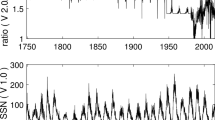
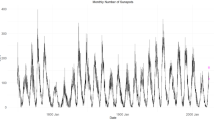
Abstract
This article proposes a new model for predicting sunspot activity based on the inverse number and intelligent fixed point. Firstly, in the training phase, the optimal parameters of the model are selected by the inverse-number formula and intelligent fixed-point algorithm. Secondly, in the validation phase, the model is verified by the data. Finally, the model is applied to the prediction of monthly mean sunspot number (MSN). The model’s predictions are compared with those of autoregressive models (AR) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) predictions. The results show that the prediction accuracy of the proposed method is higher than that of previous methods. The method is then used to predict the 13-month smoothed monthly total sunspot number (MSSN13), and a higher prediction accuracy is obtained. The model proposed in this article is theoretically complete and robust.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Rahman, H.I., Marzouk, B.A.: 2018, Statistical method to predict the sunspots number. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 7, 175. DOI.
Aldrich, J.: 1995, Correlations genuine and spurious in Pearson and Yule. Stat. Sci. 10, 364. DOI.
Baranovski, A.L., Clette, F., Nollau, V.: 2008, Nonlinear solar cycle forecasting: theory and perspectives. Ann. Geophys. 26, 231. DOI.
Box, G.E.P., Jenkins, G.M., Reinsel, G.C.: 1976, Time series analysis: forecasting and control. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 22, 199. DOI.
Chen, S.M.: 2002, Forecasting enrollments based on high-order fuzzy time series. Cybern. Syst. 33, 1. DOI.
Chen, M.Y.: 2014, A high-order fuzzy time series forecasting model for internet stock trading. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 37, 461. DOI.
Cher, E., Rigozo, N.R., Nordemann, D.J.R., Vieira, L.E.A.: 2004, Prediction of solar activity on the basis of spectral characteristics of sunspot number. Ann. Geophys. 22, 2239. DOI.
Clette, F., Svalgaard, L., Vaquero, J.M., Cliver, E.W.: 2014, Revisiting the sunspot number. Space Sci. Rev. 186, 35. DOI.
Du, Z.L.: 2020a, Predicting the amplitude of solar cycle 25 using the value 39 months before the solar minimum. Solar Phys. 295, 147. DOI.
Du, Z.L.: 2020b, The solar cycle: predicting the peak of solar cycle 25. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 365, 104. DOI.
Fessant, F., Pierret, C., Lantos, P.: 1996, Comparison of neural network and McNish and Lincoln methods for the prediction of the smoothed sunspot index. Solar Phys. 168, 423. DOI.
Gray, L.J., Beer, J., Geller, M., Haigh, J.D., Lockwood, M., Matthes, K., Cubasch, U., Fleitmann, D., Harrison, G., Hood, L., Luterbacher, J., Meehl, G.A., Shindell, D., Van Geel, B., White, W.: 2010, Solar influences on climate. Rev. Geophys. 48, RG4001. DOI.
Hamid, R.H., Galal, A.A.: 2013, An early prediction of the maximum amplitude of the solar cycle 25. J. Adv. Res. 4, 275. DOI.
Hathaway, D.H.: 2009, Solar cycle forecasting. Space Sci. Rev. 144, 401. DOI.
Kane, R.P.: 2008, Prediction of solar cycle maximum using solar cycle lengths. Solar Phys. 248, 203. DOI.
Liu, Z., Zhang, T.: 2019, A second-order fuzzy time series model for stock price analysis. J. Appl. Stat. 46, 2514. DOI.
Liu, J.H., Zhao, J., Lin, H.B.: 2019, Prediction of the sunspot number with a new model based on the revised data. Solar Phys. 294, 157. DOI.
Mamdanni, E.H., Assilian, S.: 1975, An experiment in linguistic synthesis with a fuzzy logic controller. Int. J. Man-Mach. Stud. 7, 1. DOI.
Robert, N., Dmitri, V., Anton, A.: 2020, Solar wind transient currents: statistical properties and impact on Earth’s magnetosphere. Solar Phys. 295, 125. DOI.
Schatten, K., Myers, D.J., Sofia, S.: 1996, Solar activity forecast for solar cycle 23. Geophys. Res. Lett. 23, 605. DOI.
Song, Q., Chissom, B.S.: 1993a, Forecasting enrollments with fuzzy time series – part I. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 54, 1. DOI.
Song, Q., Chissom, B.S.: 1993b, Fuzzy time series and its model. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 54, 269. DOI.
Wang, N.Y., Chen, S.M.: 2009, Temperature prediction and TAIFEX forecasting based on automatic clustering techniques and two-factors high-order fuzzy time series. Expert Syst. Appl. 36, 2143. DOI.
Wang, H.X., Yin, C.G., Lu, X.L., Feng, H., Fu, X.F.: 2017, Set of time series forecasting models using the ordered difference. Adv. Intell. Sys. Res. 153, 128. DOI.
Wittmann, A.: 1978, The sunspot cycle before the Maunder Minimum. Astron. Astrophys. 66, 93.
Yule, G.U.: 1927, On a method of investigating periodicities in disturbed series, with special reference to Wolfer’s sunspot numbers. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London A 226, 267. DOI.
Zadeh, L.A.: 1965, Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8, 338. DOI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Zhang, T. & Wang, H. Predicting Sunspot Numbers Based on Inverse Number and Intelligent Fixed Point. Sol Phys 296, 83 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01835-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01835-z