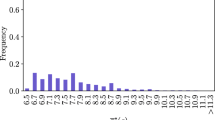
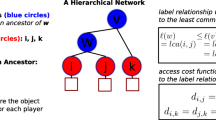
Abstract
Content Distribution Networks (CDNs) are widely used to distribute data to large number of users. Traditionally, content is being replicated among a number of surrogate servers, leading to high operational costs. In this context, Peer-to-Peer (P2P) CDNs have emerged as a viable alternative. An issue of concern in P2P networks is that of free riders, i.e., selfish peers who download files and leave without uploading anything in return. Free riding must be discouraged. In this paper, we propose a criterion, the Give-and-Take (G&T) criterion, that disallows free riders. Incorporating the G&T criterion in our model, we study a problem that arises naturally when a new peer enters the system: viz., the problem of downloading a ‘universe’ of segments, scattered among other peers, at low cost. We analyse this \(\mathcal {N}\mathcal {P}-\)hard problem, and characterize the optimal download cost under the G&T criterion. We propose an optimal algorithm, and provide a sub-optimal algorithm that is nearly optimal, but runs much more quickly; this provides an attractive balance between running time and performance. Finally, we compare the performance of our algorithms with that of a few existing P2P downloading strategies in use. We also study the computation time for prescribing the strategy for initial segment and peer selection for the newly arrived peer for various existing and proposed algorithms, and quantify cost–computation time trade-offs.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
X c denotes the complement of set X.
Peer 0’s augmented set will always be considered for exchange. Hence, the order of peers in which exchanges are carried out by peer 0 also matters.
We note that all minimum cost set cover solutions are considered in arriving at Γ∗,e.
For solving set cover problem, we write the same as binary integer program. We use bintprog function of the Optimization toolbox, MATLAB 2013b for evaluating the solution. Bintprog uses the branch and bound method for solving binary integer program.
References
Aggarwal V, Feldmann A and Scheideler C 2007 Can isps and p2p users cooperate for improved performance? SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 37: 29–40
Alon N, Moshkovitz D and Safra S 2006 Algorithmic construction of sets for k-restrictions. ACM Trans. Algorithms 2: 153–177
Caprara A, Toth P and Fischetti M 2000 Algorithms for the set covering problem. Ann. Oper. Res. 98: 353–371
Choffnes D R and Bustamante F E 2008 Taming the torrent: a practical approach to reducing cross-isp traffic in peer-to-peer systems. IGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 38: 363–374
Chvatal V 1979 A greedy heuristic for the set-covering problem. Math. Oper. Res. 4: 233–235
Feige U 1998 A threshold of ln n for approximating set cover. J. ACM 45: 634–652
Feldman M and Chuang J 2005 Overcoming free-riding behavior in peer-to-peer systems. SIGecom Exch. 5: 41–50
Feldman M, Papadimitriou C, Chuang J and Stoica I 2006 Free-riding and whitewashing in peer-to-peer systems, pp. 1010–1019
Karakaya M, Korpeoglu I and Ulusoy O 2009 Free riding in peer-to-peer networks. Internet Comput. IEEE, 13: 92–98
Liao W C, Papadopoulos F and Psounis K 2007 Performance analysis of bittorrent-like systems with heterogeneous users. Perform. Eval. 64: 876–891
Locher T, Moor P, Schmid S and Wattenhofer R 2006 Free Riding in BitTorrent is Cheap, in: Fifth Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks (HotNets-V), Irvine, CA, US
Menasché D S, Rocha A A A, de Souza e Silva E A, Leão R M, Towsley D and Venkataramani A 2010 Estimating self-sustainability in peer-to-peer swarming systems. Perform. Eval. 67: 1243–1258
Nishida H and Nguyen T 2010 A global contribution approach to maintain fairness in p2p networks. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst., 21: 812–826
Plissonneau L, Costeux J L and Brown P 2005 Analysis of peer-to-peer traffic on adsl, in: Dovrolis, C (Ed.), Passive and Active Network Measurement. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer. volume 3431 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 69–82
Pouwelse J, Garbacki P, Epema D and Sips H 2005 The bittorrent p2p file-sharing system: Measurements and analysis, in: Castro, M., Renesse, R. (Eds.), Peer-to-Peer Systems IV. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. volume 3640 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 205–216
Rahman R, Meulpolder M, Hales D, Pouwelse J, Epema D and Sips H 2010 Improving efficiency and fairness in p2p systems with effort-based incentives, in: Communications (ICC), 2010 IEEE International Conference on, pp. 1–5
Sharma P, Bhakuni A and Kaushal R 2013 Performance analysis of bittorrent protocol, in: National Conference on Communications (NCC), 2013, pp. 1–5
Typpi T 2009 Game theory in peer-to-peer networks, in: Seminar on Internetworking, Spring 2009
Vakali A and Pallis G 2003 Content delivery networks: status and trends. Internet Comput. IEEE 7: 68–74
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
AGGARWAL, S., KURI, J. & SAHA, C. Give-and-take based peer-to-peer content distribution networks. Sadhana 39, 843–858 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-014-0266-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-014-0266-1