Abstract
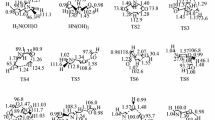
A detailed quantum chemical study is performed on the mechanism of ClOO + NO reaction at the B3LYP/6-311+G (2d) level of theory combined with CCSD (T) single point energy calculation. The possible product channels for the reaction are obtained and discussed on the basis of the singlet [ClNO3] potential energy surface. The calculation indicates that the dominant product for the title reaction is ClO + NO2 by the direct dissociation of the initial adduct, and the formation of the other products is much less likely since they are unfavorable kinetically. A comparison is also made between the title reaction and the analogous reaction of FO2 + NO to gain a deeper insight into the mechanism of the XO2 + NO reactions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Porter G, Wright FJ (1953) Discuss Faraday Soc 14:23
Vaida V, Solomon S, Richard EC, Ruhl E, Jefferson A (1989) Nature 342:405
Molina LT, Molina MJ (1987) J Phys Chem 91:433
Cox RA, Hayman GD (1988) Nature 332:796
Arkell A, Schwager J (1967) J Am Chem Soc 89:5999
Gole JL (1980) J Phys Chem 84:1333
Jafri JA, Lengsfield BH, Bauschlicher CW, Philips DH (1985) J Chem Phys 83:1693
Craven W, Knowles DB, Murrell JN, Vincent MA, Watts JD (1985) Chem Phys Lett 116:119
Jensen F (1990) Chem Phys Lett 169:519
Baer S, Hippler H, Rahn R, Siefke M, Seitzinger N, Troe J (1991) J Chem Phys 95:6463
Byberg JR (1996) J Phys Chem 100:9247
Holger SPM, Helge W (1993) J Phys Chem 97:10589
Johnson K, Engdahl A, Nelander B (1993) J Phys Chem 97:9603
Zhang JX, Pamela MA (1994) J Phys Chem 98:765
Kohsuke S, Yoshihiro S, Yasuki E, Shinichi E, Simone A, Satoshi H, Masahiro K, Satoshi N, Yutaka M (2004) J Phys Chem A 108:8096
Carsten LT, Philip RK, Søren JR (2000) J Am Chem Soc 122:12795
Mauldin RL, Burkholder JB, Ravishankara AR (1992) J Phys Chem 96:2582
Nicovich JM, Kreutter KD, Shackelford CJ, Wine PJ (1991) Chem Phys Lett 179:367
Enami S, Hoshino Y, Ito Y, Hashimoto S, Kawasaki M, Timothy JW (2006) J Phys Chem A 110:3546
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB et al (2003) Gaussian 03, Revision B.04. Gaussian Inc., Pittsburgh, PA
Zhang JX, Hase WL (2010) J Phys Chem A 114:9635
Plane JMC, Joseph DM, Allan BJ, Ashworth SH, Francisco JS (2006) J Phys Chem A 110:93
Zhu RS, Lin MC (2003) J Chem Phys 118:8645
Zhu RS, Lin MC (2005) ChemPhysChem 6:1514
Goodarzi M, Piri F, Hajari N, Karimi L (2010) Chem Phys Lett 499:51
Sun Y, Yao JZ, Sun M, Zhang H, Zhang ML (2009) J Mol Struct (THEOCHEM) 916:10
Li Z, Friedl RR, Sander SP (1995) J Phys Chem 99:13445
Sehested J, Sehested K, Nielsen OJ (1994) J Phys Chem 98:6731
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Harbin key Sci-tech project (No. 2010AA4BG004), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC No. 21001035) and Harbin Engineering University Fundamental Research Funding Project (No. 002100260727).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Sun, M. Theoretical study of the mechanism for the ClOO + NO reaction on the singlet potential energy surface. Struct Chem 23, 107–114 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-011-9845-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-011-9845-5