Abstract
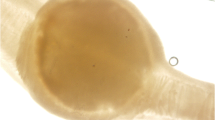
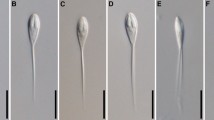
Pseudomurraytrema fergusoni n. sp. is described from the Pealip Redhorse, Moxostoma pisolabrum from the Black River (White River drainage), Lawrence County, Arkansas, USA. This represents the second monogenean described from M. pisolabrum as well as the second species of Pseudomurraytrema reported from an Arkansas catostomid. The description includes partial 18S rRNA and 28S rRNA gene sequences (732 bp and 851 bp, respectively), helping fill a void in sequence data from North American monogeneans, particularly those in the genus Pseudomurraytrema. In addition, histopathologic changes associated with the infection resulted in severe localized pathologic lesions in gills of the host, suggesting compromise of respiratory surfaces within affected areas adjacent to the worms.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Beverley-Burton, M. & Suriano, D. M. (1980). Cleidodiscus robustus Mueller, 1934 (Monogenea: Ancyrocephalinae) from Lepomis gibbosus L. (Pisces: Centrarchidae) in Ontario, Canada: Anatomy and systematic position. Canadian Journal of Zoology 58, 654–660. https://doi.org/10.1139/z80-094
Boeger, W. A. & Kritsky, D. C. (2001). Phylogenetic relationships of the Monogenoidea. In Interrelationships of the Platyhelminthes, D. T. J. Littlewood & R. A. Bray (eds.). Taylor & Francis, London, U.K., p. 92–102. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781482268218
Boeger, W. A., Kritsky, D. C., Domingues, M. V. & Bueno-Silva, M. (2014). The phylogenetic position of the Loimoidae Price, 1936 (Monogenoidea: Monocotylidea) based on analyses of partial rDNA sequences and morphological data. Parasitology International 63, 492–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2014.01.005
Bush, A. O., Lafferty, K. D., Lotz, J. M. & Shostak, A. W. (1997). Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. Journal of Parasitology 83, 575–583.https://doi.org/10.2307/3284227
Chang, C. Y. & Ji, G. I. (1978). A new species of Pseudomurraytrema from the gills ofMyxocyprinus asiaticus [Chinese text: English summary]. Acta Hydrobiologia Sinica 6, 349–352.
Chien, S. M. (1969). Monogenean parasites of Hypentelium nigricans with description of a new species. Journal of Parasitology 55, 737–739. https://doi.org/10.2307/3277206
Chisholm, L. A., Morgan, J. A. T., Adlard R. D. & Whittington, J. D. (2001). Phylogenetic analysis of the Monocotylidae (Monogenea) inferred from 28S rDNA sequences. International Journal of Parasitology 31, 1253–1263. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-7519(01)00223-5
Cloutman, D. G., McAllister, C. T. & Robison, H. W. (2020). Dactylogyrus pisolabrae n. sp. (Monogenoidea: Dactylogyridae) parasitizing the Pealip Redhorse, Moxostoma pisolabrum (Teleostei: Catostomidae), from Oklahoma, U.S.A. Journal of Parasitology 106, 53–55. https://doi.org/10.1645/19-133
Dechtiar, A. O. (1972). New parasite records for Lake Erie fish. Great Lakes Fishery Commission Technical Report No. 17, 1–19.
Domingues, M. & Boeger, W. (2008). Phylogeny and revision of Diplectanidae Monticelli, 1903 (Platyhelminthes: Monogenoidea). Zootaxa 1698, 1–40. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.1698.1.1
Harris, P. M., Mayden, R. L., Espinosa Pérez, H. S. & García de Leon, F. (2002). Phylogenetic relationships of Moxostoma and Scartomyzon (Catostomidae) based on mitochondrial cytochrome b sequence data. Journal of Fish Biology 61, 1433–1452. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2002.tb02488.x
Hoffman, G. L. (1999). Parasites of North American Freshwater Fishes. 2nd ed. Ithaca, New York: Comstock Publishing Associates, pp. 539. https://doi.org/10.7591/9781501735059
ICZN (2012). International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature: Amendment of articles 8, 9, 10, 21 and 78 of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature to expand and refine methods of publication. Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature, 69, 161–169.
Kmentová, N., Steenberge, M. V., Raeymaekers, J. A. M. Koblmüller, S., Hablützel, P. I., Bukinga, F. M., N’sibula, T. M., Mulungula, P. M., Nzigidahera, B. & Ntakimazi, G., et al. (2018). Monogenean parasites of sardines in Lake Tanganyika: diversity, origin and instraspecific variability. Contributions to Zoology 87, 105–132. https://doi.org/10.1163/18759866-08702004
Kritsky, D. C. & Hathaway, R. P. (1969). New and previously described species of Dactylogyridae (Monogenea) from Illinois fishes. Journal of Parasitology 55, 143–148. https://doi.org/10.2307/3277365
Kritsky, D. C., Leiby, P. D. & Kayton, R. J. (1978). A rapid stain technique for the haptoral bars of Gyrodactylus species (Monogenea). Journal of Parasitology 64, 174–175. https://doi.org/10.2307/3279642
Kritsky, D. C., Mizelle, J. D. & Bilqees, F. M. (1978). Studies on Monogenea of Pakistan part 3 status of the Calceostomatidae with a redescription of Neocalceostoma elongatum 1957 and the proposal of Neocalceostomoides new genus. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington 45, 149–154.
Littlewood, D. T., Rohde, J. K. & Clough, K. A. (1998). The phylogenetic position of Udonella (Platyhelminthes). International Journal for Parasitology 28, 1241–1250. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-7519(98)00108-8
Mariaux, J. (1998). A molecular phylogeny of the Eucestoda. Journal of Parasitology 84, 114–124. https://doi.org/10.2307/3284540
McAllister, C. T., Cloutman, D. G., Choudhury, A. & Robison, H. W. (2017). Noteworthy records of helminth (Monogenoidea, Cestoda, Nematoda) and crustacean (Copepoda) parasites from Pealip Redhorses, Moxostoma pisolabrum (Catostomidae), from Oklahoma. Proceedings of the Oklahoma Academy of Science 97, 50–53. https://doi.org/10.1645/19-133
McAllister, C. T., Cloutman, D. G., Choudhury, A., Scholz, T., Trauth, S. E., Fayton, T. J. & Robison, H. W. (2018). Parasites of the Spotted Sucker, Minytrema melanops (Cypriniformes: Catostomidae) from Arkansas and Oklahoma. Journal of the Arkansas Academy of Science 72, 87–93. https://doi.org/10.54119/jaas.2018.7224
McAllister, C. T., Robison, H. W., Woodyard, E. T., Rosser, T. G. & Fayton, T. J. (2021). Novel reproductive data on Pealip Redhorse, Moxostoma pisolabrum (Cypriniformes: Catostomidae), from northeastern Arkansas. Journal of the Arkansas Academy of Science 75, 74–76. https://doi.org/10.54119/jaas.2021.7506
Mergo Jr., J. C. & White, A. M. (1982). Two new species of Dactylogyridae (Monogenea) from the Silver Redhorse, Moxostoma anisurum. Journal of Parasitology 68, 946–948. https://doi.org/10.2307/3281011
Mueller, J. F. (1938). Additional species of North American Gyrodactyloidea (Trematoda). American Midland Naturalist 19, 220–235. https://doi.org/10.2307/2420432
Nelson, J. S., Crossman, E. J., Espinosa-Pérez, H., Findley, L. T., Gilbert C. R., Lea, R. N. & Williams, J. D. (2004). Common and scientific names of fishes from the United States, Canada, and Mexico. American Fisheries Society, Special Publication 29, Bethesda, Maryland, 386 pp. https://doi.org/10.1086/431099
Page, L. M. & Burr, B. M. (2011). Peterson Field Guide to Freshwater Fishes of North America North of Mexico, 2nd ed. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, Boston, Massachusetts, 663 p.
Price, C. E. (1967). Taxonomic notes on the monogenetic trematode genus Pseudomurraytrema, with description of a new species. Texas Journal of Science 19, 87–93.
Robison, H. W. & Buchanan, T. M. (2020). Fishes of Arkansas. University of Arkansas Press, Fayetteville, Arkansas, 959 p. https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctvwh8bnv
Rogers, W. A. (1966). Three new species of Pseudomurraytrema (Trematoda: Monogenea) from gills of catostomid fishes. Journal of Parasitology 52, 462–465. https://doi.org/10.2307/3276311
Rogers, W. A. (1969). Two new species of Pseudomurraytrema from gills of Alabama catostomid fishes. Journal of Parasitology 55, 321–323. https://doi.org/10.2307/3277397
Speare, D. J. & Ferguson, H. W. (2006) Gills and pseudobranchs. In Systemic pathology of fish; a text and atlas of normal tissues in teleosts and their responses to disease. H. W. Ferguson (ed.). Scotian Press, London, U.K., p. 24–63.
Suriano, D. M. & Beverley-Burton, M. (1981). Urocleidus aculeatus (Van Cleave and Mueller, 1932) (Monogenea: Ancyrocephalinae) from Stizostedion vitreum (Mitchill) (Pisces: Percidae) in eastern North America: Anatomy and systematic position. Canadian Journal of Zoology 59, 240–245. https://doi.org/10.1139/z81-038
Wong, W. L., Tan, W. B. & Lim, L. H. (2006). Sodium dodecyl sulphate as a rapid clearing agent for studying the hard parts of monogeneans and nematodes. Journal of Helminthology 80, 87–90. https://doi.org/10.1079/joh2005320
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. T. Graham Rosser (Mississippi State University, Mississippi, USA) for assistance with processing fish, Jeff Seslar (photographer; Columbus, Ohio, USA) for his help creating the composite image of the MCO, Dr. Becky A. Lasee (La Crosse Fish Health Center, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service [USFWS]) for illustrative assistance with the line drawings, Dr. Stanley E. Trauth (Morrilton, Arkansas, USA) for some preliminary images, and John Fisher (National Conservation Training Center, USFWS, for assistance locating reference articles. This work was supported in part by the Mississippi State University College of Veterinary Medicine. Usage of trade names does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government. The findings and conclusions in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the USFWS.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CTM, EML, & DGC conceived the study, designed the analysis, and prepared Figs. 1-3. ACC prepared Fig. 4. CTM, DGC, & HWR collected the data. EML, DGC, ETW, & ACC performed analyses. CTM, DGC, EML, ETW, & ACC wrote the main manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional, national and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. The Arkansas Game and Fish Commission issued a Scientific Collecting Permit to CTM.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article was registered in the Official Register of Zoological Nomenclature (ZooBank) as urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:CC629C98-34B5-4CFE-AF2A-48295170DE4B.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
McAllister, C.T., Leis, E.M., Cloutman, D.G. et al. Pseudomurraytrema fergusoni n. sp. (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae) from gills of Pealip Redhorse, Moxostoma pisolabrum (Catostomidae) from Arkansas, USA, with a description of gill pathology. Syst Parasitol 100, 159–170 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-022-10078-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-022-10078-w