower genome Theor. Appl. Genet. 99 218–234
G Jeannin R Bronner G Hahne (1995) ArticleTitleSomatic embryogenesis and organogenesis induced on the immature zygotic embryo of sunflower cultivated in vitro: role of sugar Plant Cell Rep. 15 200–204
CS Haley SA Knott (1992) ArticleTitleA simple regression method for mapping quantitative trait loci in line crosses using flanking markers Heredity 69 315–324
MJ Kearsey HS Pooni (1996) The genetical analysis of quantitative traits Chapman & Hall London, UK
HG Knaus T Moshammer HC Kang RP Haugland H Glossmann (1992) ArticleTitleA unique fluorescent phenylalkylamine probe for L-type Ca2+-channels J. Biol. Chem. 267 2179–2189
P Lu R Porat JA Nadeau SD O’Neill (1996) ArticleTitleIdentification of a meristem L1 layer specific gene in Arabidopsis that is expressed during embryonic pattern formation and defines a new class of homeobox genes Plant Cell 8 2155–2168 Occurrence Handle10.1105/tpc.8.12.2155
T Murashige F Skoog (1962) ArticleTitleA revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures Physiol. Plant 15 473–497
JS Nonohay JEA Mariath H Winge (1999) ArticleTitleHistological analysis of somatic embryogenesis in Brazilian cultivars of barley Plant Cell Rep. 18 929–934
DK Norris HF Bradford (1985) ArticleTitleOn the specificity of verapamil as a calcium channel blocker Biochem. Pharmacol. 34 1953–1956
P Pelissier O Bouchefra R Pépin G Freyssinet (1990) ArticleTitleProduction of isolated somatic embryos from sunflower thin cell layers Plant Cell Rep. 9 47–50
P Thuleau A Graziana H Canut R Ranjeva (1990) ArticleTitleA 75 kDa polypeptide, located primarily at the plasma membrane of carrot cell-suspension cultures, is photoaffinity labelled by the calcium channel blocker LU 49888 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87 10000–10004
ACJ Timmers HD Reiss J Boshung K Traxel JHN Schel (1996) ArticleTitleLocalization of calcium during somatic embryogenesis of carrot Protoplasma 190 107–118
N Vallée C Brière M Petitprez A Souvré G Alibert (1997) ArticleTitleStudies on ion channel antagonist binding sites in sunflower protoplasts FEBS Lett. 411 115–118
CW Vroemen S Langeveld U Mayer G Ripper G Jürgens A Kammen ParticleVan SC Vries Particlede (1996) ArticleTitleFormation in the Arabidopsis embryo revealed by position-specific lipid transfer protein gene expression Plant Cell 8 783–791
Y Wan TR Rocheford JM Widholm (1992) ArticleTitleRFLP analysis to identify putative chromosomal regions involved in the anther culture response and callus formation in maize Theor. Appl. Genet. 85 360–365
XuHan Xu C Brière N Vallée C Borin A Lammeren Particlevan G Alibert A Souvré (1999) ArticleTitleIn vivo labelling of sunflower embryonic tissues by fluorescently labelled phenylalkylamine Protoplasma 210 52–58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petitprez, M., Sarrafi, A., Flores-Berrios, E. et al. Somatic embryogenesis by liquid culture of epidermal layers in sunflower: from genetic control to cell development. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 81, 331–337 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-004-6661-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-004-6661-2