Abstract
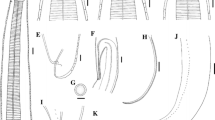
Baylisascaris transfuga (Rudolphi, 1819) is a common parasitic nematode in the digestive tract of various species of bears worldwide, with great veterinary significance. However, our present knowledge on the morphology of B. transfuga remains insufficient. In the present study, the detailed morphology of B. transfuga was studied using light and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), based on specimens collected from the polar bear Ursus maritimus Phipps (Carnivora: Ursidae) in the Shijiazhuang Zoo, China. The results revealed some morphological and morphometric variation between the present specimens and some of those from previous studies, including oesophageal length of female, number and morphology of postcloacal papillae and morphology of tail of males. Present SEM observations clearly showed the detailed morphology of lips, cervical alae, cloacal ornamentation, precloacal medioventral papilla, phasmids and tail tip. These supplementary morphological and morphometric data enable us to identify this ascaridid nematode more accurately.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baylis, H. A., & Daubney, R. (1922). Report on the parasitic nematodes in the collection of the Zoological Survey of India. Memoirs of the Indian Museum, 7, 263–347.
Bauer, C. (2013). Baylisascariosis—Infections of animals and humans with ‘unusual’ roundworms. Veterinary Parasitology, 193, 404–412.
Testini, G., Papini, R., Lia, R. P., Parisi, A., Dantas-Torres, F., Traversa, D., et al. (2011). New insights into the morphology, molecular characterization and identification of Baylisascaris transfuga (Ascaridida, Ascarididae). Veterinary Parasitology, 175, 97–102.
Sprent, J. F. A. (1968). Notes on Ascaris and Toxascaris, with a definition of Baylisascaris gen. nov. Parasitology, 58, 185–198.
Fagerholm, H.-P. (1991). Systematic implications of male caudal morphology in ascaridoid nematode parasites. Systematic Parasitology, 19, 215–228.
Li, L., Gibson, D. I., & Zhang, L.-P. (2016). An annotated catalogue of the ascaridoid parasites of Chinese vertebrates. Systematic Parasitology, 93, 1–35.
Skryabin, K. I., Schikhobalova, N. P., & Mozgovoi, A. A. (1951). Key to Parasitic Nematodes. Volume II Oxyurata and Ascaridata. Izdatei'stvo Akademii Nauk SSSR: Moskva, pp. 1–631 (In Russian).
Mozgovoi, A. A. (1953). Principles of nematodology. Vol. II. Ascaridata of animals and man and the diseases caused by them. Part II. Moscow: Izdatel’stvo Akademii Nauk SSSR, pp. 1–616 (In Russian).
Tenora, F., Mituch, J., & Hovorka, I. (1989). Scanning electron microscopic study on Toxascaris transfuga (Rudolphi, 1819) (Nematoda). Folia Parasitologica, 36, 371–374.
Okoshi, S., Takashio, M., & Nakagawa, S. (1961). Toxascaris transfuga (Rudolphi, 1819) Baylis & Daubney 1922, found in captive bears in Japan. The Japanese Journal of Veterinary Science, 24, 151–155.
Uni, S., & Takada, S. (1981). Comparison of scanning electron microscopy on Baylisascaris transfuga, Toxascaris leonina and Ascaris lumbricoides (Nematoda: Ascaridida). Japanese Journal of Parasitology, 30, 187–195.
Wu, J., He, G.-Z., & Hu, H.-G. (1987). Study on a new species, Toxascaris ailuri sp. n. (Nematoda: Ascaridae) from red panda. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 3, 1–3 (In Chinese).
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 32170442, 31750002).
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional, national and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Chen, HX. Further studies on the morphology of Baylisascaris transfuga (Rudolphi, 1819) (Nematoda: Ascaridomorpha: Ascarididae) from the polar bear Ursus maritimus Phipps (Carnivora: Ursidae). Syst Parasitol 100, 283–289 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-023-10087-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-023-10087-3