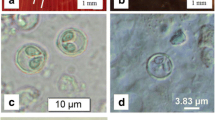
Abstract
The southern striped shiner, Luxilus chrysocephalus isolepis (Hubbs & Brown) is a relatively large minnow belonging to the true minnow family Leuciscidae Bonaparte. Between May 2020 and January 2022, 55 L. c. isolepis were collected from watersheds in Montgomery (n = 6), Polk (n = 17) and Sevier (n = 32) counties, Arkansas, USA, and their gills, gallbladders, urinary bladders, fins, integument, other major organs, and musculature were examined for myxozoans. Gills of 11 (34%) individual southern striped shiners from Sevier County were infected with a new myxozoan, Myxobolus carlhubbsi n. sp. A qualitative and quantitative morphological description was based on formalin-fixed preserved myxospores, and molecular data consisted of a 1,970 base pair sequence of the partial small subunit rRNA gene from ethanol-preserved specimens. Histologically, plasmodia filled and expanded interlamellar troughs. Hyperplastic epithelial and goblet cells filled interlamellar troughs adjacent to plasmodia, but inflammatory response was limited to scattered lymphocytes. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that M. carlhubbsi n. sp. is a member of a clade of species with pyriform myxospores parasitizing North American Pogonichthyinae Girard and North American and Eurasian Leuciscinae Bonaparte. This is the first report of a myxozoan from L. c. isolepis. This article was registered in the Official Register of Zoological Nomenclature (ZooBank) as urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D10D71C2-2C75-4A1C-80ED-B98FF36CB509.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bahri, S., Andree, K. B., & Hedrick, R. P. (2003). Morphological and phylogenetic studies of marine Myxobolus spp. from mullet in Ichkeul Lake, Tunisia. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 50, 463–470. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2003.tb00272.x
Boschung, Jr., H. T., & Mayden, R. L. (2004). Fishes of Alabama. Washington, D. C.: Smithsonian Books, 736 pp.
Bush, A. O., Lafferty, K. D., Lotz, J. M., & Shostak, A. W. (1997). Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. Journal of Parasitology 83, 575–583. https://doi.org/10.2307/3284227
Bütschli, O. (1882). Myxosporidia. In: Dr. H. G. Bronn’s Klassen und Ordnungen des Their-Reichs. II. C. F. Winter, Leipzig, pp. 590–603.
Camus, A. C., & Griffin, M. J. (2010). Molecular characterization and histopathology of Myxobolus koi infecting the gills of a koi, Cyprinus carpio, with an amended morphological description of the agent. Journal of Parasitology 96, 116–124. https://doi.org/10.1645/ge-2113.1
Cech, G., Molnár, K., & Székely, Cs. (2012). Molecular genetic studies on morphologically indistinguishable Myxobolus spp. infecting cyprinid fishes, with the description of three new species, M. alvarezae sp. nov., M. sitjae sp. nov., and M. eirasianus sp. nov. Acta Parasitologica 57, 354–366. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-012-0045-2
Clopton, R. E. (2004). Standard nomenclature and metrics of plane shapes for use in gregarine taxonomy. Comparative Parasitology 71, 130–140. https://doi.org/10.1654/4151
Cloutman, D. G., & Rogers, W. A. (2005). Determination of the Dactylogyrus banghami complex (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) from North American Gulf of Mexico coastal drainages with descriptions of three new species. Comparative Parasitology 72, 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1654/4045
Cone, D. K., Yang, J., Sun, G. L., & Easy, R. (2005). Taxonomy and molecular phylogeny of Myxobolus bilobus n. sp. (Myxozoa) parasitizing Notemigonus crysoleucas (Cyprinidae) in Algonquin Park, Ontario, Canada. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 66, 227–232. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao066227
Desser, S. S., & Paterson, W. B. (1978). Ultrastructural and cytochemical observations on sporogenesis of Myxobolus sp. (Myxosporida: Myxobolidae) from the common shiner Notropis cornutus. Journal of Protozoology 25, 314–326. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.1978.tb03897.x
Easy, R., & Cone, D. (2009). Taxonomy of Myxobolus ridouti n. sp. and M. ridgwayi n. sp. (Myxozoa) from Pimephales notatus and Semotilus atromaculatus (Cypriniformes) in Ontario. Journal of Parasitology 95, 1446–1450. https://doi.org/10.1645/ge-2232.1
Eiras, J. C., Cruz, C. F., Saraiva, A., & Adriano, E. A. (2021). Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus (Cnidaria, Myxozoa, Myxosporea) described between 2014 and 2020. Folia Parasitologica 68, 012. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2021.012
Eiras, J., Molnar, C. K., & Lu, Y. S. (2005). Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Myxobolidae). Systematic Parasitology 61, 1–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-004-6343-9
Eiras, J. C., Zhang, J., & Molnár, K. (2014). Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea, Myxobolidae) described between 2005 and 2013. Systematic Parasitology 88, 11–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-014-9484-5
Ferguson, J. A., Atkinson, S. D., Whipps, C. M., & Kent, M. L. (2008). Molecular and morphological analysis of Myxobolus spp. of salmonid fishes with the description of a new Myxobolus species. Journal of Parasitology, 94, 1322–1334. https://doi.org/10.1645/ge-1606.1
Fiala, I., Bartoŝová-Sojková, P., & Whipps, C. M. (2015). Classification and phylogenetics of Myxozoa. pp. 85–110 in B. Okamura et al. (eds.). Myxozoan Evolution, Ecology and Development, Spring International Publishing, Switzerland, 456 pp.
Gilbert, C. R. (1980). Notropis chrysocephalus (Rafinesque), Striped Shiner. pp. 256 in D. S. Lee et al., Atlas of North American Freshwater Fishes. Raleigh, North Carolina: North Carolina State Museum of Natural History, 854 pp.
Gruber, A. R., Lorenz, R., Bernhart, S. H., Neuböck, R., & Hofacker, I. L. (2008) The Vienna RNA websuite. Nucleic Acids Research 36, 70-74.
Guo, Q., Huang, M., Liu, Y., Zhang, X., & Gu, Z. (2018). Morphological plasticity in Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882: a taxonomic dilemma case and renaming of a parasite species of the common carp. Parasites & Vectors 11, 339. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-2943-0
Hambrick, P. S., Jr., & Hibbs, R. G. (1976). Spring diel feeding activity of the Southern Striped Shiner, Notropis chrysocephalus isolepis Hubbs and Brown, in Bayou Sara, Louisiana. Proceedings of the Louisiana Academy of Science 39, 16–18.
Hoffman, G. L. (1999). Parasites of North American Freshwater Fishes. 2nd ed. Ithaca, New York: Comstock Publishing Associates, 539 pp. https://doi.org/10.7591/9781501735059
Holzer, A. S., Wootten, R., & Sommerville, C. (2007). The secondary structure of the unusually long 18S ribosomal RNA of the myxozoan Sphaerospora truttae and structural evolutionary trends in the Myxozoa. International Journal of Parasitology 37, 1281–1295.
ICZN (2012). International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature: Amendment of articles 8, 9, 10, 21 and 78 of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature to expand and refine methods of publication. Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature, 69, 161–169. https://doi.org/10.21805/bzn.v69i3.a8.161
ICZN (International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature). (2017). Declaration 45 – Addition of recommendations to Article 73 and of the term “specimen, preserved” to the glossary. Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature 73, 96–97. https://doi.org/10.21805/bzn.v73i2.a2
Kerpedjiev, P., Hammer, S., & Hofacker, I. L. (2015) Forna (force-directed RNA): Simple and effective online RNA secondary structure diagrams. Bioinformatics 31, 3377-3379.
Ksepka, S. P., Hickson, B. H., Whelan, N. V., & Bullard, S. A. (2020a). A new species of Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882 (Bivalvulida: Myxobolidae) infecting stratum spongiosum of the imperiled sicklefin redhorse, Moxostoma sp. (Cypriniformes: Catostomidae) from the Little Tennessee River, North Carolina, USA. Folia Parasitologica 67, 030. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2020a.030
Ksepka, S. P., Whelan, N., Whipps, C. M., & Bullard, S. A. (2020b). A new species of Thelohanellus Kudo, 1933 (Myxozoa: Bivalvulidae) infecting skeletal muscle of blacktail shiner, Cyprinella venusta Girard, 1856 (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae) in the Chattahoochee River basin, Georgia. Journal of Parasitology 106, 350–359. https://doi.org/10.1645/19-162
Kudo, R. R. (1934). Studies on some protozoan parasites of fishes of Illinois. Illinois Biological Monographs 13, 1–45. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.50234
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., Li, M., Knyaz, C., & Tamura, K. (2018). MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Molecular Biology and Evolution 35, 1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Landsberg, J. H., & Lom, J. (1991). Taxonomy of the genera of the Myxobolus/Myxosoma group (Myxobolidae: Myxosporea), current listing of species and revision of synonyms. Systematic Parasitology 18, 165–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00009358
Leis, E. M., Rosser, T. G., Baumgartner, W. A., & Griffin, M. J. (2019). Two novel myxozoans from pirate perch Aphredoderus sayanus (Gilliams, 1824) in the Upper Mississippi River, including the first North American species of Hennegoides Lom, Tonguthai, & Dyková, 1991. Journal of Parasitology 105, 918–927. https://doi.org/10.1645/19-43
Li, L., & Desser, S. S. (1985). The protozoan parasites of fish from two lakes in Algonquin Park, Ontario. Canadian Journal of Zoology 63, 1846–1858. https://doi.org/10.1139/z85-275
Liu, Y., Whipps, C. M., Gu, Z. M., & Zeng, L. B. (2010). Myxobolus turpisrotundus (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) spores with caudal appendages: investigating the validity of the genus Henneguya with morphological and molecular evidence. Parasitology Research 107, 699–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-1924-9
Lom, J. (1969). On a new taxonomic character in Myxosporidia, as demonstrated in descriptions of two new species of Myxobolus. Folia Parasitologica 16, 97–103.
Lom, J., & Arthur, J. R. (1989). A guideline for the preparation of species descriptions in Myxosporea. Journal of Fish Diseases 12, 151–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.1989.tb00287.x
Lom, J., & Cone, D. K. (1996). Myxosporeans infecting the gills of bigmouth buffalo (Ictiobus bubalus) in Illinois, USA. Folia Parasitologica 43, 37–42.
Lom, J., & Dyková, I. (2006). Myxozoan genera: Definition and notes on taxonomy, life-cycle, terminology and pathogenic species. Folia Parasitologica 53, 1–36. https://doi.org/10.14411/fp.2006.001
McAllister, C. T., & Cloutman, D. G. (2019). Myxobolus sp. cf. angustus Kudo, 1934 (Cnidaria: Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) on the gills of Dionda sp. cf. flavipinnis (Cope) (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae) from the South Concho River, Texas. Proceedings of the Oklahoma Academy of Science 99, 54–57.
McAllister, C. T., Cloutman, D. G., Leis, E. M., Camus, A. C., Trauth, S. E., & Robison, H. W. (2022). A new species of Myxobolus (Cnidaria: Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) from the gills of creek chub, Semotilus atromaculatus (Cypriniformes: Leuciscidae: Plagiopterinae), from the Ouachita drainage of Arkansas. Journal of Parasitology 108, 476–486. https://doi.org/10.1645/22-1
McAllister, C. T., Font, W. F., Fayton, T. J., & Robison, H. W. (2014). Helminth parasites of select cyprinid fishes from the Red River drainage of southeastern Oklahoma. Proceedings of the Oklahoma Academy of Science 94, 81–86.
McAllister, C. T., Tumlison, R., Robison, H. W., & Trauth, S. E. (2013). An initial survey of black-spot disease (Digenea: Strigeoidea: Diplostomidae) in select Arkansas fishes. Journal of the Arkansas Academy of Science 67, 200–203. https://doi.org/10.54119/jaas.2013.6730
Mitchell, L. G. (1989). Myxobolid parasites (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) infecting fishes of western Montana, with notes on histopathology, seasonality, and intraspecific variation. Canadian Journal of Zoology 67, 1915–1922. https://doi.org/10.1139/z89-274
Molnár, K., Marton, SZ., Eszterbvauer, E., & Székely, Cs. (2006). Comparative morphological and molecular studies on Myxobolus spp. infecting chub from the River Danube, Hungary, and description of M. muellericus sp. n. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 73, 49–61. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao073049
Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2000). Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics. New York: Oxford University Press, 333 pp. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1055-7903(02)00245-2
Page, L. M., Espinosa-Pérez, H., Findley, L. T., Gilbert, C. R., Lea, R. N., Mandrak, N. E., Mayden, R. L., & Nelson, J. S. (2013). Common and scientific names of fishes from the United States, Canada, and Mexico. Seventh edition. American Fisheries Society Special Publication 34, 1–384. https://doi.org/10.47886/9781934874318
Robison, H. W., & Buchanan, T. M. (2020). Fishes of Arkansas. Fayetteville, Arkansas: University of Arkansas Press, 959 pp. https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctvwh8bnv
Salim, K. Y., & Desser, S. S. (2000). Descriptions and phylogenetic systematics of Myxobolus spp. from cyprinids in Algonquin Park, Ontario. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology 47, 309–318. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2000.tb00052.x
Scharpf, C. (2005). Annotated checklist of North American freshwater fishes including subspecies and undescribed forms, Part 1: Petromyzontidae through Cyprinidae. American Currents, Special Publication 31, 1–44.
Schonhuth, S., Gagne, R. B., Alda, F., Neely, D. A., Mayden, R. L., & Blum, M. J. (2018). Phylogenetic relationships and classification of the Holarctic family Leuciscidae (Cypriniformes: Cyprinoidei). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 127, 781–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2018.06.026
Shor, E. N., Rosenblatt, R. H., & Isaacs, J. D. (1987). Carl Levitt Hubbs (1894–1979), a biographical memoir. National Academy of Sciences, Washington, D.C., 249 pp. Available at: http://www.nasonline.org/publications/biographical-memoirs/memoir-pdfs/hubbs-carl-l.pdf (Accessed 23 October 2022).
Spall, R. D. (1974). A new myxosporidan in red and golden shiners. Journal of Parasitology 60, 169–171. https://doi.org/10.2307/3278694
Stilwell, J. M., Camus, A. C., Leary, J. H., Khoo, L. H., & Griffin, M. J. (2019). Pathologic changes associated with respiratory compromise and morbidity due to massive interlamellar Henneguya exilis infection in channel × blue hybrid catfish. Journal of Parasitology 105, 686–692. https://doi.org/10.1645/19-28
Thélohan, P. (1892). Obervations sur les myxosporidies et essai de classification de ces organisms. Bulletin de la Société Philomatique de Paris 4, 167–178.
Use of Fishes in Research Committee (Joint committee of the American Fisheries Society, the American Institute of Fishery Research Biologists, and the American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists). (2014). Guidelines for the use of fishes in research. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda, Maryland, 104 pp. Available at: https://fisheries.org/docs/wp/Guidelines-for Use-of Fishes.pdf. Accessed 23 October 2022.
Wang, M. M., Zhang, J. Y., & Zhao, Y. J. (2022). Morphological description and molecular identification of Myxobolus dajiangensis n. sp. (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) from the gill of Cyprinus carpio in southwest China. PeerJ 10, e13023.
Acknowledgements
Nikolas H. McAllister (North Lamar High School, Paris, Texas, USA) and Zarah S. McAllister (Lukfata Elementary, Broken Bow, Oklahoma, USA) assisted in collections. We thank Drs. Scott L. Gardner and Gabor Racz (HWML) for expert curatorial assistance. Dr. Laurence M. Hardy (Ouachita Mountains Biological Station, Big Fork, Arkansas, USA) for providing gratis housing for CTM during this study. We also thank Dr. Dennis M. Richardson (Quinnipiac University, Hamden, Connecticut, USA) for use of the electrofisher. The findings and conclusions in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the USFWS. Any use of trade, firm, or product names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the USFWS or U.S. Government.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This study was designed by CTM, DGC, and EML. Field collections were performed by CTM and HWR. Laboratory procedures for processing fish and necropsy were performed by CTM. Laboratory procedures for measurements, photomicrographs (Fig.1), and isolation of plasmodia and myxospores were performed by CTM, DGC, and EML. The line drawing (Fig. 2) was prepared by DGC. ACC performed the histopathological analysis and prepared photomicrographs in Fig. 3. EML performed molecular analyses and prepared Fig. 4 and Fig. 5. The manuscript was written by all authors and all read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional, national and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. The Arkansas Game and Fish Commission provided Scientific Collecting Permit No. 1551646 to CTM.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
McAllister, C.T., Cloutman, D.G., Leis, E.M. et al. A new Myxobolus (Cnidaria: Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) from the gills of the southern striped shiner, Luxilus chrysocephalus isolepis (Cypriniformes: Leuciscidae), from southwestern Arkansas, USA. Syst Parasitol 100, 215–229 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-023-10082-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-023-10082-8