Abstract
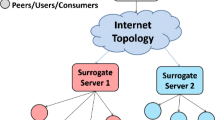
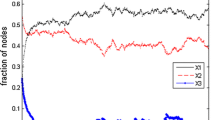
In recent years, the rapid growth of peer-to-peer (P2P) networks has provided a new paradigm for content distribution. To improve the efficiency of a P2P system, it is important to provide incentives for the peers to participate and contribute their resources. Various attempts have been made to reward/penalize peers by providing service differentiation based on a requesting peer’s history or reputation. However, in a truly distributed, non-cooperative environment, maintaining and preventing the untruthful revealing of such information within the community impose larger computation and communication overheads to the system. These problems are further magnified when large-volume contents are being distributed because of the length distribution processes and the update of history or reputation has to keep up with the distribution process. In this paper, we address the incentive provisioning problem for distribution of large-volume content in P2P networks, and present a “seeing-is-believing” incentive-compatible mechanism (protocol) in which a peer will decide how much resources will be assigned to which neighbors based on what it has experienced. The protocol applies a utility-based resource-trading concept where peers will maximize their contributions for a fair or better return, and we show that by adopting this protocol, the system will achieve Cournot Equilibrium. Furthermore, our protocol is lightweight, completely decentralized, and cheat-proof. Experimental results illustrate significant improvements on the distribution efficiency of our protocol over other adopted alternatives.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Aberer and Z. Despotovis, Managing trust in a peer-2-peer information system, in: Proc. of the Ninth International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM 2001) (Atlanta, GA, 2001) pp. 310–317.
K.G. Anagnostakis and M.B. Greenwald, Exchange-based incentive mechanisms for peer-to-peer file sharing, in: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS ‘04) (Tokyo, Japan, 2004) pp. 524–533.
P. Antoniadis, C. Courcoubetis and R. Mason, Comparing economic incentives in peer-to-peer networks. Computer Networks 46 (2004) 133–146.
J. Borland, Survey: Movie-swapping up; Kazaa down. CNET News.com. [Online] http://news.com.com/2100-1025-5267992.html (2004).
S. Buchegger and J.-Y. le Boudec, A robust reputation system for P2P and mobile ad-hoc networks, in: Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Economics of Peer-to-Peer Systems (Cambridge, MA, 2004)
C. Buragohain, D. Agrawal and S. Suri, A game theoretic framework for incentives in P2P systems, in: Proc. of the Third Interanationl Conference on Peer-to-Peer Computing (P2P’03) (2003) pp. 48–56.
B. Cohen, Incentives build robustness in BitTorrent, in: Proc. of the First Workshop on Economics of Peer-to-Peer Systems (Berkeley, CA, 2003).
A. Cournot, Research into the Mathematical Principles of the Theory of Wealth (Wiley, New York, 1960).
J. Dilley, B. Maggs, J. Parikh, H. Prokop, R. Sitaraman and B. Weihl, Globally distributed content delievery, IEEE Internet Computing (2002) 50–58.
eDonkey, [Online] http://www.edonkey2000.com/
Z. Ge, D.R. Figueiredo, S. Jaiswal, J. Kurose and D. Towsley, Modeling peer-peer file sharing system, in: Proceedings of the INFOCOM 2003 (San Francisco, CA, 2003).
D. Ghosal, B.K. Poon and K. Kong, P2P contracts: a framework for resource and service exchange. Future Generation Computer Systems 21(3) (2005) 333–347.
A. Halberstadt, L. Mui and M. Mohtashemi, A computational model of trust and reputation, in: Proc. of the 35th Hawaii International Conference on System Science (HICSS), (2002) pp. 2431–2439.
G. Hardin, The tradegy of the commons, Science 162 (1968) 1243–1248.
R. Jurca and B. Faltings, An incentive compatible reputation mechanism, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on e-Commerce (Newport Beach, CA, 2003) pp. 285–292.
S.D. Kamvar, M.T. Schlosser and H. Garcia-Molina, The eigentrust algorithm for reputation management in P2P networks, in: Proc. of the Twelfth International World Wide Web Conference (2003) pp. 640–651.
S.G.M. Koo, K. Kannan and C.S.G. Lee, A genetic-algorithm-based neighbor-selection strategy for hybrid peer-to-peer networks, in: Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN’04) (Chicago, IL, 2004) pp. 469–474.
S.G.M. Koo, C. Rosenberg and D. Xu, Analysis of parallel downloading for large file distribution, in: Proc. of the 9th IEEE International Workshop on Future Trends of Distributed Computing Systems (FTDCS 2003) (San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2003) pp. 128–135.
H.T. Kung and C. Wu, Differentiated admission for peer-to-peer systems: Incentivizing peers to contribute their resources, in: Proc. of the 2nd International Workshop on Peer-to-Peer Systems (IPTPS ‘03) (Berkeley, CA, 2003).
K. Lai, M. Feldman, I. Stoica and J. Chuang, Incentives for cooperation in peer-to-peer networks, in: Proceedings of the First Workshop on Economics of Peer-to-Peer Systems (Berkeley, CA, 2003).
J. Liang, R. Kumar, Y. Xi and K. Ross, Pollution in P2P file sharing systems, in: Proc. of the INFOCOM (Miami, FL, 2005).
D.G. Luenberger, Microeconomic Theory (McGraw-Hill, 1997).
R.T. B. Ma, S.C.M. Lee, J.C.S. Lui and D.K.Y. Yau, An incentive mechanism for P2P networks, in: Proc. of the 24th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS ‘04) (Tokyo, Japan, 2004) pp. 516–523.
T. Moreton and A. Twigg, Trading in trust, tokens, and stamps, in: Proc. of the First Workshop on Economics of Peer-to-Peer Systems (Berkeley, CA, 2003).
T.-W. Ngan, D. Wallach and P. Druschel, Enforcing fair sharing of peer-to-peer resources, in: Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Peer-to-Peer Systems (IPTPS ‘03) (Berkeley, CA, 2003).
A. Odlyzko, The case against micropayments, in: J. Camp and R. Wright (eds.), Financial Cryptography 2003 (Springer, 2003).
D. Qiu and R. Srikant, Modeling and performance analysis of BitTorrent-like peer-to-peer networks, in: Proc. of the ACM SIGCOMM (Portland, OR, 2004) pp. 367–378.
P. Resnick, R. Zeckhauser, E. Friedman and K. Kuwabara, Reputation systems. Commmunications of the ACM 43(12) (2000) 45–48.
S. Skenker, Fundamental design issues for the future internet, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 13(7) (1995) 1176–1188.
A. Stavrou, D. Rubenstein and S. Sahu, A lightweight, robust P2P system to handle flash crowds, in: Proceedings of the IEEE ICNP 2002 (Paris, France, 2002).
K. Tamilmani, V. Pai and A. Mohr, SWIFT: A system with incentives for trading, in: Proc. of the Second Workshop on Economics of Peer-to-Peer Systems (Cambridge, MA, 2004).
X. Yang and G. de Veciana, Service capacity of peer to peer networks, in: Proc. of the INFOCOM 2004 (Hong Kong, 2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Simon G. M. Koo is currently an Assistant Professor of Mathematics and Computer Science at the University of San Diego. H received his B. Eng. (Hons) in Information Engineering from the Chinese University of Hong Kong in 1997, M.S.E.E. from Polytechnic University, Brooklyn, in 1999, M.S. in Operations Research from Columbia University, NY, in 2001, and his Ph.D. from the School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, in 2005. His current research include peer-to-peer networks, distributed mechanism design, performance modeling, and location-aware wireless applications. He is a member of IEEE, ACM and Sigma Xi. He is also listed in Who's Who of Emerging Leaders in 2007.
C. S. George Lee received the B.S. and M.S. degrees in Electrical Engineering from Washington State University in 1973 and 1974, respectively, and the PhD degree from Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN in 1978.In 1978–1979, he taught at Purdue University, and in 1979–1985, at the University of Michigan. Since 1985, he has been with the School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, where he is currently Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering.His current research focuses on humanoid robotics, distributed mobile robots, and neuro-fuzzy systems. He has authored or co-authored over 150 publications in these areas, in addition to 20 book chapters and two graduate textbooks. Dr. Lee was an IEEE Computer Society Distinguished Visitor in 1983–1986, the Organizer and Chairman of the 1988 NATO Advanced Research Workshop on Sensor-Based Robots: Algorithms and Architectures. He also served as Secretary and Vice-President for Technical Affairs of the IEEE Robotics and Automation Society (RAS) in 1988–1990 and 1990–1995, respectively. He was Program Chair of the 1996 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation in Minneapolis, MN and the 1998 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems in Victoria, B.C., Canada. Dr. Lee served as an Administrative Committee member and a Distinguished Lecturer of the IEEE RAS, and the General Chair of the 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems held in Las Vegas, Nevada, on October 26–31, 2003. He currently serves as General Co-Chair of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation to be held in Orlando, Florida, on May 15–19, 2006. Dr. Lee has directed over 20 Ph.D. dissertations. He is an IEEE Fellow and a recipient of the IEEE Third Millennium Medal Award.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koo, S.G.M., Lee, C.S.G. An incentive-compatible mechanism for efficient distribution of bulk contents on peer-to-peer networks. Telecommun Syst 34, 81–90 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-006-9021-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-006-9021-1