Abstract
Photoexcited forbidden lines at visible and infrared wavelengths provide important diagnostics for the coronal magnetic field via scattering induced polarization and the Zeeman effect. In forward models, the polarized formation of these lines is often treated assuming a simplified exciting radiation field consisting only of the photospheric quiet-Sun continuum, which is both cylindrically-symmetric relative to the solar vertical and unpolarized. In particular, this assumption breaks down near active regions, especially due to the presence of sunspots and other surface features that modify the strength and anisotropy of the continuum radiation field. Here we investigate the role of symmetry-breaking on the emergent polarized emission in high resolution models of the active corona simulated with the MURaM code. We treat the full 3D unpolarized continuum radiation field of the photosphere that excites the coronal ions and compare the cases where the symmetry-breaking effects of the photospheric features are included or ignored. Our discussion focuses on the key observables soon to be available by the National Science Foundation’s Daniel K Inouye Solar Telescope. The results indicate that while symmetry breaking can in principle have a large effect, its role is relatively minor for the simulated active region, largely due to the low inherent polarization fraction emitted by forbidden lines in denser active region plasmas.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
pyCELP refers to the python package for Coronal Emission Line Polarization, which is an updated version of the code introduced in Paper I. This code is publicly available at https://github.com/tschad/pycelp. See the Appendix for more details.
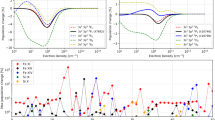
See Paper I for further discussion of the influence of the number of included levels on the calculated atomic level polarization.
We point out that there is a scale error in the top left panel of Figure 10 in Paper I which shows the magnetic field amplitude at the \(\langle\tau_{5000} \rangle\sim1\) plane. Those values need to be multiplied by a factor of \(\sqrt{4\pi}\).
We used the version of the Wittman opacity package ported to Python by Jaime de la Cruz Rodriguez and available at https://github.com/jaimedelacruz/witt/.
References
Aschwanden, M.J., Boerner, P., Schrijver, C.J., Malanushenko, A.: 2013, Automated temperature and emission measure analysis of coronal loops and active regions observed with the atmospheric imaging assembly on the solar dynamics observatory (SDO/AIA). Solar Phys. 283, 5. DOI. ADS.
Auchère, F.: 2005, Effect of the H I Ly\(\alpha\) chromospheric flux anisotropy on the total intensity of the resonantly scattered coronal radiation. Astrophys. J. 622, 737. DOI. ADS.
Carlsson, M.: 2008, 3D radiative transfer in stellar atmospheres. Phys. Scr. T 133, 014012. DOI. ADS.
Casini, R., Judge, P.G.: 1999, Spectral lines for polarization measurements of the coronal magnetic field. II. Consistent treatment of the Stokes vector for magnetic-dipole transitions. Astrophys. J. 522, 524. DOI. ADS.
Casini, R., White, S.M., Judge, P.G.: 2017, Magnetic diagnostics of the solar corona: Synthesizing optical and radio techniques. Space Sci. Rev. 210, 145. DOI. ADS.
Cox, A.N.: 2000, Allen’s Astrophysical Quantities. ADS.
Criscuoli, S.: 2019, Effects of continuum fudging on non-LTE synthesis of stellar spectra. I. Effects on estimates of UV continua and solar spectral irradiance variability. Astrophys. J. 872, 52. DOI. ADS.
Criscuoli, S., Rempel, M., Haberreiter, M., Pereira, T.M.D., Uitenbroek, H., Fabbian, D.: 2020, Comparing radiative transfer codes and opacity samplings for solar irradiance reconstructions. Solar Phys. 295, 50. DOI. ADS.
Del Zanna, G., Young, P.R.: 2020, Atomic data for plasma spectroscopy: The CHIANTI database, improvements and challenges. Atoms 8, 46. DOI. ADS.
Dere, K.P., Del Zanna, G., Young, P.R., Landi, E., Sutherland, R.S.: 2019, CHIANTI—An atomic database for emission lines. XV. Version 9, improvements for the X-ray satellite lines. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 241, 22. DOI. ADS.
Derouich, M., Badruddin: 2018, Study of the effect of active regions on the scattering polarization in the solar corona. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 130, 034203. DOI. ADS.
Dima, G.I., Schad, T.A.: 2020, Using multi-line spectropolarimetric observations of forbidden emission lines to measure single-point coronal magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. 889, 109. DOI. ADS.
Gibson, S.E., Kucera, T.A., White, S.M., Dove, J.B., Fan, Y., Forland, B.C., Rachmeler, L.A., Downs, C., Reeves, K.K.: 2016, FORWARD: A toolset for multiwavelength coronal magnetometry. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 3, 8. DOI.
Hanle, W.: 1924, Über magnetische Beeinflussung der Polarisation der Resonanzfluoreszenz. Z. Phys. 30, 93. DOI. ADS.
Harris, C.R., Millman, K.J., van der Walt, S.J., Gommers, R., Virtanen, P., Cournapeau, D., Wieser, E., Taylor, J., Berg, S., Smith, N.J., Kern, R., Picus, M., Hoyer, S., van Kerkwijk, M.H., Brett, M., Haldane, A., del Río, J.F., Wiebe, M., Peterson, P., Gérard-Marchant, P., Sheppard, K., Reddy, T., Weckesser, W., Abbasi, H., Gohlke, C., Oliphant, T.E.: 2020, Array programming with NumPy. Nature 585, 357. DOI.
Janett, G., Steiner, O., Belluzzi, L.: 2018, Formal solutions for polarized radiative transfer. IV. Numerical performances in practical problems. Astrophys. J. 865, 16. DOI. ADS.
Judge, P.G.: 2007, Spectral lines for polarization measurements of the coronal magnetic field. V. Information content of magnetic dipole lines. Astrophys. J. 662, 677. DOI. ADS.
Kano, R., Trujillo Bueno, J., Winebarger, A., Auchère, F., Narukage, N., Ishikawa, R., Kobayashi, K., Bando, T., Katsukawa, Y., Kubo, M., Ishikawa, S., Giono, G., Hara, H., Suematsu, Y., Shimizu, T., Sakao, T., Tsuneta, S., Ichimoto, K., Goto, M., Belluzzi, L., Štěpán, J., Asensio Ramos, A., Manso Sainz, R., Champey, P., Cirtain, J., De Pontieu, B., Casini, R., Carlsson, M.: 2017, Discovery of scattering polarization in the hydrogen Ly\(\alpha \) line of the solar disk radiation. Astrophys. J. Lett. 839, L10. DOI. ADS.
Khan, A., Landi Degl’Innocenti, E.: 2011, Solar coronal magnetic field diagnostics through polarimetric forward modelling of the Hanle effect. Astron. Astrophys. 532, A70. DOI. ADS.
Khan, A., Belluzzi, L., Landi Degl’Innocenti, E., Fineschi, S., Romoli, M.: 2011, Spectropolarimetric forward modelling of the lines of the Lyman-series using a self-consistent, global, solar coronal model. Astron. Astrophys. 529, A12. DOI. ADS.
Kramar, M., Inhester, B., Solanki, S.K.: 2006, Vector tomography for the coronal magnetic field. I. Longitudinal Zeeman effect measurements. Astron. Astrophys. 456, 665. DOI. ADS.
Kunasz, P., Auer, L.H.: 1988, Short characteristic integration of radiative transfer problems: Formal solution in two-dimensional slabs. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 39, 67. DOI. ADS.
Lam, S.K., Pitrou, A., Seibert, S.: 2015, Numba: A LLVM-based python JIT compiler. In: Proceedings of the Second Workshop on the LLVM Compiler Infrastructure in HPC, LLVM’15, Association for Computing Machinery, New York. ISBN 9781450340052. DOI.
Landi Degl’Innocenti, E., Landolfi, M.: 2004, Polarization in Spectral Lines 307. DOI. ADS.
Landi, E., Hutton, R., Brage, T., Li, W.: 2020, Hinode/EIS measurements of active-region magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. 904, 87. DOI. ADS.
Landi, E., Li, W., Brage, T., Hutton, R.: 2021, Hinode/EIS coronal magnetic field measurements at the onset of a C2 flare. Astrophys. J. 913, 1. DOI. ADS.
Lee, J.: 2007, Radio emissions from solar active regions. Space Sci. Rev. 133, 73. DOI. ADS.
Li, H., Landi Degl’Innocenti, E., Qu, Z.: 2017, Polarization of coronal forbidden lines. Astrophys. J. 838, 69. DOI. ADS.
Li, W., Grumer, J., Yang, Y., Brage, T., Yao, K., Chen, C., Watanabe, T., Jönsson, P., Lundstedt, H., Hutton, R., Zou, Y.: 2015, A novel method to determine magnetic fields in low-density plasma facilitated through accidental degeneracy of quantum states in Fe9+. Astrophys. J. 807, 69. DOI. ADS.
Lin, H., Penn, M.J., Tomczyk, S.: 2000, A new precise measurement of the coronal magnetic field strength. Astrophys. J. Lett. 541, L83. DOI. ADS.
Malanushenko, A., Cheung, M.C.M., DeForest, C.E., Klimchuk, J.A., Rempel, M.: 2021, The coronal veil. arXiv e-prints. arXiv. ADS.
Manso Sainz, R., Trujillo Bueno, J.: 2009, In: Berdyugina, S.V., Nagendra, K.N., Ramelli, R. (eds.) A Possible Polarization Mechanism of EUV Coronal Lines, Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series 405, 423. ADS.
Mihalas, D.: 1970, Stellar Atmospheres. ADS.
Plowman, J.: 2014, Single-point inversion of the coronal magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 792, 23. DOI. ADS.
Rempel, M.: 2017, Extension of the MURaM radiative MHD code for coronal simulations. Astrophys. J. 834, 10. DOI. ADS.
Rimmele, T.R., Warner, M., Keil, S.L., Goode, P.R., Knölker, M., Kuhn, J.R., Rosner, R.R., McMullin, J.P., Casini, R., Lin, H., Wöger, F., von der Lühe, O., Tritschler, A., Davey, A., de Wijn, A., Elmore, D.F., Fehlmann, A., Harrington, D.M., Jaeggli, S.A., Rast, M.P., Schad, T.A., Schmidt, W., Mathioudakis, M., Mickey, D.L., Anan, T., Beck, C., Marshall, H.K., Jeffers, P.F., Oschmann, J.M., Beard, A., Berst, D.C., Cowan, B.A., Craig, S.C., Cross, E., Cummings, B.K., Donnelly, C., de Vanssay, J.-B., Eigenbrot, A.D., Ferayorni, A., Foster, C., Galapon, C.A., Gedrites, C., Gonzales, K., Goodrich, B.D., Gregory, B.S., Guzman, S.S., Guzzo, S., Hegwer, S., Hubbard, R.P., Hubbard, J.R., Johansson, E.M., Johnson, L.C., Liang, C., Liang, M., McQuillen, I., Mayer, C., Newman, K., Onodera, B., Phelps, L., Puentes, M.M., Richards, C., Rimmele, L.M., Sekulic, P., Shimko, S.R., Simison, B.E., Smith, B., Starman, E., Sueoka, S.R., Summers, R.T., Szabo, A., Szabo, L., Wampler, S.B., Williams, T.R., White, C.: 2020, The Daniel K. Inouye solar telescope - observatory overview. Solar Phys. 295, 172. DOI. ADS.
Sahal-Brechot, S., Malinovsky, M., Bommier, V.: 1986, The polarization of the O VI 1032 Å line as a probe for measuring the coronal vector magnetic field via the Hanle effect. Astron. Astrophys. 168, 284. ADS.
Schad, T.A.: 2014, On the collective magnetic field strength and vector structure of dark umbral cores measured by the hinode spectropolarimeter. Solar Phys. 289, 1477. DOI. ADS.
Schad, T., Dima, G.: 2020, Forward synthesis of polarized emission in target DKIST coronal lines applied to 3D MURaM coronal simulations. Solar Phys. 295, 98. DOI. ADS.
Socas-Navarro, H., de la Cruz Rodríguez, J., Asensio Ramos, A., Trujillo Bueno, J., Ruiz Cobo, B.: 2015, An open-source, massively parallel code for non-LTE synthesis and inversion of spectral lines and Zeeman-induced Stokes profiles. Astron. Astrophys. 577, A7. DOI. ADS.
Tomczyk, S., McIntosh, S.W., Keil, S.L., Judge, P.G., Schad, T., Seeley, D.H., Edmondson, J.: 2007, Alfvén waves in the solar corona. Science 317, 1192. DOI. ADS.
Trujillo Bueno, J., Landi Degl’Innocenti, E., Belluzzi, L.: 2017, The physics and diagnostic potential of ultraviolet spectropolarimetry. Space Sci. Rev. 210, 183. DOI. ADS.
Uitenbroek, H.: 2001, Multilevel radiative transfer with partial frequency redistribution. Astrophys. J. 557, 389. DOI. ADS.
Van Vleck, J.H.: 1925, On the quantum theory of the polarization of resonance radiation in magnetic fields. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 11, 612. DOI. ADS.
Vögler, A., Shelyag, S., Schüssler, M., Cattaneo, F., Emonet, T., Linde, T.: 2005, Simulations of magneto-convection in the solar photosphere. Equations, methods, and results of the MURaM code. Astron. Astrophys. 429, 335. DOI. ADS.
Wittmann, A.: 1974, Computation and observation of Zeeman multiplet polarization in Fraunhofer lines. II: Computation of Stokes parameter profiles. Solar Phys. 35, 11. DOI. ADS.
Xie, H., Madjarska, M.S., Li, B., Huang, Z., Xia, L., Wiegelmann, T., Fu, H., Mou, C.: 2017, The plasma parameters and geometry of cool and warm active region loops. Astrophys. J. 842, 38. DOI. ADS.
Yang, Z., Bethge, C., Tian, H., Tomczyk, S., Morton, R., Del Zanna, G., McIntosh, S.W., Karak, B.B., Gibson, S., Samanta, T., He, J., Chen, Y., Wang, L.: 2020, Global maps of the magnetic field in the solar corona. Science 369, 694. DOI. ADS.
Acknowledgements
The National Solar Observatory (NSO) is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. (AURA), under cooperative agreement with the National Science Foundation. The authors extend our thanks to Matthias Rempel for providing and helping use the MURaM simulation and to Serena Criscuoli for providing the RH generated opacities. Thanks also to Jaime de la Cruz Rodriguez for making Python versions of the Wittmann opacity routines publicly available. Chianti is a collaborative project involving George Mason University, the University of Michigan (USA), University of Cambridge (UK) and NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (USA). This research has made use of NASA’s Astrophysics Data System.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix: pyCELP: Software Updates and Improvements
Appendix: pyCELP: Software Updates and Improvements
Schad and Dima (2020) introduced a code referred to as pyCLE, which is capable of multilevel atomic density calculations for the purpose of calculating the atomic level polarization of forbidden emission lines in the no-coherence hypothesis. This code has since been reformulated and updated from a Fortran code wrapped in Python to a Python-only code. The new code is called pyCELP for the python package for Coronal Emission Line Polarization. It provides an extensible class for model ion calculations and takes advantage of the Numba package for just-in-time compilation (Lam, Pitrou, and Seibert, 2015). By pre-computing all static factors in the statistical equilibrium equations, we have significantly accelerated the code. It is now primarily limited in execution speed by the time required to solve the system of linear equations using the libraries available in the Numpy package (Harris et al., 2020). The code is publicly available at https://github.com/tschad/pycelp.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schad, T., Dima, G. Polarized Forbidden Coronal Line Emission in the Presence of Active Regions. Sol Phys 296, 166 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01917-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01917-y